
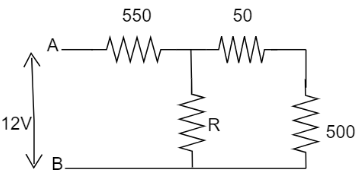
What is the value of unknown resistance R, in figure, if the voltage drop across \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor is \[2.5{\text{ V}}\]. All the resistances are in ohm.

Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint:The voltage drop across the resistor connected in parallel combination is equal. The current through \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] will be calculated with the help of the given voltage drop. Using the voltage divider rule we will find the relation between the voltage and resistance, R and thus using the voltage drop we will find the value of resistance, R.
Complete step by step answer:
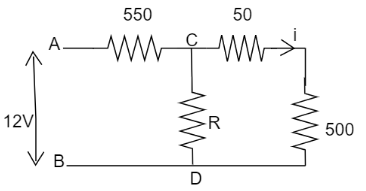
Let us assume current (i) flows through the \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor and the voltage drop across this resistor is given as \[2.5{\text{ V}}\]. Therefore we can find the current flowing through the \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor as:
\[{\text{i = }}\dfrac{V}{R}\]
For \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor,
\[{\text{i = }}\dfrac{{0.25{\text{ V}}}}{{500{\text{ }}\Omega }}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\text{i = 0}}{\text{.005 A}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\text{i = 5 mA}}\]
Now the voltage across CD branch will be calculated as:
\[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = iR}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = 5 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 550}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = 2}}{\text{.75 V}}\]
Also by using voltage divider rule for CD branch we can write as,
\[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{12{\text{ V }} \times {\text{ }}\left( {R||550} \right)}}{{R||550{\text{ + 550}}}}\] , where || denotes parallel combination of resistors
Parallel combination of R and \[550{\text{ }}\Omega \] can be calculated as:
\[{R_{eq.}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{R \times 550}}{{R + 550}}{\text{ }}\Omega \]
Thus on substituting the parallel combination we get the result as,
\[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{12{\text{ V }} \times {\text{ }}\dfrac{{R \times 550}}{{R + 550}}}}{{\dfrac{{R \times 550}}{{R + 550}}{\text{ + 550}}}}\]
On substituting \[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = 2}}{\text{.75 V}}\] and solving the equation we get the result as,
\[{\text{2}}{\text{.75 = }}\dfrac{{12{\text{(R + 550) }}}}{{R \times 550{\text{ + 550(R + 550)}}}}\]
Rearranging the terms we get the value of R as:
\[\therefore R{\text{ = 232}}{\text{.69 }}\Omega \]
Hence the value of R is \[{\text{232}}{\text{.69 }}\Omega \].
Note:Name all the nodes and branches for better understanding and representation of the problem. Apply voltage divider rule properly. We can also find the value of R by applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law in each branch respectively. The answer would be the same in both cases. Calculate the value of resistance R up to two decimal places only. Parallel combination of resistances is the ratio of product of all resistances and the sum of all resistances. In series combination, the value of current is the same through the same branch.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume current (i) flows through the \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor and the voltage drop across this resistor is given as \[2.5{\text{ V}}\]. Therefore we can find the current flowing through the \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor as:

\[{\text{i = }}\dfrac{V}{R}\]
For \[500{\text{ }}\Omega \] resistor,
\[{\text{i = }}\dfrac{{0.25{\text{ V}}}}{{500{\text{ }}\Omega }}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\text{i = 0}}{\text{.005 A}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {\text{i = 5 mA}}\]
Now the voltage across CD branch will be calculated as:
\[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = iR}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = 5 }} \times {\text{ 1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 550}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = 2}}{\text{.75 V}}\]
Also by using voltage divider rule for CD branch we can write as,
\[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{12{\text{ V }} \times {\text{ }}\left( {R||550} \right)}}{{R||550{\text{ + 550}}}}\] , where || denotes parallel combination of resistors
Parallel combination of R and \[550{\text{ }}\Omega \] can be calculated as:
\[{R_{eq.}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{R \times 550}}{{R + 550}}{\text{ }}\Omega \]
Thus on substituting the parallel combination we get the result as,
\[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{12{\text{ V }} \times {\text{ }}\dfrac{{R \times 550}}{{R + 550}}}}{{\dfrac{{R \times 550}}{{R + 550}}{\text{ + 550}}}}\]
On substituting \[{{\text{V}}_{CD}}{\text{ = 2}}{\text{.75 V}}\] and solving the equation we get the result as,
\[{\text{2}}{\text{.75 = }}\dfrac{{12{\text{(R + 550) }}}}{{R \times 550{\text{ + 550(R + 550)}}}}\]
Rearranging the terms we get the value of R as:
\[\therefore R{\text{ = 232}}{\text{.69 }}\Omega \]
Hence the value of R is \[{\text{232}}{\text{.69 }}\Omega \].
Note:Name all the nodes and branches for better understanding and representation of the problem. Apply voltage divider rule properly. We can also find the value of R by applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law in each branch respectively. The answer would be the same in both cases. Calculate the value of resistance R up to two decimal places only. Parallel combination of resistances is the ratio of product of all resistances and the sum of all resistances. In series combination, the value of current is the same through the same branch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




