
How many unpaired electrons are there in lead(I)?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: The number of unpaired electrons is evaluated using Hund's rule and Pauli Exclusion Principle. Lead is an element which is positioned in the p-block elements of the periodic table.
Complete step by step answer:
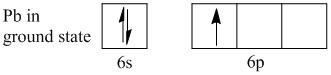
Lead is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[82\] and electronic configuration \[[Xe]4{f^{14}}5{d^{10}}6{s^2}6{p^2}\]. The valence shell of lead is \[6\] which have a total of \[4\] electrons. Of the four valence electrons two electrons are present in \[6s\] and two electrons are present in \[6p\] orbitals.
As the higher orbital is \[p\]-orbital which contains only two electrons is neither a half-filled nor a full-filled orbital, so lead is termed as a \[p\]-block element. According to Hund’s rule and Pauli Exclusion Principle the two electrons must reside on two orbitals as singly filled. The \[p\]-orbitals contain a total of three orbitals. Thus the lead atom contains two unpaired electrons.

When lead releases an electron and forms lead(I), an electron is lost from the p orbital. Thus lead(I) contains only one electron in the \[p\]-orbital. The number indicates that lead is in \[ + 1\] oxidation state. Thus the lead with a single electron is positioned in the \[p\]-orbital has one unpaired electron.
Note:
The number written in the bracket after the name of the element in Roman numerals is called the oxidation state of the element. Hund’s rule of maximum spin multiplicity states that pairing of electrons in the orbitals will not occur until all the orbitals are singly filled. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that none of the two electrons in an orbital will have the same set of four quantum numbers.
Complete step by step answer:
Lead is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[82\] and electronic configuration \[[Xe]4{f^{14}}5{d^{10}}6{s^2}6{p^2}\]. The valence shell of lead is \[6\] which have a total of \[4\] electrons. Of the four valence electrons two electrons are present in \[6s\] and two electrons are present in \[6p\] orbitals.
As the higher orbital is \[p\]-orbital which contains only two electrons is neither a half-filled nor a full-filled orbital, so lead is termed as a \[p\]-block element. According to Hund’s rule and Pauli Exclusion Principle the two electrons must reside on two orbitals as singly filled. The \[p\]-orbitals contain a total of three orbitals. Thus the lead atom contains two unpaired electrons.

When lead releases an electron and forms lead(I), an electron is lost from the p orbital. Thus lead(I) contains only one electron in the \[p\]-orbital. The number indicates that lead is in \[ + 1\] oxidation state. Thus the lead with a single electron is positioned in the \[p\]-orbital has one unpaired electron.

Note:
The number written in the bracket after the name of the element in Roman numerals is called the oxidation state of the element. Hund’s rule of maximum spin multiplicity states that pairing of electrons in the orbitals will not occur until all the orbitals are singly filled. Pauli’s exclusion principle states that none of the two electrons in an orbital will have the same set of four quantum numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




