
What type of hydrogen bonding exists in ortho-chlorophenol?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Hydrogen bonding is a form of dipole-dipole attraction that occurs between molecules rather than a covalent bond with a hydrogen atom. The attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bound to a very electronegative atom like an N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom causes it.
Complete answer:
A hydrogen bond (abbreviated H-bond) is an electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom covalently bound to a more electronegative atom or group and another electronegative atom carrying a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). The solid line denotes a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line denotes the hydrogen bond of such an interacting structure.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs as hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules of the same or different compounds.
Hydrogen bonding between water, alcohol, and ammonia, for example.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding refers to hydrogen bonding that occurs within a single molecule.
It occurs in compounds of two groups, one of which has a hydrogen atom linked to an electronegative atom and the other of which has a strongly electronegative atom linked to a less electronegative atom of the other group.
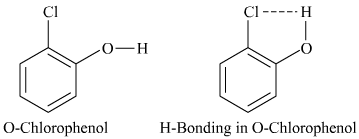
The hydrogen bond is a kind of weak bond that forms between H and most electronegative elements. A hydrogen bond exists between hydrogen and chlorine in onto-chlorophenol, resulting in a five-membered ring.
Note:
Symmetric hydrogen bonding is a type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is normally positioned in the centre of two atoms that are otherwise similar. The frequency of each atom's bond is the same. The symmetric hydrogen bond is a four-electron bond with three centres. This bond is therefore much thicker than the “normal” hydrogen bond, and it resembles a covalent bond in strength.
Complete answer:
A hydrogen bond (abbreviated H-bond) is an electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom covalently bound to a more electronegative atom or group and another electronegative atom carrying a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). The solid line denotes a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line denotes the hydrogen bond of such an interacting structure.
Intermolecular hydrogen bonding occurs as hydrogen bonds are formed between molecules of the same or different compounds.
Hydrogen bonding between water, alcohol, and ammonia, for example.
Intramolecular hydrogen bonding refers to hydrogen bonding that occurs within a single molecule.
It occurs in compounds of two groups, one of which has a hydrogen atom linked to an electronegative atom and the other of which has a strongly electronegative atom linked to a less electronegative atom of the other group.

The hydrogen bond is a kind of weak bond that forms between H and most electronegative elements. A hydrogen bond exists between hydrogen and chlorine in onto-chlorophenol, resulting in a five-membered ring.
Note:
Symmetric hydrogen bonding is a type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is normally positioned in the centre of two atoms that are otherwise similar. The frequency of each atom's bond is the same. The symmetric hydrogen bond is a four-electron bond with three centres. This bond is therefore much thicker than the “normal” hydrogen bond, and it resembles a covalent bond in strength.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




