
How do you verify the second law of reflection of light with an experiment?
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Firstly, you could recall what this second law of reflection is. Then you could approach this verification using an experiment in the usual way you do in the laboratory. Also, try to include a proper diagram for clarity of your experiment. Also remember to list out the apparatus required.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are asked to verify the second law of reflection of light with the help of an experiment. In order to do that, firstly we have to know what the second law of reflection is.
We know that the second law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence.
Let us do the experiment in the traditional way. So, the aim of our experiment will be verification of the second law of reflection. We will require a mirror strip, drawing board on which a white paper is fixed, pins, a scale and a pencil. Now, we could discuss the procedure.
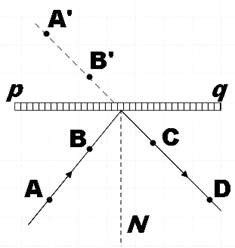
You could first draw a straight line $pq$ on which we will be keeping the mirror strip and then draw a normal to this surface. Now you could draw a straight line $AB$ making an angle with the normal and then fix pins on it. After which you will find the image of these points $A'B'$ somewhere behind the mirror. Now you could hold the scale parallel to this line on which the images of the points lie and then mark it with pins.
Thereby, you will get the incident ray and reflected ray and then you could measure the angle made by the incident ray with the normal (incident angle) and the angle made by the reflected ray (reflected angle) with the normal and will find them equal too.
Hence, the second law of reflection is verified.
Note:
You could also do this by using a laser pointer which when light at an angle with the normal will give you the reflected ray and then you could easily do the necessary measurements. Also, if the light were to incident normally on the reflecting surface, you may not see a reflected ray. This is because this ray gets reflected back in the same path.
Complete answer:
In the question, we are asked to verify the second law of reflection of light with the help of an experiment. In order to do that, firstly we have to know what the second law of reflection is.
We know that the second law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence.
Let us do the experiment in the traditional way. So, the aim of our experiment will be verification of the second law of reflection. We will require a mirror strip, drawing board on which a white paper is fixed, pins, a scale and a pencil. Now, we could discuss the procedure.

You could first draw a straight line $pq$ on which we will be keeping the mirror strip and then draw a normal to this surface. Now you could draw a straight line $AB$ making an angle with the normal and then fix pins on it. After which you will find the image of these points $A'B'$ somewhere behind the mirror. Now you could hold the scale parallel to this line on which the images of the points lie and then mark it with pins.
Thereby, you will get the incident ray and reflected ray and then you could measure the angle made by the incident ray with the normal (incident angle) and the angle made by the reflected ray (reflected angle) with the normal and will find them equal too.
Hence, the second law of reflection is verified.
Note:
You could also do this by using a laser pointer which when light at an angle with the normal will give you the reflected ray and then you could easily do the necessary measurements. Also, if the light were to incident normally on the reflecting surface, you may not see a reflected ray. This is because this ray gets reflected back in the same path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




