
Two point, monochromatic and coherent sources of light of wavelength \[\lambda \] each are placed as shown in the figure. The initial pressure difference between the sources is zero 0. (D>>d). mark the correct statement(s).
(This question has multiple correct options)
A. If \[d=\dfrac{7\lambda }{2}\], O will be a minima
B. If \[d=\lambda \], only one maxima can be observed on the screen
C. If \[d=4.8\lambda \], then total 10 minima would be there on the screen
D. If \[d=\dfrac{5\lambda }{2}\], the intensity at O would be minimum
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Young's double-slit experiment refers to the experiment involving interference between the waves of light. When a monochromatic light passing through the two narrow slits illuminates a distant screen we can see a characteristic pattern of bright and dark fringes is observed. This interference pattern is caused by the superposition of overlapping the light waves which originate from the two slits. We can find the minimal and maximal by considering the above relations.
\[d=\left( n+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \] for the point in consideration O to be minima.
\[d=n\lambda \] for the point in consideration O to be maxima.
Where d is the path difference, n is any integer and λ is the wavelength of the light used.
Complete step-by-step answer:
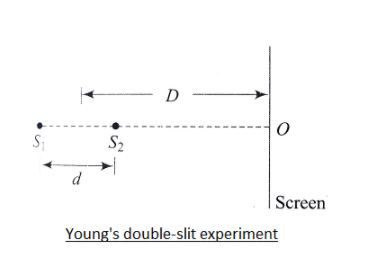
Consider the diagram given above which shows the Young's double-slit experiment conducted. The path difference between the light reaching point O from source \[{{S}_{1}}\] and \[{{S}_{2}}\], \[\Delta x=d\].
For the reaching point O to be minima, \[\Delta x=\left( n+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \]
So, \[d=\left( n+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \]
Thus for n=2,3 the values of will be as follows
\[d=\dfrac{5\lambda }{2}\],\[d=\dfrac{7\lambda }{2}\].
We get option A and D as correct statements.
Hence the point O will be minima for the above mentioned values of d.
For the reaching point O to be maxima, \[\Delta x=n\lambda \]
So, \[d=n\lambda \]
Now for d = λ implies n=1 means the point will be the only bright spot on the screen.
Hence, statement B is correct.
At any point say P, path difference will be, \[\Delta y=d\cos \theta \]
For P to be minima, \[d\cos \theta =\left( m+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \]
For d=4.8λ ⟹\[\cos \theta =\left( m+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\dfrac{1}{4.8}\]
But \[\left| \cos \theta \right|\le 1\]
As we can see the above equation is followed for the given values of m.
m=−5,−4,−3,−2,−1,0,1,2,3 and 4 satisfy the relation.
Hence there will be 10 minimas in the number which is option C.
So, the correct answer is “Option A,B,C and D”.
Note: The interference can be defined as a phenomenon in which the two given waves superpose to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or maybe the same amplitude. It is the process in which two or more light, sound, or electromagnetic waves of the same frequency combine to reinforce each other, the amplitude of the resulting wave being equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the combining waves.
\[d=\left( n+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \] for the point in consideration O to be minima.
\[d=n\lambda \] for the point in consideration O to be maxima.
Where d is the path difference, n is any integer and λ is the wavelength of the light used.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the diagram given above which shows the Young's double-slit experiment conducted. The path difference between the light reaching point O from source \[{{S}_{1}}\] and \[{{S}_{2}}\], \[\Delta x=d\].
For the reaching point O to be minima, \[\Delta x=\left( n+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \]
So, \[d=\left( n+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \]
Thus for n=2,3 the values of will be as follows
\[d=\dfrac{5\lambda }{2}\],\[d=\dfrac{7\lambda }{2}\].
We get option A and D as correct statements.
Hence the point O will be minima for the above mentioned values of d.
For the reaching point O to be maxima, \[\Delta x=n\lambda \]
So, \[d=n\lambda \]
Now for d = λ implies n=1 means the point will be the only bright spot on the screen.
Hence, statement B is correct.
At any point say P, path difference will be, \[\Delta y=d\cos \theta \]
For P to be minima, \[d\cos \theta =\left( m+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\lambda \]
For d=4.8λ ⟹\[\cos \theta =\left( m+\dfrac{1}{2} \right)\dfrac{1}{4.8}\]
But \[\left| \cos \theta \right|\le 1\]
As we can see the above equation is followed for the given values of m.
m=−5,−4,−3,−2,−1,0,1,2,3 and 4 satisfy the relation.
Hence there will be 10 minimas in the number which is option C.
So, the correct answer is “Option A,B,C and D”.
Note: The interference can be defined as a phenomenon in which the two given waves superpose to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or maybe the same amplitude. It is the process in which two or more light, sound, or electromagnetic waves of the same frequency combine to reinforce each other, the amplitude of the resulting wave being equal to the sum of the amplitudes of the combining waves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE

Calculate the equivalent resistance between a and b class 12 physics CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE

Which of the following is the best conductor of electricity class 12 physics CBSE




