
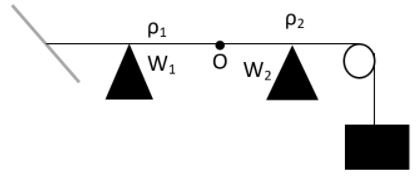
Two wires ${{W}_{1}}$ and ${{W}_{2}}$ have the same radius $r$ and respective densities ${{\rho }_{2}}=4{{\rho }_{1}}$. They are joined together at the point $O$, as shown in the figure. This combination is used as a sonometer wire and kept under tension $T$. The point $O$ is midway between the two bridges. If a stationary wave is created up in the composite wire, then the joint is found to be a node. Therefore, the ratio of the number of antinodes formed in ${{W}_{1}}$ to ${{W}_{2}}$ will be given as,

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The frequency in a stretched string is given as the product of the ratio of the number of antinodes to twice the length and the square root of the ratio of tension to the mass per unit length. The mass per unit length is the product of volume and the density. From this we can say that the number the density is found to be inversely proportional to the square root of density. These all may help you to solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we can see that the frequency of the wave in a stretched string is given by the equation,
$n=\dfrac{p}{2l}\sqrt{\dfrac{T}{m}}$
Where $n$ be the frequency of the string, $p$ be the number of antinodes, $l$ be the length of the wire, $m$ be the mass per unit length and $T$ be the tension of the wire. The mass per unit length can be written as,
$m=V\times \rho $
Where $V$ be the volume given as,
$\begin{align}
& V=\pi {{r}^{2}}\times l \\
& \dfrac{m}{l}=\pi {{r}^{2}}\times \rho \\
\end{align}$
Therefore we can substitute this value in the equation,
$n=\dfrac{p}{2l}\sqrt{\dfrac{T}{\pi {{r}^{2}}\rho }}$
From this we can write that,
As,
$n,T,r,l$ are same in both the cases, we can say that,
$p\propto \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\rho }}$
That is when we compare the strings $1\text{ and }2 $, we can write that,
$\dfrac{{{p}_{1}}}{{{p}_{2}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{2}}}{{{\rho }_{1}}}}$
It is already mentioned in the question that,
${{\rho }_{2}}=4{{\rho }_{1}}$
Substituting this in this equation will give,
$\dfrac{{{p}_{2}}}{{{p}_{1}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore the correct answer is obtained.
Note: The node of a wave is defined as the points on a standing wave where the amplitudes are minimum. Whereas the antinode of a wave is given as the points on the standing wave where the amplitude is maximum. This is the difference between the terms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we can see that the frequency of the wave in a stretched string is given by the equation,
$n=\dfrac{p}{2l}\sqrt{\dfrac{T}{m}}$
Where $n$ be the frequency of the string, $p$ be the number of antinodes, $l$ be the length of the wire, $m$ be the mass per unit length and $T$ be the tension of the wire. The mass per unit length can be written as,
$m=V\times \rho $
Where $V$ be the volume given as,
$\begin{align}
& V=\pi {{r}^{2}}\times l \\
& \dfrac{m}{l}=\pi {{r}^{2}}\times \rho \\
\end{align}$
Therefore we can substitute this value in the equation,
$n=\dfrac{p}{2l}\sqrt{\dfrac{T}{\pi {{r}^{2}}\rho }}$
From this we can write that,
As,
$n,T,r,l$ are same in both the cases, we can say that,
$p\propto \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\rho }}$
That is when we compare the strings $1\text{ and }2 $, we can write that,
$\dfrac{{{p}_{1}}}{{{p}_{2}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{{{\rho }_{2}}}{{{\rho }_{1}}}}$
It is already mentioned in the question that,
${{\rho }_{2}}=4{{\rho }_{1}}$
Substituting this in this equation will give,
$\dfrac{{{p}_{2}}}{{{p}_{1}}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore the correct answer is obtained.
Note: The node of a wave is defined as the points on a standing wave where the amplitudes are minimum. Whereas the antinode of a wave is given as the points on the standing wave where the amplitude is maximum. This is the difference between the terms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




