
Two plane mirrors are placed parallel to each other at a distance $L$ apart. A point object O placed between them, at a distance $\dfrac{L}{5}$ from one mirror. Both mirrors form multiple images. The distance between two images cannot be:
(A). $\dfrac{3L}{2}$
(B). $\dfrac{4L}{5}$
(C). $2L$
(D). $L$
Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint: Two mirrors are kept parallel to each other and an object is placed between them at some distance to both mirrors. Image formation in mirrors takes place by reflection and follows the laws of reflection. When two mirrors are kept at some angle to each other, multiple images are formed by each mirror.
Complete answer:
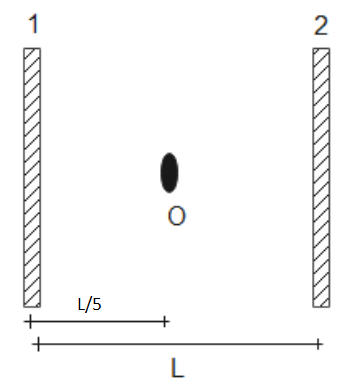
Given two mirrors are placed parallel to each other and an object is placed between them. The number of images formed when two mirrors are kept at an angle is given by-
$n=\dfrac{360}{\theta }$
Here, $n$ is the number of images formed
$\theta $ is the angle between the mirrors
Substituting for above condition,
$n=\dfrac{360}{0}=\infty $
Infinite number of images are formed.
Object is at distance $\dfrac{L}{5}$ from mirror 1, then its distance from mirror 2 will be- $L-\dfrac{L}{5}=\dfrac{4L}{5}$
We know that the distance of the image formed by a plane mirror is the same as the distance of the object from the mirror.
The first image in mirror 1 will be at distance $\dfrac{L}{3}$, the second image will be a reflection of the image in mirror 2, that is, at $L$ and we can say that the other images after these two images will be at distances which are multiples of $\dfrac{L}{5}$ and $L$.
For mirror 2, the fist image will be at distance $\dfrac{4L}{5}$ and the second image will be a reflection of image in mirror 1 so, it will be at distance $L+L=2L$ behind the mirror. So, we can say that all other images formed by mirror 2 will be at distances which are multiples of $\dfrac{4L}{5}$ and $2L$.
Therefore, the difference of image distances can be multiples of $L$ or $\dfrac{L}{5}$.
Therefore, distance between two images can be multiples of $L$ or $\dfrac{L}{5}$.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
As the angle between the mirrors increases, the number of images formed decreases. Light rays along the normal trace their original path after reflection. The multiple images formed are reflections of objects as well as reflections. Reflection can only take place on a smooth, shiny surface.
Complete answer:

Given two mirrors are placed parallel to each other and an object is placed between them. The number of images formed when two mirrors are kept at an angle is given by-
$n=\dfrac{360}{\theta }$
Here, $n$ is the number of images formed
$\theta $ is the angle between the mirrors
Substituting for above condition,
$n=\dfrac{360}{0}=\infty $
Infinite number of images are formed.
Object is at distance $\dfrac{L}{5}$ from mirror 1, then its distance from mirror 2 will be- $L-\dfrac{L}{5}=\dfrac{4L}{5}$
We know that the distance of the image formed by a plane mirror is the same as the distance of the object from the mirror.
The first image in mirror 1 will be at distance $\dfrac{L}{3}$, the second image will be a reflection of the image in mirror 2, that is, at $L$ and we can say that the other images after these two images will be at distances which are multiples of $\dfrac{L}{5}$ and $L$.
For mirror 2, the fist image will be at distance $\dfrac{4L}{5}$ and the second image will be a reflection of image in mirror 1 so, it will be at distance $L+L=2L$ behind the mirror. So, we can say that all other images formed by mirror 2 will be at distances which are multiples of $\dfrac{4L}{5}$ and $2L$.
Therefore, the difference of image distances can be multiples of $L$ or $\dfrac{L}{5}$.
Therefore, distance between two images can be multiples of $L$ or $\dfrac{L}{5}$.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note:
As the angle between the mirrors increases, the number of images formed decreases. Light rays along the normal trace their original path after reflection. The multiple images formed are reflections of objects as well as reflections. Reflection can only take place on a smooth, shiny surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




