
Two thin lenses are placed 5cm apart along the same axis and illuminated with a beam of light parallel to that axis. The first lens in the path of the beam is a converging lens of focal length 10cm whereas the second is a diverging lens of focal length $5cm$. If the second lens is now moved toward the first the emergent light.
A) Remains parallel
B) Remains convergent
C) Remains divergent
D) Changes from parallel to divergent
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: When image distance tends to infinity there emerges a parallel beam and this condition can be found by using a formula that is used to find the image distance.
Formula used:
\[\left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{{({v_1} + D + 5)}}\]
The above-mentioned formula is known as the lens formula.
Where \[v\] is the image distance.
Complete step by step answer:
For the first case, let us consider the distance between two lenses as $5cm$ and the parallel beam of light converges at a distance of $10cm$ from the converging lens.
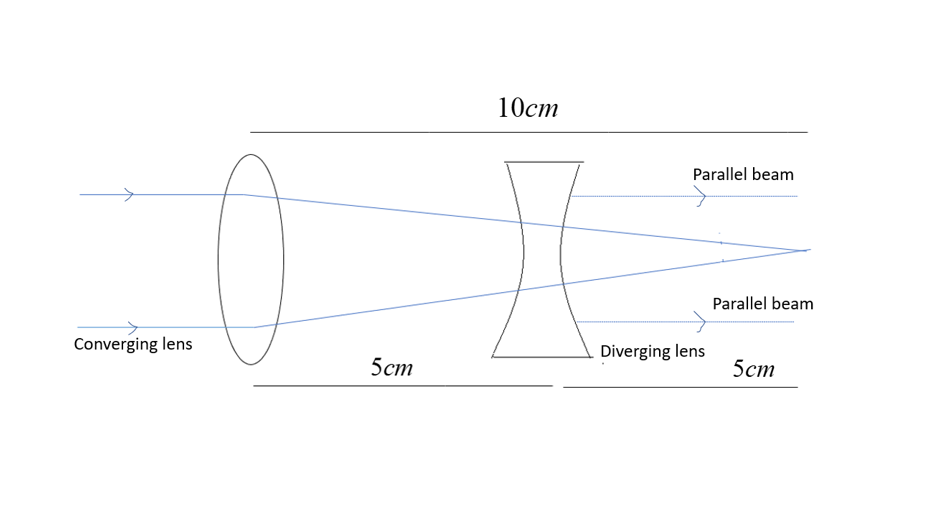
The image formed, as a result, acts as an object for the divergent lens.
Thus, for the diverging lens,
\[\left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{{10 - 5}}} \right)\]
\[{\text{ = }}0 - \left( { - \dfrac{1}{5}} \right)\]
Where,
\[{\text{ }}v = \infty .\]
Therefore, a parallel beam of light emerges.
In the second case, let us consider the distance is reduced by d cm,
Refraction through the first lens \[{v_1} = 10{\text{ }}cm\]
Then, let us consider the object for the second lens becomes: \[{v_1} + d - 5\]
Thus, for the diverging lens,
\[\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{{({v_1} + D + 5)}}\]
\[ = - \dfrac{1}{5}\]
We shall now substitute the value of \[{v_1} = 10cm\]in the previous equation, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right){\text{ }} = \dfrac{1}{{(D + 5)}} - \dfrac{1}{5}\]
\[ = > \dfrac{1}{v} < 0,\]
This means that the emergent beam of light is divergent.
$\therefore $ The correct answer is that the beam of light changes from parallel to divergent. Option (D) is the correct option.
Note:
Lenses are curved pieces of glass designed to refract light in a specific way. There are two types of lenses-concave and convex.
Irrespective of the type, each lens refracts light using the lens formula, which is, \[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}\] where, $f$=focal length of lens; $u$=object distance; $v$=image distance.
There are totally two types of images. They are known as Real and Virtual images.
The virtual images can be formed or protected at the screen like the real image.
The perfect images are not produced by the lens and some distortions occur. The distortions are known as aberrations.
By using a single lens we can calculate the linear magnification,
\[M = - \dfrac{{{S_2}}}{{{S_1}}}\]
\[ = \dfrac{f}{{(f - {s_1})}}\]
Formula used:
\[\left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{{({v_1} + D + 5)}}\]
The above-mentioned formula is known as the lens formula.
Where \[v\] is the image distance.
Complete step by step answer:
For the first case, let us consider the distance between two lenses as $5cm$ and the parallel beam of light converges at a distance of $10cm$ from the converging lens.

The image formed, as a result, acts as an object for the divergent lens.
Thus, for the diverging lens,
\[\left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{1}{{10 - 5}}} \right)\]
\[{\text{ = }}0 - \left( { - \dfrac{1}{5}} \right)\]
Where,
\[{\text{ }}v = \infty .\]
Therefore, a parallel beam of light emerges.
In the second case, let us consider the distance is reduced by d cm,
Refraction through the first lens \[{v_1} = 10{\text{ }}cm\]
Then, let us consider the object for the second lens becomes: \[{v_1} + d - 5\]
Thus, for the diverging lens,
\[\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right) - \dfrac{1}{{({v_1} + D + 5)}}\]
\[ = - \dfrac{1}{5}\]
We shall now substitute the value of \[{v_1} = 10cm\]in the previous equation, we get,
\[\Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{1}{v}} \right){\text{ }} = \dfrac{1}{{(D + 5)}} - \dfrac{1}{5}\]
\[ = > \dfrac{1}{v} < 0,\]
This means that the emergent beam of light is divergent.
$\therefore $ The correct answer is that the beam of light changes from parallel to divergent. Option (D) is the correct option.
Note:
Lenses are curved pieces of glass designed to refract light in a specific way. There are two types of lenses-concave and convex.
Irrespective of the type, each lens refracts light using the lens formula, which is, \[\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}\] where, $f$=focal length of lens; $u$=object distance; $v$=image distance.
There are totally two types of images. They are known as Real and Virtual images.
The virtual images can be formed or protected at the screen like the real image.
The perfect images are not produced by the lens and some distortions occur. The distortions are known as aberrations.
By using a single lens we can calculate the linear magnification,
\[M = - \dfrac{{{S_2}}}{{{S_1}}}\]
\[ = \dfrac{f}{{(f - {s_1})}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




