
Two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle $\theta $ Light ray is incident parallel to one of the mirrors. For what value of $\theta $ ray will retrace its path after the third reflection?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question, we will first draw the diagram to show the path of light and then using geometry of lines and angles we will find the value of $\theta $ for which light will retrace its path after third reflection, also a light ray only retrace its path after reflection if it incident normally to the mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw a diagram in which PM and PN are two mirrors inclined at an angle $\theta $ and a light ray AB parallel to one of mirror say MN incident on mirror PM with angle of incidence $\theta $ at point B and then the second reflection of light ray takes place on mirror MN at point C and then after third reflection of light ray takes place on mirror PM at point D normally and due to normal incidence light ray will retrace it’s path back as shown in the diagram.
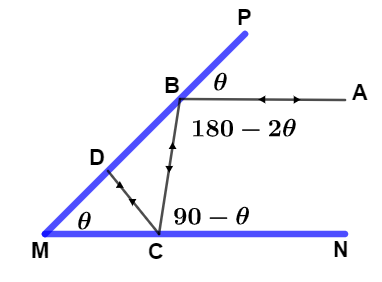
From the diagram’s geometry we see that,
$\angle CDM = {90^o}$ so in right angle triangle CDM we have,
$\angle DCM = 90 - \theta $ which is angle of reflection at point C and
$\angle BCN = \angle DCM = 90 - \theta \to (i)$ angle of incidence at point C equals to angle of reflection.
Also,
$\angle PBA = \theta $ angle of incidence at point B
$\angle CBD = \angle PBA = \theta $ angle of reflection equals to angle of incidence at point B.
Now for straight line PM,
$\angle PBA + \angle ABC + \angle CBD = {180^o}$ on putting the values we get,
$\angle ABC = 180 - 2\theta \to (ii)$
Now, we see that lines $AB||MN$ and BC is a intercept so, by the property of geometry of lines we know that, Sum of angles on same side by intercept line between two lines is ${180^o}$ which can be written as
$\angle ABC + \angle BCN = {180^o}$ on putting the value of these angles from equation (i) and (ii) we get,
$180 - 2\theta + 90 - \theta = 180$
$3\theta = 90$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {30^o}$
Hence, two mirrors must be inclined at an angle of ${30^o}$ so that light retraces its path after third reflection.
Note:It should be remembered that, it’s the law of reflection in ray optics that, angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection and when a ray of light incident normally on a mirror its angle of reflection and angle of incidence with respect to normal is zero that’s why a light ray retrace its path.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first draw a diagram in which PM and PN are two mirrors inclined at an angle $\theta $ and a light ray AB parallel to one of mirror say MN incident on mirror PM with angle of incidence $\theta $ at point B and then the second reflection of light ray takes place on mirror MN at point C and then after third reflection of light ray takes place on mirror PM at point D normally and due to normal incidence light ray will retrace it’s path back as shown in the diagram.

From the diagram’s geometry we see that,
$\angle CDM = {90^o}$ so in right angle triangle CDM we have,
$\angle DCM = 90 - \theta $ which is angle of reflection at point C and
$\angle BCN = \angle DCM = 90 - \theta \to (i)$ angle of incidence at point C equals to angle of reflection.
Also,
$\angle PBA = \theta $ angle of incidence at point B
$\angle CBD = \angle PBA = \theta $ angle of reflection equals to angle of incidence at point B.
Now for straight line PM,
$\angle PBA + \angle ABC + \angle CBD = {180^o}$ on putting the values we get,
$\angle ABC = 180 - 2\theta \to (ii)$
Now, we see that lines $AB||MN$ and BC is a intercept so, by the property of geometry of lines we know that, Sum of angles on same side by intercept line between two lines is ${180^o}$ which can be written as
$\angle ABC + \angle BCN = {180^o}$ on putting the value of these angles from equation (i) and (ii) we get,
$180 - 2\theta + 90 - \theta = 180$
$3\theta = 90$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {30^o}$
Hence, two mirrors must be inclined at an angle of ${30^o}$ so that light retraces its path after third reflection.
Note:It should be remembered that, it’s the law of reflection in ray optics that, angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection and when a ray of light incident normally on a mirror its angle of reflection and angle of incidence with respect to normal is zero that’s why a light ray retrace its path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




