
How do you use the quadratic formula to solve \[12{\sin ^2}x - 13\sin x + 3 = 0\] in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$?
Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: First, substitute $u$ for all occurrences of $\sin x$ and find the value of $u$ using quadratic formula. Then, compare the given quadratic equation to the standard quadratic equation and find the value of numbers $a$, $b$ and $c$ in the given equation. Then, substitute the values of $a$, $b$ and $c$ in the formula of discriminant and find the discriminant of the given equation. Finally, put the values of $a$, $b$ and $D$ in the roots of the quadratic equation formula. Next, replace all occurrences of $u$ with $\sin x$ solve for $x$ using trigonometric properties. Then, we will get all solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Formula used:
The quantity $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ is known as the discriminant of the equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ and its roots are given by
$x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}$ or $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation: \[12{\sin ^2}x - 13\sin x + 3 = 0\]
We have to find all possible values of $x$ satisfying a given equation in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
So, first put $u = \sin x$, i.e., substitute $u$ for all occurrences of $\sin x$.
$ \Rightarrow 12{u^2} - 13u + 3 = 0$
Now, we have to find the value of $u$ using a quadratic formula.
We know that an equation of the form $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, $a,b,c,x \in R$, is called a Real Quadratic Equation.
The numbers $a$, $b$ and $c$ are called the coefficients of the equation.
The quantity $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ is known as the discriminant of the equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ and its roots are given by
$x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}$ or $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$
First, compare $3{x^2} + 5x = 0$ quadratic equation to standard quadratic equation and find the value of numbers $a$, $b$ and $c$.
Comparing $12{u^2} - 13u + 3 = 0$ with $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, we get
$a = 12$, $b = - 13$ and $c = 3$
Now, substitute the values of $a$, $b$ and $c$ in $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ and find the discriminant of the given equation.
$D = {\left( { - 13} \right)^2} - 4\left( {12} \right)\left( 3 \right)$
After simplifying the result, we get
$ \Rightarrow D = 169 - 144$
$ \Rightarrow D = 25$
Which means the given equation has real roots.
Now putting the values of $a$, $b$ and $D$ in $u = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}$, we get
$u = \dfrac{{ - \left( { - 13} \right) \pm 5}}{{2 \times 12}}$
It can be written as
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{13 \pm 5}}{{24}}$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{3}{4}$ and $u = \dfrac{1}{3}$
Now, replace all occurrences of $u$ with $\sin x$.
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \dfrac{3}{4}$ and $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{3}$
First, we will find the values of $x$ satisfying $\sin x = \dfrac{3}{4}$.
So, take the inverse sine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the sine.
$x = \arcsin \left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right)$
Since, the exact value of $\arcsin \left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) = 0.848062079$.
$ \Rightarrow x = 0.848062079$
Since, the sine function is positive in the first and second quadrants.
So, to find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $\pi $ to find the solution in the second quadrant.
$x = 3.14 - 0.848062079$
$ \Rightarrow x = 2.293530575$
Since, the period of the $\sin x$ function is $2\pi $ so values will repeat every $2\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = 0.848062079 + 2n\pi ,2.293530575 + 2n\pi $, for any integer $n$.
First, we will find the values of $x$ satisfying $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{3}$.
So, take the inverse sine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the sine.
$x = \arcsin \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$
Since, the exact value of $\arcsin \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right) = 0.3398369095$.
$ \Rightarrow x = 0.3398369095$
Since, the sine function is positive in the first and second quadrants.
So, to find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $\pi $ to find the solution in the second quadrant.
$x = 3.14 - 0.3398369095$
$ \Rightarrow x = 2.801755744$
Since, the period of the $\sin x$ function is $2\pi $ so values will repeat every $2\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = 0.3398369095 + 2n\pi ,2.801755744 + 2n\pi $, for any integer $n$.
Thus, $x = 0.848062079 + 2n\pi ,2.293530575 + 2n\pi ,0.3398369095 + 2n\pi ,2.801755744 + 2n\pi $
Where, $n$ is any integer, i.e., $n = 0, \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 3,......$
Now, find all values of $x$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
Since, it is given that $x \in \left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$, hence put $n = 0$ in the general solution.
So, putting $n = 0$ in the general solution, $x = 0.848062079 + 2n\pi ,2.293530575 + 2n\pi ,0.3398369095 + 2n\pi ,2.801755744 + 2n\pi $, we get
$\therefore x = 0.848062079,2.293530575,0.3398369095,2.801755744$
Final solution: Hence, $x = 0.848062079,2.293530575,0.3398369095,2.801755744$ are the solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Note:
In above question, we can find the solutions of given equation by plotting the equation, \[12{\sin ^2}x - 13\sin x + 3 = 0\] on graph paper and determine all solutions which lie in the interval, $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
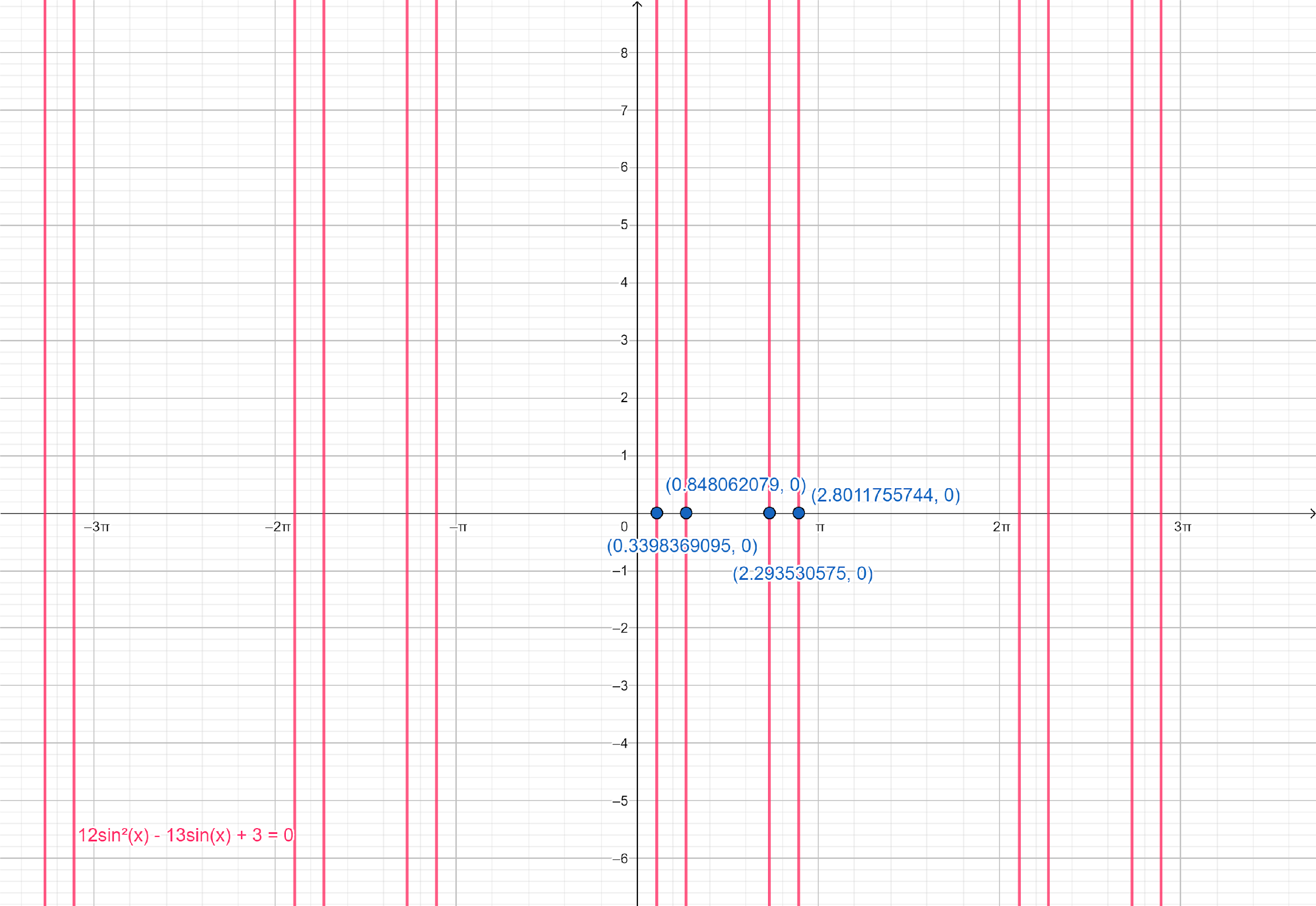
From the graph paper, we can see that there are four values of $x$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
So, these will be the solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Final solution: Hence, $x = 0.848062079,2.293530575,0.3398369095,2.801755744$ are the solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Formula used:
The quantity $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ is known as the discriminant of the equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ and its roots are given by
$x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}$ or $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Given equation: \[12{\sin ^2}x - 13\sin x + 3 = 0\]
We have to find all possible values of $x$ satisfying a given equation in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
So, first put $u = \sin x$, i.e., substitute $u$ for all occurrences of $\sin x$.
$ \Rightarrow 12{u^2} - 13u + 3 = 0$
Now, we have to find the value of $u$ using a quadratic formula.
We know that an equation of the form $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, $a,b,c,x \in R$, is called a Real Quadratic Equation.
The numbers $a$, $b$ and $c$ are called the coefficients of the equation.
The quantity $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ is known as the discriminant of the equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ and its roots are given by
$x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}$ or $x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt {{b^2} - 4ac} }}{{2a}}$
First, compare $3{x^2} + 5x = 0$ quadratic equation to standard quadratic equation and find the value of numbers $a$, $b$ and $c$.
Comparing $12{u^2} - 13u + 3 = 0$ with $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, we get
$a = 12$, $b = - 13$ and $c = 3$
Now, substitute the values of $a$, $b$ and $c$ in $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ and find the discriminant of the given equation.
$D = {\left( { - 13} \right)^2} - 4\left( {12} \right)\left( 3 \right)$
After simplifying the result, we get
$ \Rightarrow D = 169 - 144$
$ \Rightarrow D = 25$
Which means the given equation has real roots.
Now putting the values of $a$, $b$ and $D$ in $u = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}$, we get
$u = \dfrac{{ - \left( { - 13} \right) \pm 5}}{{2 \times 12}}$
It can be written as
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{13 \pm 5}}{{24}}$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{3}{4}$ and $u = \dfrac{1}{3}$
Now, replace all occurrences of $u$ with $\sin x$.
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \dfrac{3}{4}$ and $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{3}$
First, we will find the values of $x$ satisfying $\sin x = \dfrac{3}{4}$.
So, take the inverse sine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the sine.
$x = \arcsin \left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right)$
Since, the exact value of $\arcsin \left( {\dfrac{3}{4}} \right) = 0.848062079$.
$ \Rightarrow x = 0.848062079$
Since, the sine function is positive in the first and second quadrants.
So, to find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $\pi $ to find the solution in the second quadrant.
$x = 3.14 - 0.848062079$
$ \Rightarrow x = 2.293530575$
Since, the period of the $\sin x$ function is $2\pi $ so values will repeat every $2\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = 0.848062079 + 2n\pi ,2.293530575 + 2n\pi $, for any integer $n$.
First, we will find the values of $x$ satisfying $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{3}$.
So, take the inverse sine of both sides of the equation to extract $x$ from inside the sine.
$x = \arcsin \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$
Since, the exact value of $\arcsin \left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right) = 0.3398369095$.
$ \Rightarrow x = 0.3398369095$
Since, the sine function is positive in the first and second quadrants.
So, to find the second solution, subtract the reference angle from $\pi $ to find the solution in the second quadrant.
$x = 3.14 - 0.3398369095$
$ \Rightarrow x = 2.801755744$
Since, the period of the $\sin x$ function is $2\pi $ so values will repeat every $2\pi $ radians in both directions.
$x = 0.3398369095 + 2n\pi ,2.801755744 + 2n\pi $, for any integer $n$.
Thus, $x = 0.848062079 + 2n\pi ,2.293530575 + 2n\pi ,0.3398369095 + 2n\pi ,2.801755744 + 2n\pi $
Where, $n$ is any integer, i.e., $n = 0, \pm 1, \pm 2, \pm 3,......$
Now, find all values of $x$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
Since, it is given that $x \in \left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$, hence put $n = 0$ in the general solution.
So, putting $n = 0$ in the general solution, $x = 0.848062079 + 2n\pi ,2.293530575 + 2n\pi ,0.3398369095 + 2n\pi ,2.801755744 + 2n\pi $, we get
$\therefore x = 0.848062079,2.293530575,0.3398369095,2.801755744$
Final solution: Hence, $x = 0.848062079,2.293530575,0.3398369095,2.801755744$ are the solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Note:
In above question, we can find the solutions of given equation by plotting the equation, \[12{\sin ^2}x - 13\sin x + 3 = 0\] on graph paper and determine all solutions which lie in the interval, $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.

From the graph paper, we can see that there are four values of $x$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$.
So, these will be the solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Final solution: Hence, $x = 0.848062079,2.293530575,0.3398369095,2.801755744$ are the solutions of the given equation in the given interval.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




