
How many valence electrons do a carbon atom in a carbene contain?
(A) 6
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 2
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint:
Complete step by step solution:
The carbene is a common intermediate in the organic reactions.it is molecules that contain the neutral carbon atom which has the two valence and two non –bonding electron pairs.
The carbene is an uncharged and electron efficient species. Its molecular species contains the divalent carbon atom which is surrounded by the sextet of the electrons and the two substituents on the carbon atom.
The carbene has a structure such that the carbon forms the two bonds and the 4 valence electrons are on the central carbon atom.
The general formula is depicted as:
\[\text{ R}-\underset{..}{\overset{..}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\text{R }\]
The central carbon bonded to the two R groups.
Let's find out the number of valence electrons in the carbon atom of a carbene.
The atomic number of carbon atom is equal to 6.the electronic configuration of the carbon atom is depicted as follows:
$\text{ C = 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{2}}\text{ }$
The carbon has the 4 electrons in its valence shell$\text{ ( n = 2) }$.
In carbene, the carbon atom is bonded to the two atoms. These are covalent bonds formed by sharing the electron. The total number of the valence electrons in the carbene is from the carbon and the R $\text{ ( let R = H) }$ has the one valence electron from each hydrogen.
Therefore, total valence electrons in the carbene molecule equal to $\text{V}\text{.E}\text{. in carbene = V}\text{.E}\text{. of C + 2 (V}\text{.E}\text{. of H) = 4 + 2 = 6 }{{\text{e}}^{-}}\text{ }$
The carbon atom in the carbene has six valence electrons.
The structure of the carbene atom is:
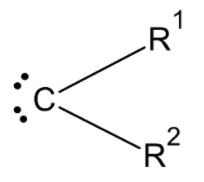
Here, we know that the carbon atom of the carbene has 6 valence electrons.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Additional information:
In carbene, the lone of electrons are accommodated in the unhybridized p – orbital. The electrons can be arranged in different forms.
The carbene exists in the two forms. These are:
1) Triplet state: the triplet carbene has the two unshared electrons. One of the electrons is present $\text{ s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ }$ in hybrid orbitals and the one-electron is in the unhybridized p-orbital. These electrons have the same spin.
2) Singlet state: In singlet state, non-bonding pair of electrons are in the $\text{ s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ }$ hybrid orbitals and one in the p orbitals. These electrons have the opposite spins.
The two carbene forms are different, not only in the structure but also concerning the reactivity.
Note: The carbene is very commonly intermediated in various organic reactions. The three major reactions of the carbene are:
1) Carbene insertions
2) Carbene additions
3) Carbene rearrangements
The two nonbonding and 2 unshared electrons make it more reactive.
Complete step by step solution:
The carbene is a common intermediate in the organic reactions.it is molecules that contain the neutral carbon atom which has the two valence and two non –bonding electron pairs.
The carbene is an uncharged and electron efficient species. Its molecular species contains the divalent carbon atom which is surrounded by the sextet of the electrons and the two substituents on the carbon atom.
The carbene has a structure such that the carbon forms the two bonds and the 4 valence electrons are on the central carbon atom.
The general formula is depicted as:
\[\text{ R}-\underset{..}{\overset{..}{\mathop{C}}}\,-\text{R }\]
The central carbon bonded to the two R groups.
Let's find out the number of valence electrons in the carbon atom of a carbene.
The atomic number of carbon atom is equal to 6.the electronic configuration of the carbon atom is depicted as follows:
$\text{ C = 1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{2}}\text{ }$
The carbon has the 4 electrons in its valence shell$\text{ ( n = 2) }$.
In carbene, the carbon atom is bonded to the two atoms. These are covalent bonds formed by sharing the electron. The total number of the valence electrons in the carbene is from the carbon and the R $\text{ ( let R = H) }$ has the one valence electron from each hydrogen.
Therefore, total valence electrons in the carbene molecule equal to $\text{V}\text{.E}\text{. in carbene = V}\text{.E}\text{. of C + 2 (V}\text{.E}\text{. of H) = 4 + 2 = 6 }{{\text{e}}^{-}}\text{ }$
The carbon atom in the carbene has six valence electrons.
The structure of the carbene atom is:

Here, we know that the carbon atom of the carbene has 6 valence electrons.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Additional information:
In carbene, the lone of electrons are accommodated in the unhybridized p – orbital. The electrons can be arranged in different forms.
The carbene exists in the two forms. These are:
1) Triplet state: the triplet carbene has the two unshared electrons. One of the electrons is present $\text{ s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ }$ in hybrid orbitals and the one-electron is in the unhybridized p-orbital. These electrons have the same spin.
2) Singlet state: In singlet state, non-bonding pair of electrons are in the $\text{ s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ }$ hybrid orbitals and one in the p orbitals. These electrons have the opposite spins.
The two carbene forms are different, not only in the structure but also concerning the reactivity.
Note: The carbene is very commonly intermediated in various organic reactions. The three major reactions of the carbene are:
1) Carbene insertions
2) Carbene additions
3) Carbene rearrangements
The two nonbonding and 2 unshared electrons make it more reactive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




