
How do you use a triple integral to find the volume of the given tetrahedron enclosed by the coordinate planes $2x + y + z = 3$ ?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: To do this question with the help of triple integral, first you have to integrate one variable by taking limits in terms of other two variables. When we go for the second integral only one variable left which we can put on limits and on third time integration there would be no variable on the constant left.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we have
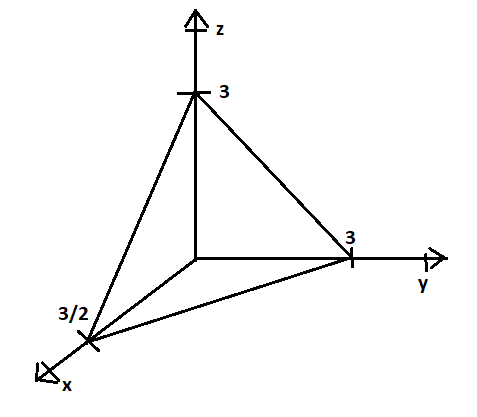
The equation of coordinate planes is $2x + y + z = 3$.
We can also write it as $z = 3 - 2x - y$ .
Now, by setting $z = 0$ , we know that it cuts the x-y plane to $2x + y = 3$.
By setting $\left( {x,y} \right)\, = \,0$, we know that the plane hits the z axis at z $ = \,3$.
Similarly, it hits the x axis at $x\, = \,\dfrac{3}{2}$and y axis at $y\, = \,3$
So, we can draw it in the first octant
Now, we can put the limits as follows $z = 0\,\,to\,\,z = \,3 - 2x - y$
$y = 0\,\,to\,\,y = 3 - 2x$
$x\, = \,0\,\,to\,\,x = \dfrac{3}{2}$
The triple integral is
$ \Rightarrow \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\int\limits_{y = 0}^{3 - 2x} {\int\limits_{z = 0}^{3 - 2x - y} {dzdydx} } } $
$=\int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\int\limits_{y = 0}^{3 - 2x} {\left[ z \right]_0^{3 - 2x - y}} } dydx$
$= \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\int\limits_{y = 0}^{3 - 2x} {\left( {3 - 2x - y} \right)} } dydx$
$= \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left( {3y - 2xy - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{2}} \right)} _0^{3 - 2x}dx$
\[= \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left[ {3\left( {3 - 2x} \right) - 2x\left( {3 - 2x} \right) - \dfrac{{{{\left( {3 - 2x} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \right] - } \left[ {3\left( 0 \right) - 2x\left( 0 \right) - \dfrac{{{{\left( 0 \right)}^2}}}{2}} \right]dx\]
$= \int\limits_0^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left( {9 - 6x - 6x + 4{x^2} - \dfrac{{9 + 4{x^2} - 12x}}{2}} \right)dx} $
\[= \dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left( {18 - 24x + 8{x^2} - 9 - 4{x^2} + 12x} \right)dx} \]
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {18x - \dfrac{{24{x^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{{8{x^3}}}{3} - 9x - \dfrac{{4{x^3}}}{3} + \dfrac{{12{x^2}}}{2}} \right)_0^{\dfrac{3}{2}}$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {18\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right) - 12{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2} + \dfrac{8}{3}{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^3} - 9\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right) - \dfrac{4}{3}{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^3} + 6{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right)$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {27 - 27 + 9 - \dfrac{{27}}{2} - \dfrac{9}{2} + \dfrac{{27}}{2}} \right)$
$= \dfrac{9}{4}$
Therefore, the volume of tetrahedron is $\dfrac{9}{4}$ cubic units.
Note: This is a very useful application of triple integral. We can easily find the volume of three-dimensional bodies using triple integration by knowing the limits from where to where they are varying. In triple integration when we solve the integral for one variable then we have to eliminate that variable in limits for further integration.
Complete step by step solution:
In the given question, we have
The equation of coordinate planes is $2x + y + z = 3$.
We can also write it as $z = 3 - 2x - y$ .
Now, by setting $z = 0$ , we know that it cuts the x-y plane to $2x + y = 3$.
By setting $\left( {x,y} \right)\, = \,0$, we know that the plane hits the z axis at z $ = \,3$.
Similarly, it hits the x axis at $x\, = \,\dfrac{3}{2}$and y axis at $y\, = \,3$
So, we can draw it in the first octant

Now, we can put the limits as follows $z = 0\,\,to\,\,z = \,3 - 2x - y$
$y = 0\,\,to\,\,y = 3 - 2x$
$x\, = \,0\,\,to\,\,x = \dfrac{3}{2}$
The triple integral is
$ \Rightarrow \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\int\limits_{y = 0}^{3 - 2x} {\int\limits_{z = 0}^{3 - 2x - y} {dzdydx} } } $
$=\int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\int\limits_{y = 0}^{3 - 2x} {\left[ z \right]_0^{3 - 2x - y}} } dydx$
$= \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\int\limits_{y = 0}^{3 - 2x} {\left( {3 - 2x - y} \right)} } dydx$
$= \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left( {3y - 2xy - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{2}} \right)} _0^{3 - 2x}dx$
\[= \int\limits_{x = 0}^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left[ {3\left( {3 - 2x} \right) - 2x\left( {3 - 2x} \right) - \dfrac{{{{\left( {3 - 2x} \right)}^2}}}{2}} \right] - } \left[ {3\left( 0 \right) - 2x\left( 0 \right) - \dfrac{{{{\left( 0 \right)}^2}}}{2}} \right]dx\]
$= \int\limits_0^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left( {9 - 6x - 6x + 4{x^2} - \dfrac{{9 + 4{x^2} - 12x}}{2}} \right)dx} $
\[= \dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{3}{2}} {\left( {18 - 24x + 8{x^2} - 9 - 4{x^2} + 12x} \right)dx} \]
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {18x - \dfrac{{24{x^2}}}{2} + \dfrac{{8{x^3}}}{3} - 9x - \dfrac{{4{x^3}}}{3} + \dfrac{{12{x^2}}}{2}} \right)_0^{\dfrac{3}{2}}$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {18\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right) - 12{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2} + \dfrac{8}{3}{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^3} - 9\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right) - \dfrac{4}{3}{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^3} + 6{{\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)}^2}} \right)$
$= \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {27 - 27 + 9 - \dfrac{{27}}{2} - \dfrac{9}{2} + \dfrac{{27}}{2}} \right)$
$= \dfrac{9}{4}$
Therefore, the volume of tetrahedron is $\dfrac{9}{4}$ cubic units.
Note: This is a very useful application of triple integral. We can easily find the volume of three-dimensional bodies using triple integration by knowing the limits from where to where they are varying. In triple integration when we solve the integral for one variable then we have to eliminate that variable in limits for further integration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




