
Using a punnett square workout the distribution of phenotypic features in the first filial generation after a cross between a homozygous female and heterozygous male for a single locus.

Answer
501.3k+ views
Hint: First filial or progeny is the generation of hybrids comprising a cross among the genetically different individuals known as the parents. The filial generations are arranged in a sequence of mating such that the successive generations after a parental generation are represented by the symbol \[F1\] for the first filial generation, \[F2\] for the second filial generation, and so on. A cross among homozygous and heterozygous parents for a single locus will produce \[1:1\] ratio of phenotypic capabilities in the \[F1\] generation.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the example of Guinea pigs, a homozygous female with white colour (bb) is crossed with the heterozygous male having black colour (Bb). The male gamete will produce two kinds of gametes, i.e., B and b, at the same time as the female will produce only one kind of gamete, that’s b. The \[F1\] progeny will display each individual with black colour and white colour in a ratio of \[1:1\]. Here, the phenotypic, in addition to the genotypic ratio, can be \[1:1\].
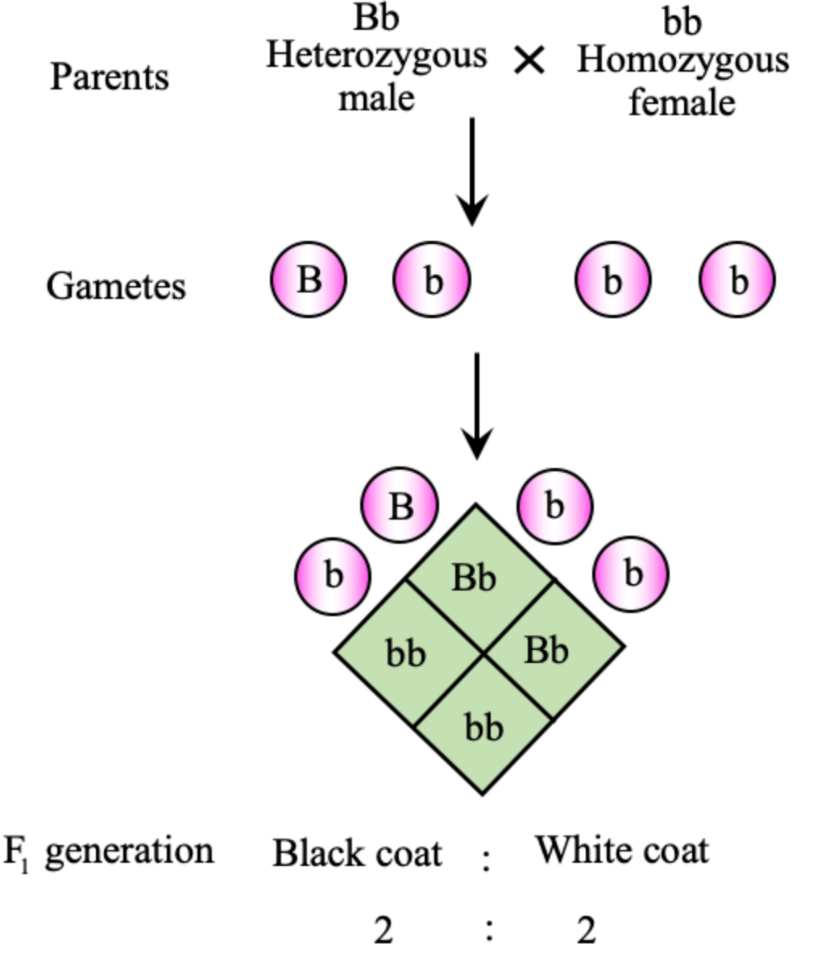
Black colour: White colour
Genotypic ratio- \[Bb:bb{\text{ }}1:1\]
Phenotypic ratio- Black colour : white colour \[1:1\]
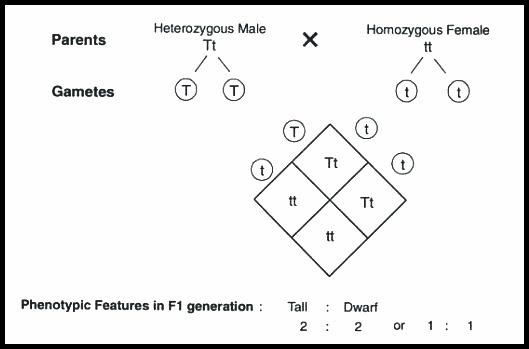
In the above figure, it’s clear that it is a cross between a heterozygous male with a homozygous female. In the \[F1\] generation the following phenotypic functions are observed:
\[\dfrac{1}{2}\] of the progeny are Heterozygous Tall (Tt).
Another \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] of the population is Homozygous short (tt).
Hence, the ratio for phenotypic ratio is equal to the genotype ratio, that is \[2:2\] or \[1:1\]
Note:
The filial generation is represented with the symbol F. Successive generations of progeny in a sequence of crosses, beginning with two specific individuals and selfing or intercrossing the progeny of every new \[\left( {F1;{\text{ }}F2;...} \right)\] generation. The offspring of distinctly different parents will produce a new and uniform phenotype with a combination of traits from the parents.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the example of Guinea pigs, a homozygous female with white colour (bb) is crossed with the heterozygous male having black colour (Bb). The male gamete will produce two kinds of gametes, i.e., B and b, at the same time as the female will produce only one kind of gamete, that’s b. The \[F1\] progeny will display each individual with black colour and white colour in a ratio of \[1:1\]. Here, the phenotypic, in addition to the genotypic ratio, can be \[1:1\].

Black colour: White colour
Genotypic ratio- \[Bb:bb{\text{ }}1:1\]
Phenotypic ratio- Black colour : white colour \[1:1\]
In the above figure, it’s clear that it is a cross between a heterozygous male with a homozygous female. In the \[F1\] generation the following phenotypic functions are observed:
\[\dfrac{1}{2}\] of the progeny are Heterozygous Tall (Tt).
Another \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] of the population is Homozygous short (tt).
Hence, the ratio for phenotypic ratio is equal to the genotype ratio, that is \[2:2\] or \[1:1\]
Note:
The filial generation is represented with the symbol F. Successive generations of progeny in a sequence of crosses, beginning with two specific individuals and selfing or intercrossing the progeny of every new \[\left( {F1;{\text{ }}F2;...} \right)\] generation. The offspring of distinctly different parents will produce a new and uniform phenotype with a combination of traits from the parents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




