
Using the Hess’ Law, how to calculate the standard heat of formation of copper(I) oxide given in the following data?
\[CuO(s)\, \to \,Cu(s)\, + \,\dfrac{1}{2}{O_2}\,\Delta H = 157.3\,kJ/mol\]
\[4CuO(s)\, \to \,2C{u_2}O(s)\, + \,\dfrac{1}{2}{O_2}(g)\,\Delta H = 292.0\,kJ/mol\]
Answer
556.8k+ views
Hint: The Hess’s law is major in physical chemistry which states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the route by which the chemical change takes place. Formation of heat is defined as the enthalpy change which accompanies the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of substance in a standard state from its elements also taken in standard state.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that Hess law takes the independent route for the reaction. In thermodynamics, we need the initial and final states. So, we need to construct a Hess Cycle using the given information;
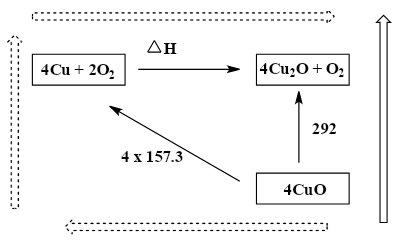
While we observe the diagram, in the terms of energy, the dashed long route is equal to the black arrow route as the arrows start and finish in the same place. This diagram represents and follows the Hess law.
So, we can write as; \[(4\, \times \,157.3)\, + \,\Delta H\, = \,292\]
Therefore, \[\Delta H\, = \, - 337.2\,kJ\]
Enthalpy of formation is defined as the enthalpy change which accompanies the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of substance in a standard state from its elements also taken in standard state under the standard conditions.
We have found\[\Delta H\]for below equation;
\[4Cu\, + \,2{O_2}\, \to \,\,2C{u_2}O\, + \,{O_2}\]
That means, it is the same as:
\[4Cu\, + \,{O_2}\, \to \,\,2C{u_2}O\]
This means the formation of \[2{\text{ }}moles\] of copper(I) oxide.
So, we need to find the change in enthalpy for the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of copper(I) oxide.
Therefore,
\[\Delta {H_f}\left[ {Cu2O} \right]\, = \,\dfrac{{\Delta \,H}}{2}\, = \, - \dfrac{{337.2}}{2}\, = \, - 168.6\,kJ/mol\]
So, for the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of copper(I) oxide we need \[ - 168.6\,kJ/mol\] enthalpy.
Note: We must know that Hess’s law is a version of the first law of thermodynamics. So, it means the energy is always conserved. Often Hess’s law cycles are used to measure the change in enthalpy for a reaction that can’t be measured directly by experiments. Instead, the alternative method/ reactions are carried out that can be measured experimentally.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that Hess law takes the independent route for the reaction. In thermodynamics, we need the initial and final states. So, we need to construct a Hess Cycle using the given information;

While we observe the diagram, in the terms of energy, the dashed long route is equal to the black arrow route as the arrows start and finish in the same place. This diagram represents and follows the Hess law.
So, we can write as; \[(4\, \times \,157.3)\, + \,\Delta H\, = \,292\]
Therefore, \[\Delta H\, = \, - 337.2\,kJ\]
Enthalpy of formation is defined as the enthalpy change which accompanies the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of substance in a standard state from its elements also taken in standard state under the standard conditions.
We have found\[\Delta H\]for below equation;
\[4Cu\, + \,2{O_2}\, \to \,\,2C{u_2}O\, + \,{O_2}\]
That means, it is the same as:
\[4Cu\, + \,{O_2}\, \to \,\,2C{u_2}O\]
This means the formation of \[2{\text{ }}moles\] of copper(I) oxide.
So, we need to find the change in enthalpy for the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of copper(I) oxide.
Therefore,
\[\Delta {H_f}\left[ {Cu2O} \right]\, = \,\dfrac{{\Delta \,H}}{2}\, = \, - \dfrac{{337.2}}{2}\, = \, - 168.6\,kJ/mol\]
So, for the formation of \[1{\text{ }}mole\] of copper(I) oxide we need \[ - 168.6\,kJ/mol\] enthalpy.
Note: We must know that Hess’s law is a version of the first law of thermodynamics. So, it means the energy is always conserved. Often Hess’s law cycles are used to measure the change in enthalpy for a reaction that can’t be measured directly by experiments. Instead, the alternative method/ reactions are carried out that can be measured experimentally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




