
Two point charges $1\times 10^{-3}C$ and $4\times 10^{-3}C$ are located $0.0\;6m$ apart in air. Find the location of the point between them where the resultant electric field is zero.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Electric field is the electric force due to a unit positive charge which is at rest would exert on its surrounding. We can find the electric field due to the individual charges and then equate them to each other, to find the point where they are equal.
Formula used: $E=\dfrac{F}{q}$or$E=\dfrac{kq}{r^{2}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the electric force due to a pair of charges is given by Coulomb's law. An electric field can be produced by a time-varying electric field or an electrical charge. These can be either attracting or repelling in nature.
An electric field E is defined as the electric force F per unit positive charge q , which is infinitesimally small and at rest, and is given as $E=\dfrac{F}{q}$. Then$E=\dfrac{kq}{r^{2}}$, where $k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}$ which is a constant and $r$ is the distance between the unit charges.
Given that the charges are $q_{1}=1\times 10^{-3}C$ and $q_{2}=4\times 10^{-3}C$, also given that they are at a distance $r=0.0\;6m$ from each other. For the electric fields to cancel each other, another point charge $q$ must be placed at a distance $x$ from $q_{1}$
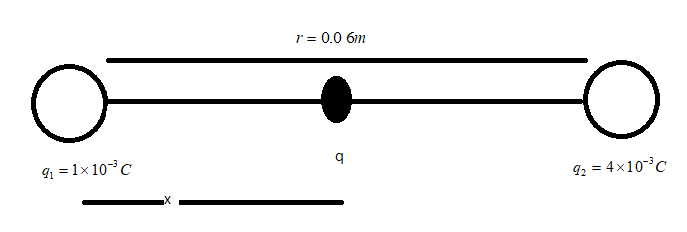
Then the electric field on $q$ is given as,
$\dfrac{kq_{1}}{x^{2}}=\dfrac{kq_{2}}{(r-x)^{2}}$
$\implies \dfrac{(r-x)^{2}}{x^{2}}=\dfrac{q_{2}}{q_{1}}$
$\implies \dfrac{r-x}{x}=\sqrt{\dfrac{q_{1}}{q_{2}}}$
Substituting the values we get,
$\implies\dfrac{0.06-x}{x}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1\times 10^{-3}}{4\times 10^{-3}}}$
$\implies\dfrac{0.06-x}{x}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}}$
$\implies\dfrac{0.06-x}{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\implies0.12-2x=x$
$\implies0.12=3x$
$\implies x=0.04m$
Hence the distance at a distance $0.04\;m$ from $q_{1}=10^{-3}C$ the electric field cancels each other.
Note: Electric field is in the direction of the force. Usually, the electric field of a point positive charge is radially outwards, whereas the electric field of a point negative charge is radially inwards to the charge. However, the electric field also depends on the symmetry of the charge carrying conductor.
Formula used: $E=\dfrac{F}{q}$or$E=\dfrac{kq}{r^{2}}$
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the electric force due to a pair of charges is given by Coulomb's law. An electric field can be produced by a time-varying electric field or an electrical charge. These can be either attracting or repelling in nature.
An electric field E is defined as the electric force F per unit positive charge q , which is infinitesimally small and at rest, and is given as $E=\dfrac{F}{q}$. Then$E=\dfrac{kq}{r^{2}}$, where $k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}}$ which is a constant and $r$ is the distance between the unit charges.
Given that the charges are $q_{1}=1\times 10^{-3}C$ and $q_{2}=4\times 10^{-3}C$, also given that they are at a distance $r=0.0\;6m$ from each other. For the electric fields to cancel each other, another point charge $q$ must be placed at a distance $x$ from $q_{1}$

Then the electric field on $q$ is given as,
$\dfrac{kq_{1}}{x^{2}}=\dfrac{kq_{2}}{(r-x)^{2}}$
$\implies \dfrac{(r-x)^{2}}{x^{2}}=\dfrac{q_{2}}{q_{1}}$
$\implies \dfrac{r-x}{x}=\sqrt{\dfrac{q_{1}}{q_{2}}}$
Substituting the values we get,
$\implies\dfrac{0.06-x}{x}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1\times 10^{-3}}{4\times 10^{-3}}}$
$\implies\dfrac{0.06-x}{x}=\sqrt{\dfrac{1}{4}}$
$\implies\dfrac{0.06-x}{x}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\implies0.12-2x=x$
$\implies0.12=3x$
$\implies x=0.04m$
Hence the distance at a distance $0.04\;m$ from $q_{1}=10^{-3}C$ the electric field cancels each other.
Note: Electric field is in the direction of the force. Usually, the electric field of a point positive charge is radially outwards, whereas the electric field of a point negative charge is radially inwards to the charge. However, the electric field also depends on the symmetry of the charge carrying conductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




