
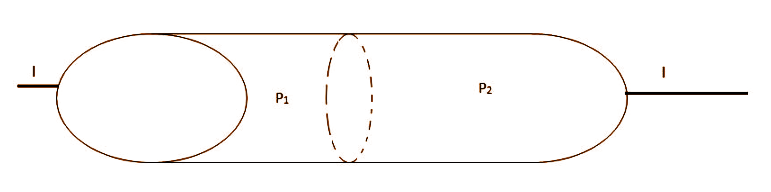
Two long straight cylindrical conductors with resistivity ${\rho _1}$ and ${\rho _2}$ respectively are joined together as shown in the figure. If current $I$ flows through the conductors, the magnitude of the total free charge at the interface of the two conductors is:
A. Zero
B. $\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right)I{\varepsilon _0}}}{2}$
C. ${\varepsilon _0}I\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$
D. ${\varepsilon _0}I\left| {{\rho _1} + {\rho _2}} \right|$

Answer
560.1k+ views
Hint: This question can be solved by concepts of Gauss Law. We need to find the electric fields for the two conductors separately and use Gauss Law to find the answer.
Formula used: The formulae used in the solution are given here.
$\oint {E.ds = \dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}q} $ where $q$ is the charge, $E$ is the electric field and $s$ represents the surface area.
Complete step by step answer:
The electric field of an infinite line charge with a uniform linear charge density can be obtained by using Gauss' law. Considering a Gaussian surface in the form of a cylinder at radius $r$, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the cylinder and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just the electric field times the area of the cylinder.
Gauss Law states that the total electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity. The electric flux in an area is defined as the electric field multiplied by the area of the surface projected in a plane and perpendicular to the field.
Thus, the total flux linked with a closed surface is $\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ times the charge enclosed by the closed surface. $\oint {E.ds = \dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}q} $ where $q$ is the charge, $E$ is the electric field and $s$ represents the surface area.
In the case of conductor 1, we have,
${E_1} = \dfrac{{{\rho _1}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}}$ where ${\rho _1}$ is the resistivity of the conductor material, $R$ is the radius of the circular face of the cylinder and $I$ is the current passing through it.
In case of conductor 2, we have,
${E_2} = \dfrac{{{\rho _2}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}}$ where ${\rho _2}$ is the resistivity of the conductor material.
Thus, we have
$ - {E_1} \cdot ds + {E_2} \cdot ds = - \dfrac{{{\rho _1}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}} \cdot ds + \dfrac{{{\rho _2}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}} \cdot ds$
$ = \dfrac{1}{{\pi {R^2}}}\left( {{\rho _2} - {\rho _1}} \right) \cdot ds$
Thus, by applying Gauss’s law, charge at the boundary is given by, $I{\varepsilon _0}\left( {{\rho _2} - {\rho _1}} \right)$.
The magnitude of the total free charge at the interface of the two conductors is ${\varepsilon _0}I\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Alternatively, by Ohm’s Law, the voltage across a conductor is proportional to the product of current and resistance of the conductor.
$V = IR$
The resistance of a conductor is given by, $R = \rho \dfrac{l}{{\pi {R^2}}}$ where $\pi {R^2}$ is the area of cross-section and $l$ is the length of the cylinder.
Appling Gauss's theorem to a small cylindrical pill-box at the boundary:
$\dfrac{{{q_{in}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = I\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$
$ \Rightarrow {q_{in}} = I{\varepsilon _0}\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$
Formula used: The formulae used in the solution are given here.
$\oint {E.ds = \dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}q} $ where $q$ is the charge, $E$ is the electric field and $s$ represents the surface area.
Complete step by step answer:
The electric field of an infinite line charge with a uniform linear charge density can be obtained by using Gauss' law. Considering a Gaussian surface in the form of a cylinder at radius $r$, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the cylinder and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just the electric field times the area of the cylinder.
Gauss Law states that the total electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity. The electric flux in an area is defined as the electric field multiplied by the area of the surface projected in a plane and perpendicular to the field.
Thus, the total flux linked with a closed surface is $\dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ times the charge enclosed by the closed surface. $\oint {E.ds = \dfrac{1}{{{\varepsilon _0}}}q} $ where $q$ is the charge, $E$ is the electric field and $s$ represents the surface area.
In the case of conductor 1, we have,
${E_1} = \dfrac{{{\rho _1}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}}$ where ${\rho _1}$ is the resistivity of the conductor material, $R$ is the radius of the circular face of the cylinder and $I$ is the current passing through it.
In case of conductor 2, we have,
${E_2} = \dfrac{{{\rho _2}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}}$ where ${\rho _2}$ is the resistivity of the conductor material.
Thus, we have
$ - {E_1} \cdot ds + {E_2} \cdot ds = - \dfrac{{{\rho _1}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}} \cdot ds + \dfrac{{{\rho _2}I}}{{\pi {R^2}}} \cdot ds$
$ = \dfrac{1}{{\pi {R^2}}}\left( {{\rho _2} - {\rho _1}} \right) \cdot ds$
Thus, by applying Gauss’s law, charge at the boundary is given by, $I{\varepsilon _0}\left( {{\rho _2} - {\rho _1}} \right)$.
The magnitude of the total free charge at the interface of the two conductors is ${\varepsilon _0}I\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Alternatively, by Ohm’s Law, the voltage across a conductor is proportional to the product of current and resistance of the conductor.
$V = IR$
The resistance of a conductor is given by, $R = \rho \dfrac{l}{{\pi {R^2}}}$ where $\pi {R^2}$ is the area of cross-section and $l$ is the length of the cylinder.
Appling Gauss's theorem to a small cylindrical pill-box at the boundary:
$\dfrac{{{q_{in}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = I\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$
$ \Rightarrow {q_{in}} = I{\varepsilon _0}\left| {{\rho _1} - {\rho _2}} \right|$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




