
What is the value of $ Z $ for a body-centred unit cell $ ? $
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint :First we know that a unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice that shows the three-dimensional pattern of the entire crystal. There are three types of unit cells: simple cubic (primitive cubic), Face-Centred Cubic (FCC) , and Body-Centred Cubic (BCC).
$ Z $ is the number of formula units in a given unit cell (Number of atoms or molecules in a given unit cell). $ Z $ is the number of asymmetric units. This is $ Z $ divided by the lowest multiplicity in your list of Wyckoff positions.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A BCC unit cell has atoms at each corner of the cube and an atom at the centre of the structure. The diagram shown below is an open structure. According to this structure, the atom at the body centre wholly belongs to the unit cell in which it is present.
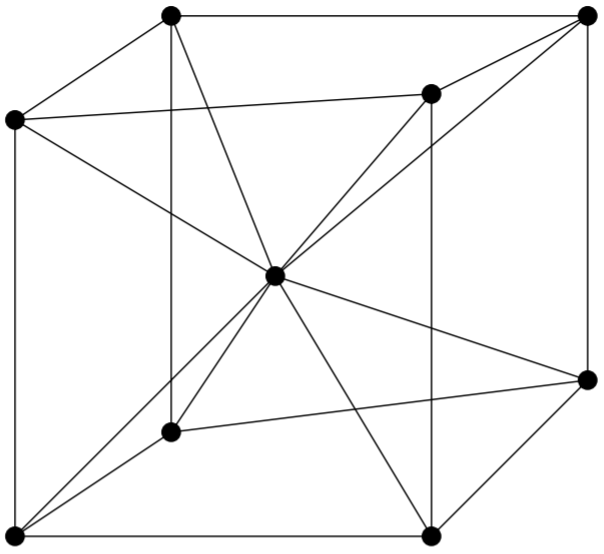
In the BCC unit cell every corner has atoms.
There is one atom present at the centre of the structure.
In the BCC cell we have, $ 1 $ atoms are present at the centre of the body and $ 8 $ atoms are present at the $ 8 $ corners of the body. Then the number of atoms present at each corner is $ = 8 \times \dfrac{1}{8} = 1 $ atom. The atom at the centre of the body contributes fully to the unit cell. Then $ 1 $ body centre atom $ = 1 \times 1 = 1 $ atom.
Therefore, the total number of atoms present per unit cell $ = 1 + 1 = 2 $ atoms.
Since the number of atoms for a body-centred cubic unit cell is $ 2 $ ,
Hence the value of $ Z $ is $ 2 $ .
Note :
Alpha iron, Tungsten, Chromium, and Beta titanium are the examples of metals with the BCC structure. Note that a crystal can be thought of as the same unit cell repeated over and over in three dimensions. The number of atoms in a face-centred cubic unit cell is four. Also, the number of atoms in a simple cubic unit cell is one.
$ Z $ is the number of formula units in a given unit cell (Number of atoms or molecules in a given unit cell). $ Z $ is the number of asymmetric units. This is $ Z $ divided by the lowest multiplicity in your list of Wyckoff positions.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
A BCC unit cell has atoms at each corner of the cube and an atom at the centre of the structure. The diagram shown below is an open structure. According to this structure, the atom at the body centre wholly belongs to the unit cell in which it is present.

In the BCC unit cell every corner has atoms.
There is one atom present at the centre of the structure.
In the BCC cell we have, $ 1 $ atoms are present at the centre of the body and $ 8 $ atoms are present at the $ 8 $ corners of the body. Then the number of atoms present at each corner is $ = 8 \times \dfrac{1}{8} = 1 $ atom. The atom at the centre of the body contributes fully to the unit cell. Then $ 1 $ body centre atom $ = 1 \times 1 = 1 $ atom.
Therefore, the total number of atoms present per unit cell $ = 1 + 1 = 2 $ atoms.
Since the number of atoms for a body-centred cubic unit cell is $ 2 $ ,
Hence the value of $ Z $ is $ 2 $ .
Note :
Alpha iron, Tungsten, Chromium, and Beta titanium are the examples of metals with the BCC structure. Note that a crystal can be thought of as the same unit cell repeated over and over in three dimensions. The number of atoms in a face-centred cubic unit cell is four. Also, the number of atoms in a simple cubic unit cell is one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




