
Uterus masculine opens at
(a)Uterus anteriorly
(b)Prostatic portion of the urethra
(c)Vagina
(d)None of the above
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Uterus masculinus is a double-lobed sac-like structure present in the excretory system of some vertebrates. It starts from the base part of the Mullerian duct in mammals and located at the back of the urinary bladder.
Complete answer:
Uterus masculine opens at the prostatic portion of the urethra. When organisms are involved In sexual activity it fills the prostate gland using its secretion. The prostatic portion of the urethra begins in the area of the bladder neck and ends in the membranous urethra.
Additional Information: -By the convexity points forward, the lateral part of the canal as it lies in the prostate is in horse-shoe-shape. Due to a dilated bladder and prostatic urethra, in an ultrasound scan, a keyhole sign is observed.
-Even though the prostatic utricle, uterus, and vagina are occasionally disputed, they all are derived from the paramesonephric duct.
-Uterus masculinus is also called the vagina masculina or vesicula prostatica.
So, the correct answer is ‘prostatic portion of urethra’.
Note: -Menorrhagia: an abnormal condition where very longed and high menstrual bleeding occurs due to hormonal imbalances, the formation of fibroids, polyps, several kinds of birth control, or tumours.
-Uterine prolapse: takes place when the muscles and ligaments which keep the uterus in position become weak and because of this, the uterus will descend near the bladder. As women get older they develop mild to moderate uterine prolapse.
-In rare conditions, the uterus will be abnormally shaped which can create problems in pregnancy and sometimes leads to miscarriage. It can be identified using an ultrasound scan or an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan.
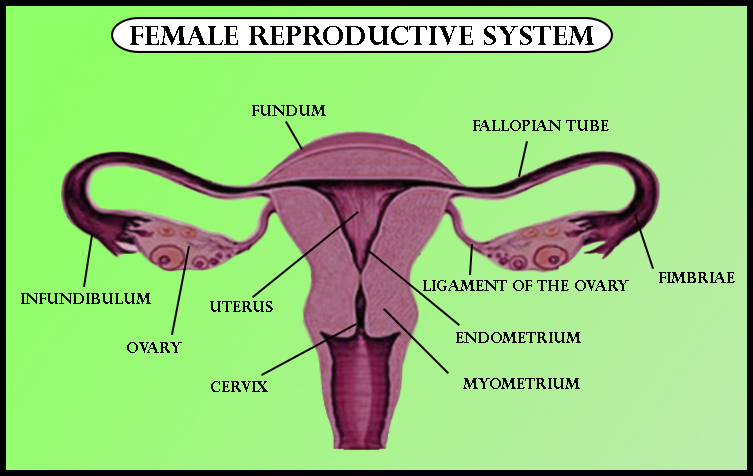
Complete answer:
Uterus masculine opens at the prostatic portion of the urethra. When organisms are involved In sexual activity it fills the prostate gland using its secretion. The prostatic portion of the urethra begins in the area of the bladder neck and ends in the membranous urethra.
Additional Information: -By the convexity points forward, the lateral part of the canal as it lies in the prostate is in horse-shoe-shape. Due to a dilated bladder and prostatic urethra, in an ultrasound scan, a keyhole sign is observed.
-Even though the prostatic utricle, uterus, and vagina are occasionally disputed, they all are derived from the paramesonephric duct.
-Uterus masculinus is also called the vagina masculina or vesicula prostatica.
So, the correct answer is ‘prostatic portion of urethra’.
Note: -Menorrhagia: an abnormal condition where very longed and high menstrual bleeding occurs due to hormonal imbalances, the formation of fibroids, polyps, several kinds of birth control, or tumours.
-Uterine prolapse: takes place when the muscles and ligaments which keep the uterus in position become weak and because of this, the uterus will descend near the bladder. As women get older they develop mild to moderate uterine prolapse.
-In rare conditions, the uterus will be abnormally shaped which can create problems in pregnancy and sometimes leads to miscarriage. It can be identified using an ultrasound scan or an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




