
Under what condition will the strength of current in a wire of resistance \[R\] be the same for connection is series and in parallel of $ n $ identical cells each of the interval resistance $ r $ ? When
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }R=nr \\
& \text{B}\text{. }R=\dfrac{r}{n} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }R=r \\
& \text{D}\text{. }R\to \infty ,r\to 0 \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: Use Kirchhoff’s law. There are two kinds of circuit used- series and parallel. In series, current in the branch is the same while in parallel series circuit, voltage is the same across resistance. In our home we preferred parallel circuits than series. Every battery or cell has its own internal resistance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First understand what question want to convey-
Question explanation- We have two circuits in series and in parallel combination. Resistance which we have applied to the circuit is \[R\] and internal resistance of $ n $ cells $ E $ is $ r $ . Then at what condition current flowing through two different circuits will be the same.
Aim: Find conditions at which both the current in two different circuits will be the same.
Consider two circuits as shown in figure. In circuit one which is in series combination, connect resistance \[R\] with $ n $ different cells $ E $ and internal resistance of cell $ E $ is $ r $ in series. In circuit two which is in parallel combination, connect resistance \[R\] with $ n $ different cells $ E $ and internal resistance of cell $ E $ is $ r $ in parallel.
Circuit-
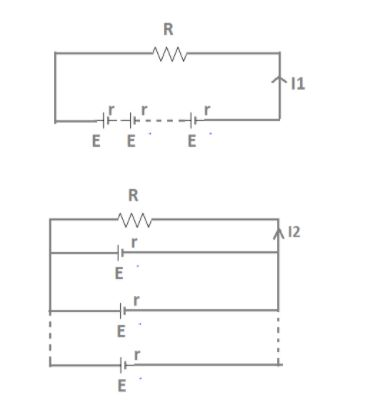
Current in first circuit-
By Kirchhoff’s voltage law,
$ \begin{align}
& {{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{nE}{R+nr} \\
& \\
\end{align} $
Current in second circuit-
By Kirchhoff’s voltage law, net voltage $ E $ is given by
$ {{E}_{net}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{r}_{1}}}+.....\dfrac{{{E}_{n}}}{{{r}_{n}}}}{\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}+........\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{n}}}}..............(1) $
Since all cells are equal i.e. $ E $ and all internal resistive $ r $ are the same.
\[{{E}_{net}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{E}{r}+.....\dfrac{E}{r}}{\dfrac{1}{r}+........\dfrac{1}{r}}\]
By solving
\[{{E}_{net}}=E\]
And
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}+......\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{n}}}=\dfrac{n}{r} \\
& {{r}_{eq}}=\dfrac{r}{n} \\
\end{align}\]
$ {{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{nE}{R+\dfrac{r}{n}} $ .
According to the given condition, current flow in the series circuit must be equal to current in parallel circuit.
$ {{I}_{1}}={{I}_{2}} $
Put values and we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{nE}{R+nr}=\dfrac{nE}{nR+r} \\
& nr+E=r=nR \\
& R(n-1)=r(n-1) \\
& R=r \\
\end{align} $
This is the condition where current in both circuits will be the same.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: This is a tricky question but I can be solved in an easy way which we have already solved. But you can keep keywords to memorize it easily. Just remember equation (1), from this you will get an idea and key equation. Equation (1) is derived from \[V=IR\]. Do not mug equation (1). Just use the \[V=IR\] equation.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First understand what question want to convey-
Question explanation- We have two circuits in series and in parallel combination. Resistance which we have applied to the circuit is \[R\] and internal resistance of $ n $ cells $ E $ is $ r $ . Then at what condition current flowing through two different circuits will be the same.
Aim: Find conditions at which both the current in two different circuits will be the same.
Consider two circuits as shown in figure. In circuit one which is in series combination, connect resistance \[R\] with $ n $ different cells $ E $ and internal resistance of cell $ E $ is $ r $ in series. In circuit two which is in parallel combination, connect resistance \[R\] with $ n $ different cells $ E $ and internal resistance of cell $ E $ is $ r $ in parallel.
Circuit-

Current in first circuit-
By Kirchhoff’s voltage law,
$ \begin{align}
& {{I}_{1}}=\dfrac{nE}{R+nr} \\
& \\
\end{align} $
Current in second circuit-
By Kirchhoff’s voltage law, net voltage $ E $ is given by
$ {{E}_{net}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{E}_{1}}}{{{r}_{1}}}+.....\dfrac{{{E}_{n}}}{{{r}_{n}}}}{\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}+........\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{n}}}}..............(1) $
Since all cells are equal i.e. $ E $ and all internal resistive $ r $ are the same.
\[{{E}_{net}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{E}{r}+.....\dfrac{E}{r}}{\dfrac{1}{r}+........\dfrac{1}{r}}\]
By solving
\[{{E}_{net}}=E\]
And
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{r}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{1}}}+......\dfrac{1}{{{r}_{n}}}=\dfrac{n}{r} \\
& {{r}_{eq}}=\dfrac{r}{n} \\
\end{align}\]
$ {{I}_{2}}=\dfrac{nE}{R+\dfrac{r}{n}} $ .
According to the given condition, current flow in the series circuit must be equal to current in parallel circuit.
$ {{I}_{1}}={{I}_{2}} $
Put values and we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{nE}{R+nr}=\dfrac{nE}{nR+r} \\
& nr+E=r=nR \\
& R(n-1)=r(n-1) \\
& R=r \\
\end{align} $
This is the condition where current in both circuits will be the same.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: This is a tricky question but I can be solved in an easy way which we have already solved. But you can keep keywords to memorize it easily. Just remember equation (1), from this you will get an idea and key equation. Equation (1) is derived from \[V=IR\]. Do not mug equation (1). Just use the \[V=IR\] equation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




