
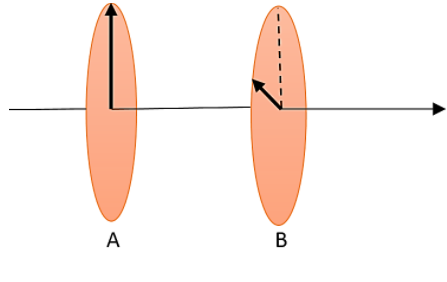
Two Polaroids A and B are placed with their Polaroid axes $30{}^\circ $ to each other as shown in the figure. A plane polarised light passes through the Polaroid A and after passing through it, intensity of light becomes ${{I}_{0}}$. What will be the intensity of finally transmitted light after passing through the Polaroid B?
\[\begin{align}
& A.0.75{{I}_{0}} \\
& B.0.866{{I}_{0}} \\
& A.0.025{{I}_{0}} \\
& A.0.5{{I}_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The intensity $I$ of the transmitted light is changing directly as the square of the cosine of the angle between the analyzer and transmission direction of the polariser. Substitute the angel mentioned in the relation of Malus law.
Formula used:
$I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
Where $I$ be the current intensity, ${{I}_{_{0}}}$ be the initial intensity of the light and $\theta $ be the angle between transmission axes and analyzer.
Complete answer:
As we already said, the malus law states that, the intensity $I$ of the transmitted light is changing directly as the square of the cosine of the angle between the analyzer and transmission direction of the polariser.
This can be written in the form of an equation,
$I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
As already mentioned in the question, the angle between the transmission axes and the Polaroid is given as
$\theta =30{}^\circ $
Let us substitute this in the equation of malus law,
\[I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}30\]
As we all know the value of cosine of \[30{}^\circ \] is written as,
\[\cos 30=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
Taking the square of this,
\[{{\cos }^{2}}30=0.75\]
Substituting this in the equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}30 \\
& I={{I}_{_{0}}}\times 0.75 \\
& I=0.75{{I}_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]
This has been given as the option A.
Therefore the correct answer is option A.
Note:
When light is incident on a polariser, the transmitted light will get polarised. This polarised beam of light falls on another Polaroid which will transmit light according to the orientation of its axis with the polariser. This is known as analyser. The intensity of light when the light passes through an analyser is given by the Malus law.
Formula used:
$I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
Where $I$ be the current intensity, ${{I}_{_{0}}}$ be the initial intensity of the light and $\theta $ be the angle between transmission axes and analyzer.
Complete answer:
As we already said, the malus law states that, the intensity $I$ of the transmitted light is changing directly as the square of the cosine of the angle between the analyzer and transmission direction of the polariser.
This can be written in the form of an equation,
$I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta $
As already mentioned in the question, the angle between the transmission axes and the Polaroid is given as
$\theta =30{}^\circ $
Let us substitute this in the equation of malus law,
\[I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}30\]
As we all know the value of cosine of \[30{}^\circ \] is written as,
\[\cos 30=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\]
Taking the square of this,
\[{{\cos }^{2}}30=0.75\]
Substituting this in the equation will give,
\[\begin{align}
& I={{I}_{_{0}}}{{\cos }^{2}}30 \\
& I={{I}_{_{0}}}\times 0.75 \\
& I=0.75{{I}_{0}} \\
\end{align}\]
This has been given as the option A.
Therefore the correct answer is option A.
Note:
When light is incident on a polariser, the transmitted light will get polarised. This polarised beam of light falls on another Polaroid which will transmit light according to the orientation of its axis with the polariser. This is known as analyser. The intensity of light when the light passes through an analyser is given by the Malus law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




