
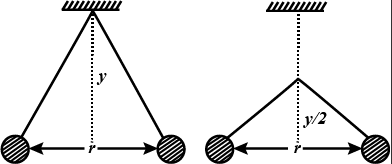
Two pin balls carrying equal charges are suspended from a common point by strings of equal length, the equilibrium separation between them is $r$ Fig. Now the strings are rigidly clamped at half the height. The equilibrium separation between the balls, now becomes.
$\eqalign{
& {\text{A}}{\text{. }}\left( {\dfrac{{2r}}{3}} \right) \cr
& {\text{B}}{\text{. }}{\left( {\dfrac{r}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} \cr
& {\text{C}}{\text{. }}\left( {\dfrac{r}{{{2^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}}} \right) \cr
& {\text{D}}{\text{. }}\left( {\dfrac{{2r}}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right) \cr} $

Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: At equilibrium the sum of the forces acting on each pin ball is zero. That means the x-component of the force is zero and also the y-component of the force is zero. Using this condition formulate a relation between the equilibrium separation and the perpendicular distances of the pin balls from the point of suspension. From that calculate the equilibrium separation when the height is halved.
Formula used:
The electrostatic force between two charges ${q_1}$ and ${q_2}$ separated by a distance $r$ is given by
${F_e} = k\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
At equilibrium means the x-component of the force is zero and also y-component of the force is zero i.e. ${F_x} = 0$ and ${F_y} = 0$.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the each of the pinballs have mass $m$ and the charge given to each pinball is $q$. Let the length of the string is $l$.
The pinballs are at a distance $y$ from the point of suspension and the equilibrium separation between them is $r$ as shown in figure below:
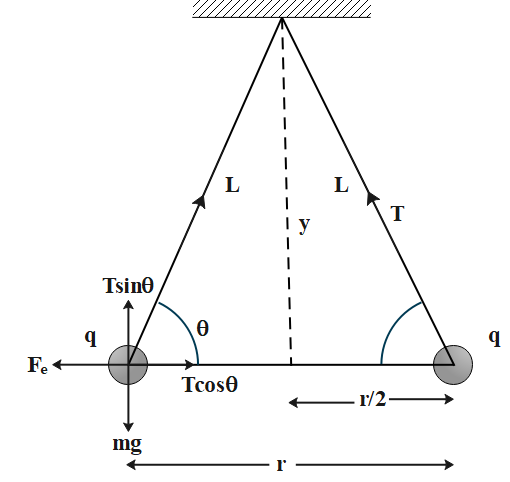
So at equilibrium the sum of all the forces is zero. i.e.
$\sum {{F_x}} = 0$and $\sum {{F_y}} = 0$.
According to the diagram.
$T\cos \theta = {F_e}$ and $T\sin \theta = mg$
Where
T= tension on the string
${F_e}$= electrostatic force
$\theta $= angle which the string makes with perpendicular
g= acceleration due to gravity
The electrostatic force of repulsion between the two pin balls is
${F_e} = k\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where $k = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$
So the above equation becomes.
$T\cos \theta = k\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Dividing this equation with $T\sin \theta = mg$, we get
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{T\cos \theta }}{{T\sin \theta }} = \dfrac{{k\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}{{mg}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta = \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{mg{r^2}}} \cr} $
But $\cot \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{r}{2}}}{y} = \dfrac{r}{{2y}}$
Putting the value of $\cot \theta $ in above equation we get
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{r}{{2y}} = \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{mg{r^2}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2k{q^2}}}{r^3} \cr
& \Rightarrow y \propto {r^3} \cr
& \therefore r \propto {y^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \cr} $
This is the relation between the equilibrium distance and the height.
So when the height is halved i.e. $y' = \dfrac{y}{2}$ , let the equilibrium distance be $r'$
Then
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{r'}}{r} = {\left( {\dfrac{{y'}}{y}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{y}{2}}}{y}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \cr
& \therefore r' = \dfrac{r}{{{2^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}} \cr} $
So the correct option is C.
Note:
For problems like this first draw the diagram. Then point out all the forces acting and resolve them into their x- component and y- components. For equilibrium the sum of all the forces is equal to zero so the sum of forces in x-direction will be zero and the sum of the forces in y-direction will be zero. Then see what is given and what is asked and try to find a relation among them. Then you can get your answer.
Formula used:
The electrostatic force between two charges ${q_1}$ and ${q_2}$ separated by a distance $r$ is given by
${F_e} = k\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
At equilibrium means the x-component of the force is zero and also y-component of the force is zero i.e. ${F_x} = 0$ and ${F_y} = 0$.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the each of the pinballs have mass $m$ and the charge given to each pinball is $q$. Let the length of the string is $l$.
The pinballs are at a distance $y$ from the point of suspension and the equilibrium separation between them is $r$ as shown in figure below:

So at equilibrium the sum of all the forces is zero. i.e.
$\sum {{F_x}} = 0$and $\sum {{F_y}} = 0$.
According to the diagram.
$T\cos \theta = {F_e}$ and $T\sin \theta = mg$
Where
T= tension on the string
${F_e}$= electrostatic force
$\theta $= angle which the string makes with perpendicular
g= acceleration due to gravity
The electrostatic force of repulsion between the two pin balls is
${F_e} = k\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where $k = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _ \circ }}}$
So the above equation becomes.
$T\cos \theta = k\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Dividing this equation with $T\sin \theta = mg$, we get
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{T\cos \theta }}{{T\sin \theta }} = \dfrac{{k\dfrac{{{q^2}}}{{{r^2}}}}}{{mg}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \cot \theta = \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{mg{r^2}}} \cr} $
But $\cot \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{r}{2}}}{y} = \dfrac{r}{{2y}}$
Putting the value of $\cot \theta $ in above equation we get
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{r}{{2y}} = \dfrac{{k{q^2}}}{{mg{r^2}}} \cr
& \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2k{q^2}}}{r^3} \cr
& \Rightarrow y \propto {r^3} \cr
& \therefore r \propto {y^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \cr} $
This is the relation between the equilibrium distance and the height.
So when the height is halved i.e. $y' = \dfrac{y}{2}$ , let the equilibrium distance be $r'$
Then
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{r'}}{r} = {\left( {\dfrac{{y'}}{y}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{y}{2}}}{y}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}} \cr
& \therefore r' = \dfrac{r}{{{2^{\dfrac{1}{3}}}}} \cr} $
So the correct option is C.
Note:
For problems like this first draw the diagram. Then point out all the forces acting and resolve them into their x- component and y- components. For equilibrium the sum of all the forces is equal to zero so the sum of forces in x-direction will be zero and the sum of the forces in y-direction will be zero. Then see what is given and what is asked and try to find a relation among them. Then you can get your answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




