
Two large horizontal and parallel metal plates having a separation of $1cm$ are connected to a DC voltage source of potential difference X. A proton is released at rest midway between the two plates. It remains at rest in the air, then X is:
A. $1\times {{10}^{-5}}V$
B. $1\times {{10}^{-7}}V$
C. $1\times {{10}^{-9}}V$
D. $1\times {{10}^{-10}}V$
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Calculate the electric force on the proton due the electric field produced due to the potential difference across the parallel plates. Use the fact that the electric field due a large charged plate is constant at every point near it. Then equate the electric force to the gravitational force on the proton.
Formula used:
$\Delta V=Ed$
$\Rightarrow{{F}_{E}}=qE$
$\Rightarrow{{F}_{E}}=qE$
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that two large horizontal and parallel metal plates are kept in air. They are separated by a distance of $1cm$. Then these two plates are connected to a DC voltage source of potential difference X. Therefore, a constant potential difference is created across the plates.
Wherever is a potential difference, it means that the region contains an electric field. In this case, it is given that the two plates are large and the electric field due a large charged plate is constant at every point near it.
For a constant electric field, the potential difference between two parallel plates is given as $\Delta V=Ed$, where E is the magnitude of the electric field and d is the distance of separation of the two plates.
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{\Delta V}{d}$
In this case, $\Delta V=X$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{X}{d}$ …. (i)
It is given that when a proton is placed in the midway between the two plates, the proton remains at rest. Let us analyse why this is happening.Proton is charged a particle and when a particle is placed in an electric field, it experiences an electric force whose magnitude is equal to ${{F}_{E}}=qE$,
where q is the charge on the particle.
Substitute the value of E from (i).
${{F}_{E}}=q\dfrac{X}{d}$.
Since proton has some mass, it will also experience a gravitational force exerted by earth in the downward direction whose magnitude is equal to ${{F}_{g}}=mg$,
where m is the mass of the particle and g is acceleration due to gravity.
However, it should have fallen down due to this force. This means that another force is applied on the particle in the upward direction such that the net force on the particle is zero. In this way, the proton stays at rest.
This means that the upwards force is the electric force.
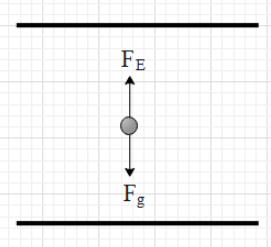
Therefore, the net force on the proton is ${{F}_{net}}={{F}_{g}}-{{F}_{E}}$.
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=mg-q\dfrac{X}{d}$.
But ${{F}_{net}}=0$.
$\Rightarrow mg-q\dfrac{X}{d}=0$
$\Rightarrow X=\dfrac{mgd}{q}$.
Here, $d=1cm=0.01m$, $m=1.67\times {{10}^{-27}}kg$, $q=1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}C$ and $g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$.
$\therefore X=\dfrac{\left( 1.67\times {{10}^{-27}} \right)(9.8)(0.01)}{\left( 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}} \right)}=1\times {{10}^{-9}}V$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:You much have learnt that for an electric field to exist there must be some charge present. Therefore, when the potential difference is applied across the parallel plates, the plates get charged and an electric field is created. The plate with higher potential gets positively charged and the plate with lower potential gets negatively charged. An electric field is always directed from a higher potential to a lower potential. Since the electric field is directed upwards, the lower plate is positively charged and the upper plate is negatively charged.
Formula used:
$\Delta V=Ed$
$\Rightarrow{{F}_{E}}=qE$
$\Rightarrow{{F}_{E}}=qE$
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that two large horizontal and parallel metal plates are kept in air. They are separated by a distance of $1cm$. Then these two plates are connected to a DC voltage source of potential difference X. Therefore, a constant potential difference is created across the plates.
Wherever is a potential difference, it means that the region contains an electric field. In this case, it is given that the two plates are large and the electric field due a large charged plate is constant at every point near it.
For a constant electric field, the potential difference between two parallel plates is given as $\Delta V=Ed$, where E is the magnitude of the electric field and d is the distance of separation of the two plates.
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{\Delta V}{d}$
In this case, $\Delta V=X$
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{X}{d}$ …. (i)
It is given that when a proton is placed in the midway between the two plates, the proton remains at rest. Let us analyse why this is happening.Proton is charged a particle and when a particle is placed in an electric field, it experiences an electric force whose magnitude is equal to ${{F}_{E}}=qE$,
where q is the charge on the particle.
Substitute the value of E from (i).
${{F}_{E}}=q\dfrac{X}{d}$.
Since proton has some mass, it will also experience a gravitational force exerted by earth in the downward direction whose magnitude is equal to ${{F}_{g}}=mg$,
where m is the mass of the particle and g is acceleration due to gravity.
However, it should have fallen down due to this force. This means that another force is applied on the particle in the upward direction such that the net force on the particle is zero. In this way, the proton stays at rest.
This means that the upwards force is the electric force.

Therefore, the net force on the proton is ${{F}_{net}}={{F}_{g}}-{{F}_{E}}$.
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=mg-q\dfrac{X}{d}$.
But ${{F}_{net}}=0$.
$\Rightarrow mg-q\dfrac{X}{d}=0$
$\Rightarrow X=\dfrac{mgd}{q}$.
Here, $d=1cm=0.01m$, $m=1.67\times {{10}^{-27}}kg$, $q=1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}C$ and $g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$.
$\therefore X=\dfrac{\left( 1.67\times {{10}^{-27}} \right)(9.8)(0.01)}{\left( 1.6\times {{10}^{-19}} \right)}=1\times {{10}^{-9}}V$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note:You much have learnt that for an electric field to exist there must be some charge present. Therefore, when the potential difference is applied across the parallel plates, the plates get charged and an electric field is created. The plate with higher potential gets positively charged and the plate with lower potential gets negatively charged. An electric field is always directed from a higher potential to a lower potential. Since the electric field is directed upwards, the lower plate is positively charged and the upper plate is negatively charged.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




