
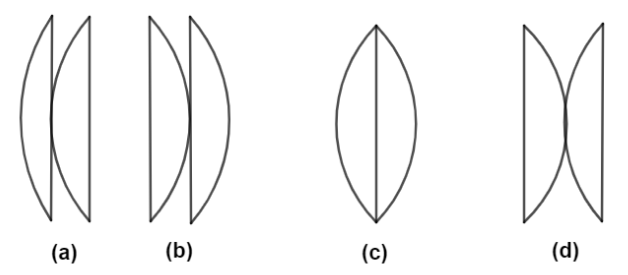
Two identical plano convex lenses are placed as shown below. If ${f_a},{f_b},{f_c}$ and ${f_d}$ re
 presents effective focal length of the combinations then,
presents effective focal length of the combinations then,
A. ${f_a} > {f_b} > {f_c} > {f_d}$
B. ${f_a} = {f_b} > {f_c} > {f_d}$
C. ${f_a} < {f_b} < {f_c} < {f_d}$
D. ${f_a} = {f_b} = {f_c} = {f_d}$

Answer
504k+ views
Hint: In the above diagram there are plano convex lenses which are identical . By using those lenses we have to prove the identical convex lens from pictures a, b, c, d which are identical. For this we are assuming the convex lenses are all equal. Let's discuss it step by step.
Complete step by step answer:
Above figure represents the focal lengths of the plano convex lens. From this diagram we are going to discuss whether the focal lengths are equal or unequal or greater to each other or less than to each other or few are greater and few are equal. Let's discuss deeply,
Case (i) $\dfrac{1}{{{f_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}$
Where as all the focal lengths are equal that means, $f = {f_1} = {f_2} = {f_3} = {f_4}$
So the diagram (a) is,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{f} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f_a}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} \\ $
Similarly we are going to find for the remaining three focal lengths,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_b}}} = \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{f} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f_b}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} \\ $
Whereas,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_c}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} \\
\therefore \dfrac{1}{{{f_d}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} $
From the above calculations we have proved that all the focal lengths are equal ${f_a} = {f_b} = {f_c} = {f_d}$.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: It should be remembered that, a plano convex lens has a flat surface on one side and at other converging portion of biconvex lens and it behave as a converging lens when light passes through it and if net focal length of any combination of lenses is negative it will behave as a concave lens otherwise if its positive it will behave as a convex lens.
Complete step by step answer:
Above figure represents the focal lengths of the plano convex lens. From this diagram we are going to discuss whether the focal lengths are equal or unequal or greater to each other or less than to each other or few are greater and few are equal. Let's discuss deeply,
Case (i) $\dfrac{1}{{{f_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{f_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{f_2}}}$
Where as all the focal lengths are equal that means, $f = {f_1} = {f_2} = {f_3} = {f_4}$
So the diagram (a) is,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_a}}} = \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{f} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f_a}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} \\ $
Similarly we are going to find for the remaining three focal lengths,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_b}}} = \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{f} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f_b}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} \\ $
Whereas,
$\dfrac{1}{{{f_c}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} \\
\therefore \dfrac{1}{{{f_d}}} = \dfrac{2}{f} $
From the above calculations we have proved that all the focal lengths are equal ${f_a} = {f_b} = {f_c} = {f_d}$.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: It should be remembered that, a plano convex lens has a flat surface on one side and at other converging portion of biconvex lens and it behave as a converging lens when light passes through it and if net focal length of any combination of lenses is negative it will behave as a concave lens otherwise if its positive it will behave as a convex lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




