
Using integration, find the area of $\Delta ABC$, whose vertices are A (2, 0), B (4, 5) and C (6, 3).
Answer
605.1k+ views
Hint: We will first right the equation of line which represents the three sides of the triangle whose area we have to find. Then we will break the area of the triangle into two parts and find the area of each part by integration.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, before we start finding the area of the triangle through integration. We will first draw the graph of the given triangle.
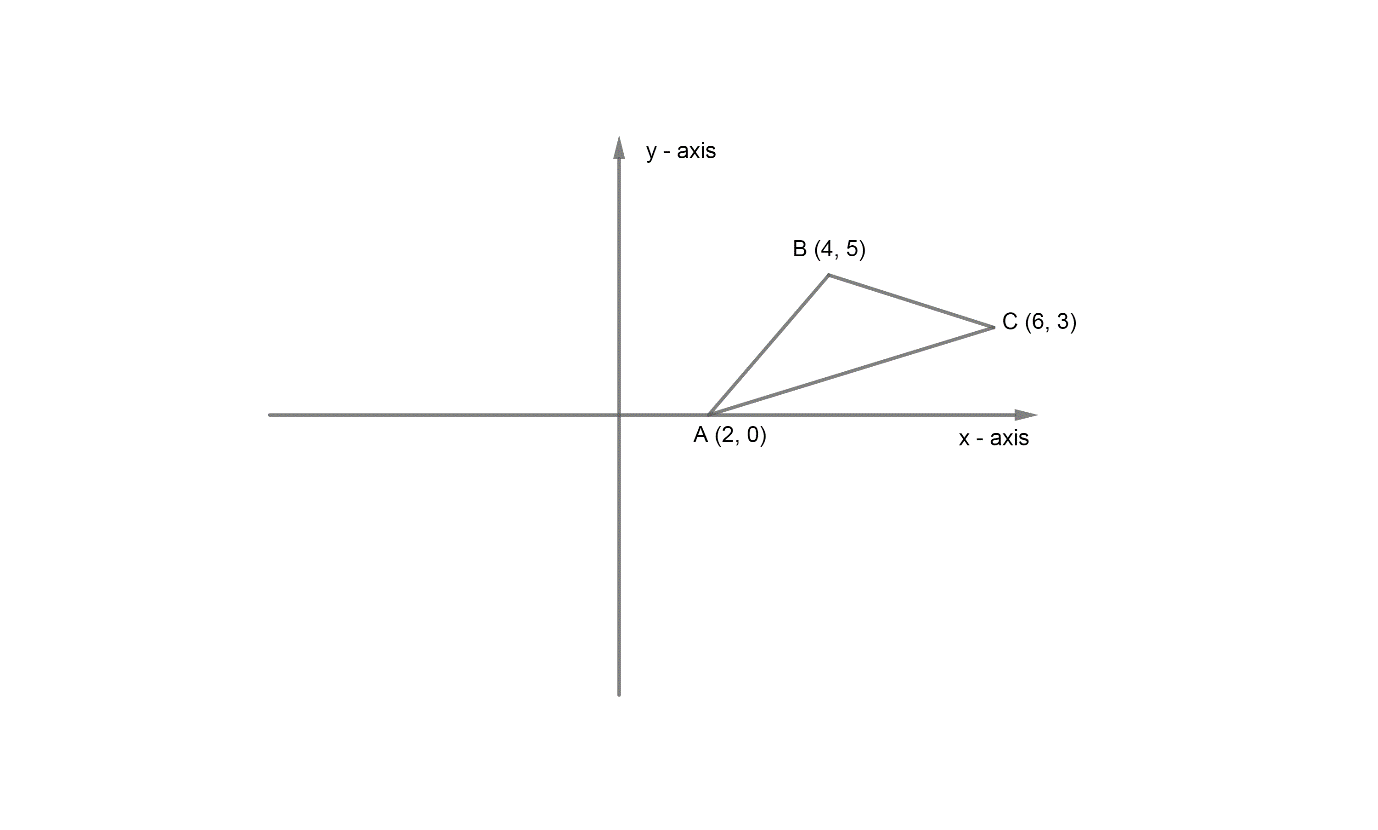
Now, to find the area of $\Delta ABC$ by integration one should know that if there is function \[f\left( x \right)\] such that,
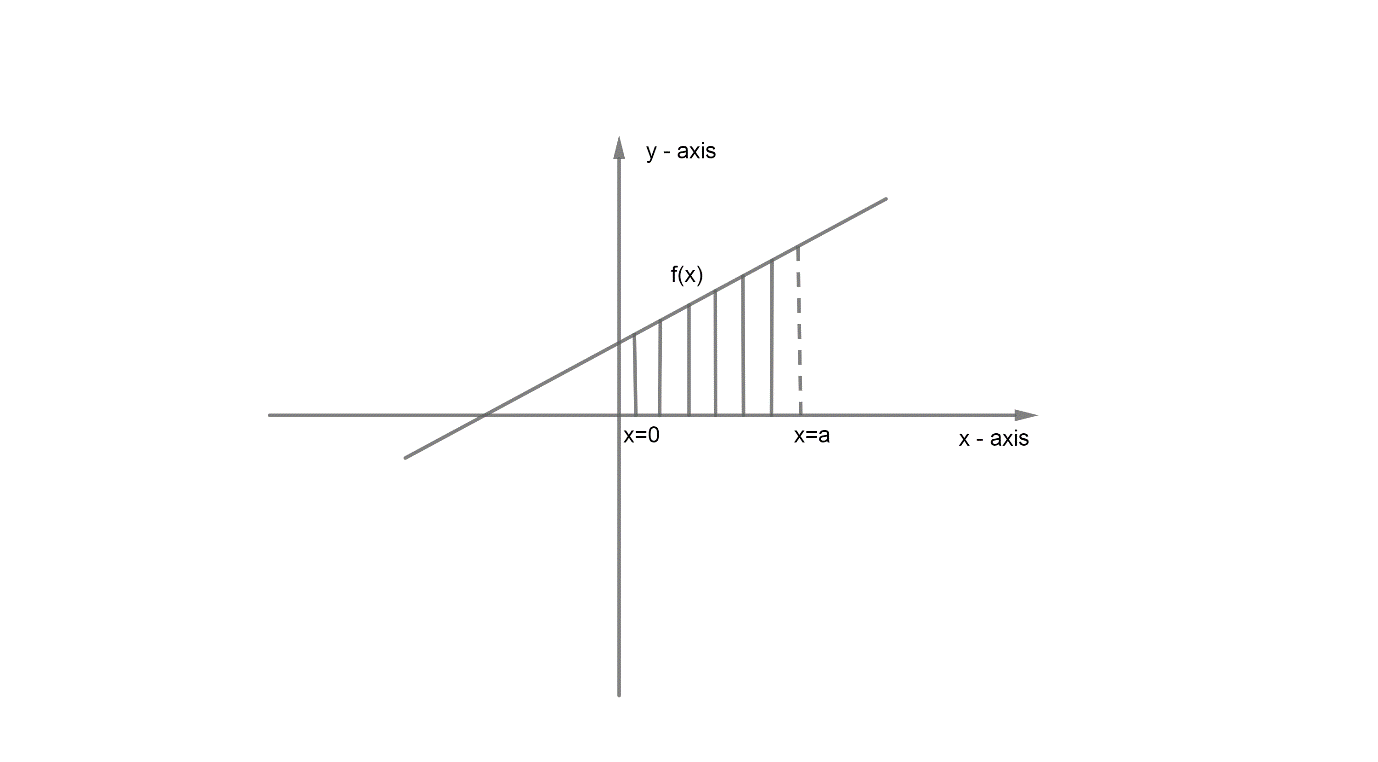
The area of the shaded region is given by $\int\limits_{x=0}^{x=a}{f\left( x \right)dx}$. Therefore, we will use the following concept in finding the area of $\Delta ABC$.
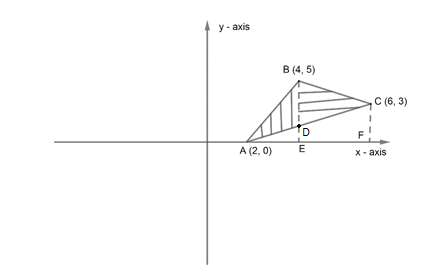
Now, we will find the area of $\Delta ABC$ as a sum of the area of $\Delta ABD$ and or $\Delta BDC$. So, we have to first find the equation of sides of the triangle.
We know that the equation of line in two points form is,
$\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Equation of line AB is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-0 \right)=\left( \dfrac{5-0}{4-2} \right)\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \left( y-0 \right)=\dfrac{5}{2}\left( x-2 \right) \\
& 2y=5x-10 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 5x-10 \right).........\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Equation of line BC is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-5 \right)=\dfrac{5-3}{4-6}\left( x-4 \right) \\
& \left( y-5 \right)=\dfrac{2}{-2}\left( x-4 \right) \\
& y-5=-x+4 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-x+9.........\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Equation of line AC is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{3-0}{6-2} \right)\left( x-6 \right) \\
& \left( y-3 \right)=\dfrac{3}{4}\left( x-6 \right) \\
& y=3+\dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{4}\times 6 \\
& y=\dfrac{3}{4}x+3-\dfrac{9}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{2}.........\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have to first find the area of $\Delta ABD$ for this we will find the area of $\Delta ABE$ and subtract the area of $\Delta ADE$. So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& ar\Delta ABD=ar\Delta ABE-ar\Delta ADE \\
& =\int{\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 5x-10 \right)dx-\int{\left( \dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{2} \right)dx}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, the limit of both the integral will be from x = 2 to x = 4 as we can see from the graph. Therefore, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}\left( 5x-10 \right)-\left( \dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{2} \right) \right)} \\
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \dfrac{5}{2}x-5-\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}dx \\
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \left( \dfrac{10-3}{4} \right)x-\dfrac{10+3}{2} \right)}dx \\
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \dfrac{7}{4}x-\dfrac{7}{2} \right)}dx \\
& =\dfrac{7}{4}\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}-\left. \dfrac{7}{2}x \right|_{2}^{4} \\
& =\dfrac{7}{4}\left( \dfrac{16-4}{2} \right)-\dfrac{7}{2}\left( 4-2 \right) \\
& =\dfrac{7}{4}\dfrac{\left( 12 \right)}{2}-\dfrac{7}{2}\left( 2 \right) \\
& =-\dfrac{35}{2}+\dfrac{42}{2} \\
& =\dfrac{42-35}{2} \\
& =\dfrac{7}{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}\]
So, the area of,
$\begin{align}
& ar\Delta ABC=ar\Delta ABD+ar\Delta BDE \\
& =\dfrac{7}{2}+\dfrac{7}{2} \\
& =7sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
Note: While solving this question it is important to note that we have broken the area into two parts because after point B the equation of curve is different. Therefore, we need to calculate the area separately for two curves.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, before we start finding the area of the triangle through integration. We will first draw the graph of the given triangle.

Now, to find the area of $\Delta ABC$ by integration one should know that if there is function \[f\left( x \right)\] such that,

The area of the shaded region is given by $\int\limits_{x=0}^{x=a}{f\left( x \right)dx}$. Therefore, we will use the following concept in finding the area of $\Delta ABC$.

Now, we will find the area of $\Delta ABC$ as a sum of the area of $\Delta ABD$ and or $\Delta BDC$. So, we have to first find the equation of sides of the triangle.
We know that the equation of line in two points form is,
$\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$
Equation of line AB is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-0 \right)=\left( \dfrac{5-0}{4-2} \right)\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \left( y-0 \right)=\dfrac{5}{2}\left( x-2 \right) \\
& 2y=5x-10 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 5x-10 \right).........\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Equation of line BC is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-5 \right)=\dfrac{5-3}{4-6}\left( x-4 \right) \\
& \left( y-5 \right)=\dfrac{2}{-2}\left( x-4 \right) \\
& y-5=-x+4 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-x+9.........\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Equation of line AC is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-3 \right)=\left( \dfrac{3-0}{6-2} \right)\left( x-6 \right) \\
& \left( y-3 \right)=\dfrac{3}{4}\left( x-6 \right) \\
& y=3+\dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{4}\times 6 \\
& y=\dfrac{3}{4}x+3-\dfrac{9}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{2}.........\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have to first find the area of $\Delta ABD$ for this we will find the area of $\Delta ABE$ and subtract the area of $\Delta ADE$. So, we have,
$\begin{align}
& ar\Delta ABD=ar\Delta ABE-ar\Delta ADE \\
& =\int{\dfrac{1}{2}\left( 5x-10 \right)dx-\int{\left( \dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{2} \right)dx}} \\
\end{align}$
Now, the limit of both the integral will be from x = 2 to x = 4 as we can see from the graph. Therefore, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \dfrac{1}{2}\left( 5x-10 \right)-\left( \dfrac{3}{4}x-\dfrac{3}{2} \right) \right)} \\
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \dfrac{5}{2}x-5-\dfrac{3}{4}x+\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}dx \\
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \left( \dfrac{10-3}{4} \right)x-\dfrac{10+3}{2} \right)}dx \\
& =\int\limits_{2}^{4}{\left( \dfrac{7}{4}x-\dfrac{7}{2} \right)}dx \\
& =\dfrac{7}{4}\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}-\left. \dfrac{7}{2}x \right|_{2}^{4} \\
& =\dfrac{7}{4}\left( \dfrac{16-4}{2} \right)-\dfrac{7}{2}\left( 4-2 \right) \\
& =\dfrac{7}{4}\dfrac{\left( 12 \right)}{2}-\dfrac{7}{2}\left( 2 \right) \\
& =-\dfrac{35}{2}+\dfrac{42}{2} \\
& =\dfrac{42-35}{2} \\
& =\dfrac{7}{2}sq\ units \\
\end{align}\]
So, the area of,
$\begin{align}
& ar\Delta ABC=ar\Delta ABD+ar\Delta BDE \\
& =\dfrac{7}{2}+\dfrac{7}{2} \\
& =7sq\ units \\
\end{align}$
Note: While solving this question it is important to note that we have broken the area into two parts because after point B the equation of curve is different. Therefore, we need to calculate the area separately for two curves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




