
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face $AB$ of an isosceles right angled prism $ABC$. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays $'1'$ and $'2'$ are respectively $1.35$ and $1.45$ . Trace the path of these rays after entering through the prism.

Answer
573k+ views
Hint: Monochromatic rays are those rays which have a single wavelength or of single tone colour and have the same frequency. Examples of monochromatic rays are light and sodium lamps etc. When light passes through one medium to another medium, it refracts from its original path. The refractive index of each medium is calculated with reference to air.
Complete step by step solution:
From the above data it is given that:
The refractive index ${r_1}$ is ${\mu _1} = 1.35$ and the refractive index of ${r_2}$ is ${\mu _2} = 1.45$ .
Let’s calculate the critical angle of each ray.
Critical angle is the angle of incidence when the refraction angle is 90 degree. Here when it is refracted back from the prism, the light will travel from optically denser medium glass to optically less dense medium air.
The critical angle of ray 1 is calculated as:
$\sin ({c_1}) = \dfrac{1}{{{\mu _1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin ({c_1}) = \dfrac{1}{{1.35}}$
$ \Rightarrow {c_1} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(0.7407)$
$ \Rightarrow {c_1} = {47.8^ \circ }$
The critical angle of ray 2 is calculated as:
$\sin ({c_2}) = \dfrac{1}{{{\mu _2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin ({c_2}) = \dfrac{1}{{1.45}}$
$ \Rightarrow {c_2} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(0.6896)$
$ \Rightarrow {c_2} = {43.6^ \circ }$
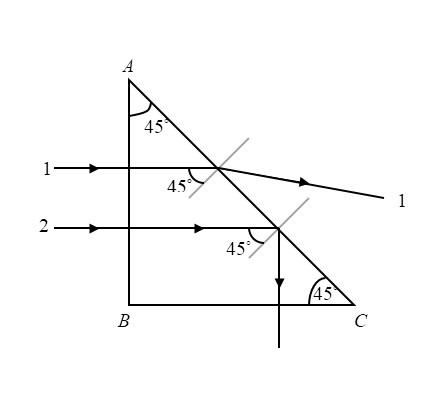
Like shown in the above diagram the angle of incidence for both the two monochromatic rays will be ${45^ \circ }$. This is because the two monochromatic rays are entering perpendicular to a right angled triangle so the angle of incidence calculated is ${45^ \circ }$ .
The ray $1$ has a critical angle greater than the incidence angle and so it will emerge from the prism whereas the critical angle of ray $2$ is less than the incidence angle and hence it will be reflected internally.
Note: The possible condition for critical angle is when a light transverse from optically denser medium to optically less medium. The conditions for total internal reflection are: When angle of incidence is greater than critical angle and light travels from optically denser medium to optically less dense medium.
Complete step by step solution:
From the above data it is given that:
The refractive index ${r_1}$ is ${\mu _1} = 1.35$ and the refractive index of ${r_2}$ is ${\mu _2} = 1.45$ .
Let’s calculate the critical angle of each ray.
Critical angle is the angle of incidence when the refraction angle is 90 degree. Here when it is refracted back from the prism, the light will travel from optically denser medium glass to optically less dense medium air.
The critical angle of ray 1 is calculated as:
$\sin ({c_1}) = \dfrac{1}{{{\mu _1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin ({c_1}) = \dfrac{1}{{1.35}}$
$ \Rightarrow {c_1} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(0.7407)$
$ \Rightarrow {c_1} = {47.8^ \circ }$
The critical angle of ray 2 is calculated as:
$\sin ({c_2}) = \dfrac{1}{{{\mu _2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin ({c_2}) = \dfrac{1}{{1.45}}$
$ \Rightarrow {c_2} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}(0.6896)$
$ \Rightarrow {c_2} = {43.6^ \circ }$

Like shown in the above diagram the angle of incidence for both the two monochromatic rays will be ${45^ \circ }$. This is because the two monochromatic rays are entering perpendicular to a right angled triangle so the angle of incidence calculated is ${45^ \circ }$ .
The ray $1$ has a critical angle greater than the incidence angle and so it will emerge from the prism whereas the critical angle of ray $2$ is less than the incidence angle and hence it will be reflected internally.
Note: The possible condition for critical angle is when a light transverse from optically denser medium to optically less medium. The conditions for total internal reflection are: When angle of incidence is greater than critical angle and light travels from optically denser medium to optically less dense medium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




