
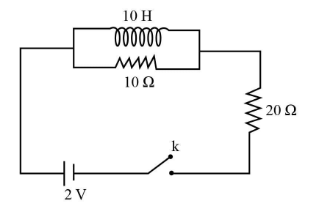
: Two resistors of $10\Omega $ and $20\Omega $ and an ideal inductor of $10H$ are connected to a $2V$ battery as shown. The key is inserted at time $t = 0$. the initial ($t = 0$) and final ($t \to \infty $) currents through battery are:
$
a)\,\,\,\dfrac{1}{{15}}A,\,\,\,\dfrac{1}{{10}}A\\
b)\,\,\,\dfrac{1}{{10}}A,\,\,\,\dfrac{1}{{15}}A\\
c)\,\,\,\dfrac{2}{{15}}A,\,\,\,\dfrac{1}{{10}}A\\
d)\,\,\,\dfrac{1}{{15}}A,\,\,\,\dfrac{2}{{25}}A
$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: In the above question we have to use the concept of current through an inductor, and current through a resistor. We have to consider the case of a combination of resistors and inductors in a circuit (L-R circuit). The cases of behaviour of inductors at different times in a circuit is considered.
Complete step by step answer:
In the above circuit we have the resistor $10\Omega $ and the $10H$ inductor in parallel combination and $20\Omega $ is in series with them. The potential difference by the battery is 2V.
We have to calculate the currents in the circuit at $t = 0$and at $t \to \infty $.
If we consider the case of $t = 0$, we know that the inductor acts like an open circuit and does not allow the flux to change, therefore the current passes through the resistor in parallel and we can ignore the inductor.
The both resistors become in series with each other therefore the formula of resistors in series is applied. In this case the equivalent resistance of the complete circuit is
$
{R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\\
\Rightarrow{R_{eq}} = 10 + 20\\
\Rightarrow{R_{eq}} = 30\Omega
$,
Now if we calculate the current through the battery it is given by Ohm’s Law:
$
V = IR\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}
$
If we put the values in the above formula, we get current as:
$
I = \dfrac{2}{{30}}\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{1}{{15}}A
$
Hence, the current through the battery at time $t = 0$ is $\dfrac{1}{{15}}A$.
Now we will consider the case of $t \to \infty $, the inductor acts like a short circuit and in this case, we have to assume that it lets all of the current to pass through it with no resistance. Once we have established this, we can conclude that there is only one resistance in the circuit and that is the $20 \Omega $resistor.
Now we have the equivalent resistance as ${{\mathop{\rm R}\nolimits} _{eq}} = 20\Omega $, we can again use Ohm's Law to calculate the current through the battery.
$
I = \dfrac{V}{R}\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{2}{{20}}\\
\therefore I = \dfrac{1}{{10}}A
$
Hence the current through the battery at time $t \to \infty $ is $\dfrac{1}{{10}}A$.
Now that we have calculated both of the currents, we know that the correct option Is (A).
Note: While solving this type of question we have to consider how an inductor behaves at different points of time and how will it affect the flow of current in a circuit. We have to consider the resistances and have to calculate the equivalent resistance to calculate the current through the battery in both cases.
Complete step by step answer:
In the above circuit we have the resistor $10\Omega $ and the $10H$ inductor in parallel combination and $20\Omega $ is in series with them. The potential difference by the battery is 2V.
We have to calculate the currents in the circuit at $t = 0$and at $t \to \infty $.
If we consider the case of $t = 0$, we know that the inductor acts like an open circuit and does not allow the flux to change, therefore the current passes through the resistor in parallel and we can ignore the inductor.
The both resistors become in series with each other therefore the formula of resistors in series is applied. In this case the equivalent resistance of the complete circuit is
$
{R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2}\\
\Rightarrow{R_{eq}} = 10 + 20\\
\Rightarrow{R_{eq}} = 30\Omega
$,
Now if we calculate the current through the battery it is given by Ohm’s Law:
$
V = IR\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{V}{R}
$
If we put the values in the above formula, we get current as:
$
I = \dfrac{2}{{30}}\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{1}{{15}}A
$
Hence, the current through the battery at time $t = 0$ is $\dfrac{1}{{15}}A$.
Now we will consider the case of $t \to \infty $, the inductor acts like a short circuit and in this case, we have to assume that it lets all of the current to pass through it with no resistance. Once we have established this, we can conclude that there is only one resistance in the circuit and that is the $20 \Omega $resistor.
Now we have the equivalent resistance as ${{\mathop{\rm R}\nolimits} _{eq}} = 20\Omega $, we can again use Ohm's Law to calculate the current through the battery.
$
I = \dfrac{V}{R}\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{2}{{20}}\\
\therefore I = \dfrac{1}{{10}}A
$
Hence the current through the battery at time $t \to \infty $ is $\dfrac{1}{{10}}A$.
Now that we have calculated both of the currents, we know that the correct option Is (A).
Note: While solving this type of question we have to consider how an inductor behaves at different points of time and how will it affect the flow of current in a circuit. We have to consider the resistances and have to calculate the equivalent resistance to calculate the current through the battery in both cases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




