
What is the value of current i in the given figure?
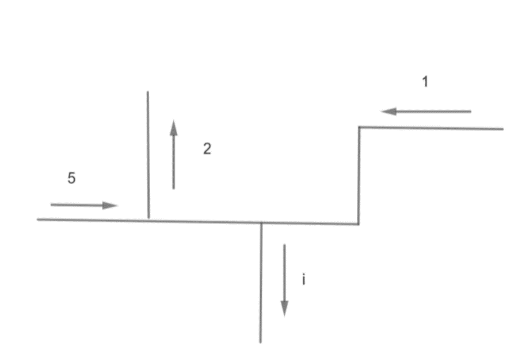
A. $- 4\,mA$
B. $+ 2\,mA$
C. $+ 4\,mA$
D. $+ 8\,mA$

Answer
500.4k+ views
Hint:By applying KCL law we can solve the above problem.Kirchhoff’s Current Law often shortens as KCL, which states that the algebraic sum of all the currents entering and exiting a node must be equal to zero. In other words we can also say that the sum of current entering a node is equal to the sum of current exiting a node.
Formula Used:
$\boxed{\sum\limits_{k = 1}^n {{i_k} = 0} }$
Where, $i = \,Current$ and k varies from $k = 1,2,3, \ldots \ldots n$.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s current law, the algebraic sum of all the currents entering and exiting a node must be equal to zero. In other words we can also say that the sum of current entering a node is equal to the sum of current exiting a node.As per the question we need to calculate the value of i that is exiting from the node. For this we have to apply Kirchhoff’s current law.As given in the diagram,
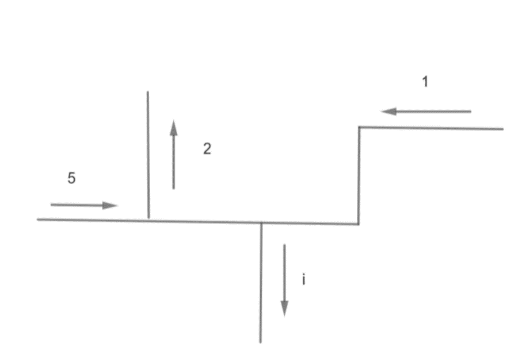
As we can see from the diagram current $5mA\,\,and\,\,1mA$ are entering current while current $2mA\,\,and\,\,i$ are exciting currents.Applying Kirchhoff Current law we can write
Method I:
$\sum\limits_{k = 1}^n {{i_k} = 0} $
Here k varies from $k = 1,2,3,4$
Now we can write,
$\sum\limits_{k = 1}^4 {{i_{1,2,3,4}}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {i_1} + {i_2} + {i_3} + {i_4} = 0$
With the help of above diagram
${i_1} = 5mA,{i_2} = 1mA,{i_3} = 2mA,{i_4} = i$
Now putting the above value in the equation we get,
$5mA + 1mA - 2mA - i = 0$
(As ${i_3}\,\,and\,\,{i_4}$ are exiting current which flows in opposite direction)
Now,
$4mA - i = 0$
$ \therefore \boxed{i = + 4mA}$
Method 2:
Entering Current=Exiting Current
$ \Rightarrow 5mA + 1mA = 2mA + i$
$ \Rightarrow 6mA = 2mA + i$
$ \Rightarrow 6mA - 2mA = i$
$ \therefore \boxed{i = + 4mA}$
Hence, the correct option is $\left( C \right)$.
Note:Always take proper sign convention when you are using method 1 to solve this kind of problem or else you will make a mistake. If in place of $ - 2mA$ I will take $ + 2mA$ then my answer will be incorrect. So be careful while solving this kind of problem. It will be better for you to solve this kind of problem using method 2.
Formula Used:
$\boxed{\sum\limits_{k = 1}^n {{i_k} = 0} }$
Where, $i = \,Current$ and k varies from $k = 1,2,3, \ldots \ldots n$.
Complete step by step answer:
According to Kirchhoff’s current law, the algebraic sum of all the currents entering and exiting a node must be equal to zero. In other words we can also say that the sum of current entering a node is equal to the sum of current exiting a node.As per the question we need to calculate the value of i that is exiting from the node. For this we have to apply Kirchhoff’s current law.As given in the diagram,

As we can see from the diagram current $5mA\,\,and\,\,1mA$ are entering current while current $2mA\,\,and\,\,i$ are exciting currents.Applying Kirchhoff Current law we can write
Method I:
$\sum\limits_{k = 1}^n {{i_k} = 0} $
Here k varies from $k = 1,2,3,4$
Now we can write,
$\sum\limits_{k = 1}^4 {{i_{1,2,3,4}}} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {i_1} + {i_2} + {i_3} + {i_4} = 0$
With the help of above diagram
${i_1} = 5mA,{i_2} = 1mA,{i_3} = 2mA,{i_4} = i$
Now putting the above value in the equation we get,
$5mA + 1mA - 2mA - i = 0$
(As ${i_3}\,\,and\,\,{i_4}$ are exiting current which flows in opposite direction)
Now,
$4mA - i = 0$
$ \therefore \boxed{i = + 4mA}$
Method 2:
Entering Current=Exiting Current
$ \Rightarrow 5mA + 1mA = 2mA + i$
$ \Rightarrow 6mA = 2mA + i$
$ \Rightarrow 6mA - 2mA = i$
$ \therefore \boxed{i = + 4mA}$
Hence, the correct option is $\left( C \right)$.
Note:Always take proper sign convention when you are using method 1 to solve this kind of problem or else you will make a mistake. If in place of $ - 2mA$ I will take $ + 2mA$ then my answer will be incorrect. So be careful while solving this kind of problem. It will be better for you to solve this kind of problem using method 2.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




