
Two plane mirrors are inclined to one another at an angle of $60^\circ $. A ray is incident on mirror ${M_1}$ at an angle $i$. The reflected ray from mirror ${M_2}$ is parallel to mirror ${M_1}$ as shown in figure. The angle of incidence $i$ is:
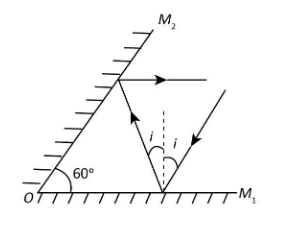

Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: First, we will draw the ray diagram according to the given conditions. We will then find the angle made by the reflected ray from the mirror ${M_2}$ with the plane of the mirror using the corresponding angle property. The normal is perpendicular to the mirror surface. We will apply this property along with the law of reflection equating the angles of incidence and reflection, and the properties of triangles and angles in the diagram to find the incident angle.
Complete answer:
The reflected ray from the mirror ${M_2}$ is given to be parallel to the mirror ${M_1}$. It is also given that the mirrors ${M_1}$ and ${M_2}$ are inclined at an angle $60^\circ $ with each other.
Therefore, the figure corresponding to the given case can be drawn as follows.
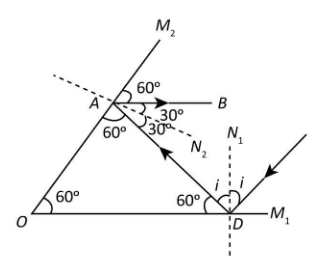
As we can see from the figure, $\angle{M_2}AB$ is the corresponding angle of $\angle{M_2}O{M_1}$. Therefore,
$\Rightarrow \angle{M_2}AB = \angle{M_2}O{M_1} = 60^\circ $
Now, the line$A{N_2}$ represents the normal to the mirror ${M_2}$. Since the normal makes an angle $90^\circ $ with the plane of the mirror ${M_2}$, we can write
\[\angle{M_2}A{N_2} = 90^\circ \]
It implies,
\[
\angle{M_2}AB + \angle BA{N_2} = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 60^\circ + \angle BA{N_2} = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow\angle BA{N_2} = 30^\circ
\]
$\angle BA{N_2}$ is the angle of reflection of the ray from the mirror ${M_2}$. Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence on a plane mirror, the angle of incidence of the ray on the mirror ${M_2}$ is, $\angle{N_2}AD = 30^\circ $. Therefore, we get
\[\angle{N_2}AO = 90^\circ \]
It implies,
\[
\angle{N_2}AD + \angle DAO = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 30^\circ + \angle DAO = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow\angle DAO = 60^\circ
\]
We know that in , the sum of all the angles is equal to $180^\circ $. Therefore,
$
\angle DAO + \angle AOD + \angle ODA = 180^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 60^\circ + 60^\circ + \angle ODA = 180^\circ \\
\Rightarrow\angle ODA = 60^\circ
$
We know that the angle of incidence of the ray on the mirror ${M_1}$ is $i$. Since the angle made by the normal ${N_2}D$ with the plane of the mirror is $90^\circ $, we can write
$
\angle ODA + \angle AD{N_2} = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 60^\circ + i = 90^\circ \\
\therefore i = 30^\circ $
Therefore, the angle of incidence $i$ is $30^\circ $.
Note: It is to be noted that the normal is a line drawn perpendicular to the surface of a mirror. The angles made by the reflected ray with the normal and the incident ray with the normal are always equal. Also, in questions of this type where it is given that the two mirrors are inclined at an angle $\theta $, and the incident ray on the first mirror reflects from the second mirror parallel to the first, the incident ray angle \[i\] is $2\theta - 90^\circ $. So, the incident angle can be found directly without doing many steps.
Complete answer:
The reflected ray from the mirror ${M_2}$ is given to be parallel to the mirror ${M_1}$. It is also given that the mirrors ${M_1}$ and ${M_2}$ are inclined at an angle $60^\circ $ with each other.
Therefore, the figure corresponding to the given case can be drawn as follows.

As we can see from the figure, $\angle{M_2}AB$ is the corresponding angle of $\angle{M_2}O{M_1}$. Therefore,
$\Rightarrow \angle{M_2}AB = \angle{M_2}O{M_1} = 60^\circ $
Now, the line$A{N_2}$ represents the normal to the mirror ${M_2}$. Since the normal makes an angle $90^\circ $ with the plane of the mirror ${M_2}$, we can write
\[\angle{M_2}A{N_2} = 90^\circ \]
It implies,
\[
\angle{M_2}AB + \angle BA{N_2} = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 60^\circ + \angle BA{N_2} = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow\angle BA{N_2} = 30^\circ
\]
$\angle BA{N_2}$ is the angle of reflection of the ray from the mirror ${M_2}$. Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence on a plane mirror, the angle of incidence of the ray on the mirror ${M_2}$ is, $\angle{N_2}AD = 30^\circ $. Therefore, we get
\[\angle{N_2}AO = 90^\circ \]
It implies,
\[
\angle{N_2}AD + \angle DAO = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 30^\circ + \angle DAO = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow\angle DAO = 60^\circ
\]
We know that in , the sum of all the angles is equal to $180^\circ $. Therefore,
$
\angle DAO + \angle AOD + \angle ODA = 180^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 60^\circ + 60^\circ + \angle ODA = 180^\circ \\
\Rightarrow\angle ODA = 60^\circ
$
We know that the angle of incidence of the ray on the mirror ${M_1}$ is $i$. Since the angle made by the normal ${N_2}D$ with the plane of the mirror is $90^\circ $, we can write
$
\angle ODA + \angle AD{N_2} = 90^\circ \\
\Rightarrow 60^\circ + i = 90^\circ \\
\therefore i = 30^\circ $
Therefore, the angle of incidence $i$ is $30^\circ $.
Note: It is to be noted that the normal is a line drawn perpendicular to the surface of a mirror. The angles made by the reflected ray with the normal and the incident ray with the normal are always equal. Also, in questions of this type where it is given that the two mirrors are inclined at an angle $\theta $, and the incident ray on the first mirror reflects from the second mirror parallel to the first, the incident ray angle \[i\] is $2\theta - 90^\circ $. So, the incident angle can be found directly without doing many steps.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




