
Two wires of resistance $ {R_1} $ and $ {R_2} $ at $ {0^0}C $ have temperature coefficient of resistance $ {\alpha _1} $ and $ {\alpha _2} $ , respectively. These are joined in series. The effective temperature coefficient of resistance is:
(A) $ \dfrac{{{\alpha _1} + {\alpha _2}}}{2} $
(B) $ \sqrt {{\alpha _1}{\alpha _2}} $
(C) $ \dfrac{{{\alpha _1}{R_1} + {\alpha _2}{R_2}}}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}} $
(D) $ \dfrac{{\sqrt {{R_1}{R_2}{\alpha _1}{\alpha _2}} }}{{\sqrt {R_1^2 + R_2^2} }} $
Answer
534.3k+ views
Hint: Here, we have the two wires with resistances and their coefficients of resistance at $ {0^0}C $ and effective temperature coefficient is asked. So, here we have to use the concept of resistances in series and increase the temperature of each resistance by $ t $ .
Complete answer:
Here, we have two resistances and we have to increase their temperature by $ t $ , $ {\alpha _1} $ and $ {\alpha _2} $ are the temperature coefficients of $ {R_1} $ and $ {R_2} $ , respectively. Let us show it by the diagram below:
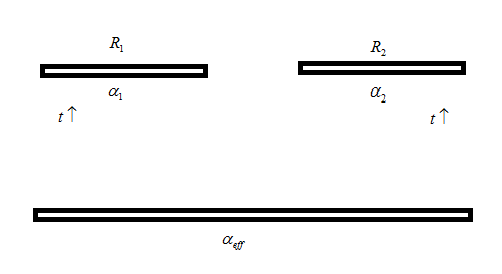
Those resistances are given by,
$ \begin{gathered}
R{t_1} = {R_1}(1 + {\alpha _1}t) \\
R{t_2} = {R_2}(1 + {\alpha _2}t) \\
\end{gathered} $ (since, temperature is increased by $ t $ )
If these resistances are joined in series then the resistances equivalent is given by
$ {R_{eq}} = R{t_1} + R{t_2} $
$ \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = {R_1}(1 + {\alpha _1}t) + {R_2}(1 + {\alpha _2}t) $ …..(putting all the values from above)
$ = {R_1} + {R_1}{\alpha _1}t + {R_2} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}t $
$ = ({R_1} + {R_2}) + t({R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}) $
$ = ({R_1} + {R_2})\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}}}{{({R_1} + {R_2})}}t} \right) $
Now, comparing this equation with $ {R_{eq}} = R(1 + {\alpha _{eff}}t) $
We observe here that
$ R = ({R_1} + {R_2}) $ and $ {\alpha _{eff}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}}}{{({R_1} + {R_2})}} $
Here, we obtained the effective temperature coefficient as $ {\alpha _{eff}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}}}{{({R_1} + {R_2})}} $
Thus the correct option is C.
Note:
Here, the wires with different resistances are joined in series and their temperature is increased. Effective temperature coefficient is the resistance-change factor per degree Celsius of temperature.
Both wires have temperature coefficient and hence we obtained the effective temperature coefficient by the above mentioned procedure in the answer.
Complete answer:
Here, we have two resistances and we have to increase their temperature by $ t $ , $ {\alpha _1} $ and $ {\alpha _2} $ are the temperature coefficients of $ {R_1} $ and $ {R_2} $ , respectively. Let us show it by the diagram below:

Those resistances are given by,
$ \begin{gathered}
R{t_1} = {R_1}(1 + {\alpha _1}t) \\
R{t_2} = {R_2}(1 + {\alpha _2}t) \\
\end{gathered} $ (since, temperature is increased by $ t $ )
If these resistances are joined in series then the resistances equivalent is given by
$ {R_{eq}} = R{t_1} + R{t_2} $
$ \Rightarrow {R_{eq}} = {R_1}(1 + {\alpha _1}t) + {R_2}(1 + {\alpha _2}t) $ …..(putting all the values from above)
$ = {R_1} + {R_1}{\alpha _1}t + {R_2} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}t $
$ = ({R_1} + {R_2}) + t({R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}) $
$ = ({R_1} + {R_2})\left( {1 + \dfrac{{{R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}}}{{({R_1} + {R_2})}}t} \right) $
Now, comparing this equation with $ {R_{eq}} = R(1 + {\alpha _{eff}}t) $
We observe here that
$ R = ({R_1} + {R_2}) $ and $ {\alpha _{eff}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}}}{{({R_1} + {R_2})}} $
Here, we obtained the effective temperature coefficient as $ {\alpha _{eff}} = \dfrac{{{R_1}{\alpha _1} + {R_2}{\alpha _2}}}{{({R_1} + {R_2})}} $
Thus the correct option is C.
Note:
Here, the wires with different resistances are joined in series and their temperature is increased. Effective temperature coefficient is the resistance-change factor per degree Celsius of temperature.
Both wires have temperature coefficient and hence we obtained the effective temperature coefficient by the above mentioned procedure in the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




