
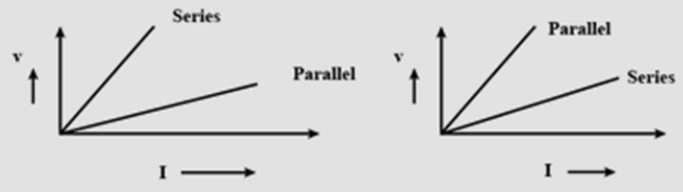
Two students perform the experiments on series and parallel combination of two given resistor \[{R_1}\] and ${R_2}$ plot the following V-I graphs. Which of the two diagrams correctly represents the label’s ‘series and parallel’ on the plotted curves? Justify your answer.

Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint:We have the ohm’s law which states that electric current in a circuit is proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance, provided physical conditions like temperature etc. are not variable.
*In series combination equivalent resistance is given as below.
${R_{equ}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$
*In parallel, equivalent resistance is given as below.
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{equ}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
Ohm’s law : V=IR
Where,
V=potential difference in volt
I=current in ampere
R=Resistance in ohm
Complete step-by-step answer:
To find out the solution we will start with ohm's law, which states that electric current in a circuit is proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Mathematically we can write the ohm’s law as follows,
$V = IR$---------- (1)
Where, V is applied voltage or potential difference in volt, I is current in the circuit in ampere and R is the resistance.
Now, from the equation we know that current and resistance are in product that means i.e. if resistance is larger than current it should be low and if resistance is low current must be large, provided voltage or potential difference remains constant or same.
Now let us discuss the series and parallel combination of two resistances. Let this resistance be${R_1}and{R_2}$.
We know series equivalent resistance is given as,
${R_{equ}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$
Parallel equivalent resistance is given as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{equ}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$.
From these two equations we can say that, equivalent resistance of series combination is more than the equivalent resistance of parallel combination.
i.e. ${({R_{eq}})_{series}} > {({R_{eq}})_{parallel}}$
So, as we discussed using ohm’s law that for the same circuit if resistance is more than current will be less and if resistance is less than current will be more. And this condition is satisfied by the first graph.
Hence, the first diagram correctly represents the label’s ‘series and parallel’ on the plotted curves.
Additional information:
In a series combination, the equivalent resistance of a circuit is calculated by adding the resistance of each l resistor.
In a parallel combination of resistors, the equivalent resistance for the circuit is found by adding the reciprocals of the resistance of each resistor.
Note:
Another way to find the correct graph is to check the slope.
The slope of the V-I graph is resistance. Hence, the slope of the series combination is more than the slope of parallel combination as series resistance is more than parallel.
*In series combination equivalent resistance is given as below.
${R_{equ}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$
*In parallel, equivalent resistance is given as below.
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{equ}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$
Ohm’s law : V=IR
Where,
V=potential difference in volt
I=current in ampere
R=Resistance in ohm
Complete step-by-step answer:
To find out the solution we will start with ohm's law, which states that electric current in a circuit is proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance.
Mathematically we can write the ohm’s law as follows,
$V = IR$---------- (1)
Where, V is applied voltage or potential difference in volt, I is current in the circuit in ampere and R is the resistance.
Now, from the equation we know that current and resistance are in product that means i.e. if resistance is larger than current it should be low and if resistance is low current must be large, provided voltage or potential difference remains constant or same.
Now let us discuss the series and parallel combination of two resistances. Let this resistance be${R_1}and{R_2}$.
We know series equivalent resistance is given as,
${R_{equ}} = {R_1} + {R_2}$
Parallel equivalent resistance is given as,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{equ}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}}$.
From these two equations we can say that, equivalent resistance of series combination is more than the equivalent resistance of parallel combination.
i.e. ${({R_{eq}})_{series}} > {({R_{eq}})_{parallel}}$
So, as we discussed using ohm’s law that for the same circuit if resistance is more than current will be less and if resistance is less than current will be more. And this condition is satisfied by the first graph.
Hence, the first diagram correctly represents the label’s ‘series and parallel’ on the plotted curves.
Additional information:
In a series combination, the equivalent resistance of a circuit is calculated by adding the resistance of each l resistor.
In a parallel combination of resistors, the equivalent resistance for the circuit is found by adding the reciprocals of the resistance of each resistor.
Note:
Another way to find the correct graph is to check the slope.
The slope of the V-I graph is resistance. Hence, the slope of the series combination is more than the slope of parallel combination as series resistance is more than parallel.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




