
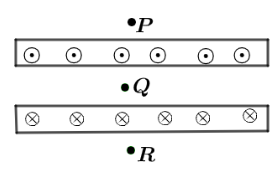
Two large metal sheets carry surface currents as shown in the figure. The current through a strip of width $dl$ is $Kdl$ where $K$ is a constant. Find the value of the magnetic field at points $P,Q$ and $R$.

Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint:In order to find magnetic field at points $P,Q$ and $R$ , we will use the ampere circuital law which is expressed as $\int {\vec B.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}I$ where $I$ is the current flowing in wire and $dl$ is the small section of area covered under magnetic field.
Complete step by step answer:
From the figure we can see that, current flowing in the upper strip is in upward direction whereas current flowing in the lower strip is in downward direction, so the magnetic field produced by each metal surface is in the opposite direction. Since, from symmetry we can say that the magnetic field at point $P$ and $R$ is the same.So, Magnetic field at point $P$ and $R$ from ampere circuital law is given as:
Current through each metal surface is $KL$ and $ - KL$,
Net current, ${I_{net}} = KL - KL$
${I_{net}} = 0$
Using ampere circuital law, $\int {\vec B.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}I$
$\int {{{\vec B}_P}.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}{I_{net}}$
Since, ${I_{net}} = 0$
${B_P} = {B_R} = 0$
Hence, magnetic fields at point $P$ and $R$ are equals to zero.
Now, since point $Q$ lies in the middle of two surfaces we will apply ampere circuital law between $Q$ and $R$ .
$\int\limits_0^L {{{\vec B}_Q}.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}{I_{net}}$
Since, current flowing in lower strip is in downward direction and has a magnitude of $KL$.So magnetic field at point $Q$ is given by,
$\int\limits_0^L {{{\vec B}_Q}.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}KL$
${B_Q}L = {\mu _0}KL$
$\therefore {B_Q} = {\mu _0}K$ In the right direction.
Hence, the magnetic field at point $Q$ is ${B_Q} = {\mu _0}K$ .
Note:Ampere circuital law is applied when a current is flowing in wire and we need to determine magnetic field around it somewhere in space. ${\mu _0}$ Is called the permeability of free space and its SI unit is $N{A^{ - 2}}$ and its numerical value is given as $4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}N{A^{ - 2}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
From the figure we can see that, current flowing in the upper strip is in upward direction whereas current flowing in the lower strip is in downward direction, so the magnetic field produced by each metal surface is in the opposite direction. Since, from symmetry we can say that the magnetic field at point $P$ and $R$ is the same.So, Magnetic field at point $P$ and $R$ from ampere circuital law is given as:
Current through each metal surface is $KL$ and $ - KL$,
Net current, ${I_{net}} = KL - KL$
${I_{net}} = 0$
Using ampere circuital law, $\int {\vec B.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}I$
$\int {{{\vec B}_P}.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}{I_{net}}$
Since, ${I_{net}} = 0$
${B_P} = {B_R} = 0$
Hence, magnetic fields at point $P$ and $R$ are equals to zero.
Now, since point $Q$ lies in the middle of two surfaces we will apply ampere circuital law between $Q$ and $R$ .
$\int\limits_0^L {{{\vec B}_Q}.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}{I_{net}}$
Since, current flowing in lower strip is in downward direction and has a magnitude of $KL$.So magnetic field at point $Q$ is given by,
$\int\limits_0^L {{{\vec B}_Q}.d\vec l} = {\mu _0}KL$
${B_Q}L = {\mu _0}KL$
$\therefore {B_Q} = {\mu _0}K$ In the right direction.
Hence, the magnetic field at point $Q$ is ${B_Q} = {\mu _0}K$ .
Note:Ampere circuital law is applied when a current is flowing in wire and we need to determine magnetic field around it somewhere in space. ${\mu _0}$ Is called the permeability of free space and its SI unit is $N{A^{ - 2}}$ and its numerical value is given as $4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}N{A^{ - 2}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




