
Two identical particles each of mass M and charge Q are placed a certain distance part. If they are in equilibrium under mutual gravitational and electric force then calculate the order of $\dfrac{Q}{M}$ in SI units.
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: Concept of mutual gravitational force and electric force. As here the electric force and gravitational forces are in equilibrium which means both forces are equal. Gravitation or just gravity is the force of attraction between any two bodies. All the objects in the universe attract each other with a certain amount of force, but in most of the cases, the force is too weak to be observed due to the very large distance of separation. Besides, gravity’s range is infinite but the effect becomes weaker as objects move away.
Formula used:
1. Gravitational force
${F_g} = \,\;G\,\;\dfrac{{\,{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
2. Electrostatic force
${F_e} = \;\;K\;\;\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Gravitational Force – According to universal law of gravitation each and every object in this universe attracts another object with a force given by
${F_g} = G\;\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
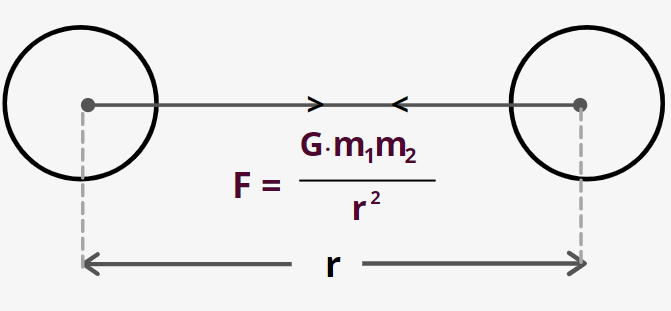
Where ${m_1}\;and\,\;{m_2}$ are two particles separated by a distance of r.
- It follows inverse square law
- Gravitational force is always attractive in nature
- G is the universal gravitational constant and $G = 6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}$
- Coulomb’s law: According to Coulomb’s s law, two charge particles of charges ${q_1}\;and\;{q_2}$ and separated by a distance r exerts an electrostatic force on each other given by
${F_e}\; = \;K\;\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
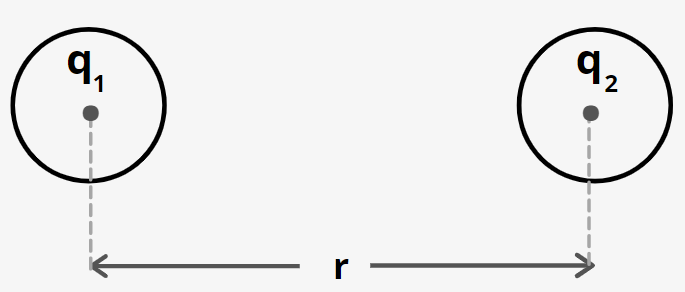
where k is a constant.
- The value of k is
$K = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}\;N{m^2}/{C^2}$
- It can be attractive or repulsive
- For similar charges, it is repulsive
- For opposite charges, it is attractive in nature.
Now, as in question the given system of charges are in equilibrium.
Hence, ${F_e} = {F_g}$ …(1)
Now, \[{F_e} = K\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}\]
and \[{F_g} = G\dfrac{{{m_1}\,{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}\]
Here ${q_1} = {q_2} = Q\;,\;\,\;{m_1} = {m_2} = M$
So, From (1)
${F_e} = {F_g}$
\[K\dfrac{{(Q)\,(Q)}}{{{r^2}}} = G\dfrac{{(M)\,(M)}}{{{r^2}}}\]
\[
\Rightarrow \;\;K\,{Q^2}\, = \;\;G{M^2} \\
\Rightarrow \;\;\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{{M^2}}}\; = \;\dfrac{G}{K} \\
\Rightarrow \;\;\dfrac{Q}{M}\; = \;\sqrt {\dfrac{G}{K}} \\
\]
$
G\; = \;6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}\;N{m^2}/K{g^2} \\
K\; = \;9 \times {10^9}\;N{m^2}/{C^2} \\ $
So,
\[\dfrac{Q}{M} = {\left( {\dfrac{{6.67 \times {{10}^{ - 11}}\;\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}}}{{9 \times {{10}^9}\;\;\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}}}} \right)^{1/2}}\]
$\implies \dfrac{Q}{M} = {[0.7411\; \times \;{10^{ - 20}}\;\;{C^2}/K{g^2}]^{1/2}}$
$\therefore \dfrac{Q}{M} = 0.86\; \times \;{10^{ - 10}}\;\;C/Kg $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
As they have asked the answer to be in SI units, so the values of K and G to be used should also be in SI. Only then the correct answer can be obtained. If values of K and G are used in some other units then the answer will be incorrect.Each body in this universe attracts other bodies towards itself with a force known as Gravitational Force, thus gravitation is a study of the interaction between two masses. Out of the two masses, the heavier one is called source mass and the lighter one is called test mass.
Formula used:
1. Gravitational force
${F_g} = \,\;G\,\;\dfrac{{\,{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
2. Electrostatic force
${F_e} = \;\;K\;\;\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
Gravitational Force – According to universal law of gravitation each and every object in this universe attracts another object with a force given by
${F_g} = G\;\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$

Where ${m_1}\;and\,\;{m_2}$ are two particles separated by a distance of r.
- It follows inverse square law
- Gravitational force is always attractive in nature
- G is the universal gravitational constant and $G = 6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}$
- Coulomb’s law: According to Coulomb’s s law, two charge particles of charges ${q_1}\;and\;{q_2}$ and separated by a distance r exerts an electrostatic force on each other given by
${F_e}\; = \;K\;\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
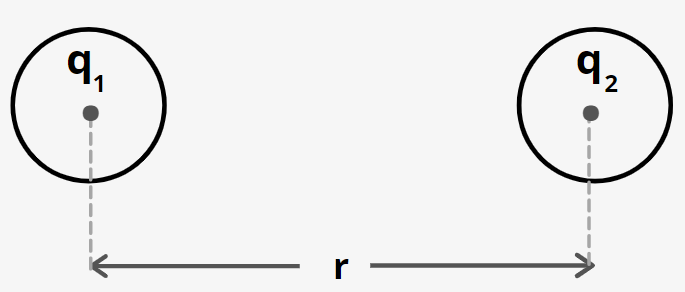
where k is a constant.
- The value of k is
$K = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} = 9 \times {10^9}\;N{m^2}/{C^2}$
- It can be attractive or repulsive
- For similar charges, it is repulsive
- For opposite charges, it is attractive in nature.
Now, as in question the given system of charges are in equilibrium.
Hence, ${F_e} = {F_g}$ …(1)
Now, \[{F_e} = K\dfrac{{{q_1}\,{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}\]
and \[{F_g} = G\dfrac{{{m_1}\,{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}\]
Here ${q_1} = {q_2} = Q\;,\;\,\;{m_1} = {m_2} = M$
So, From (1)
${F_e} = {F_g}$
\[K\dfrac{{(Q)\,(Q)}}{{{r^2}}} = G\dfrac{{(M)\,(M)}}{{{r^2}}}\]
\[
\Rightarrow \;\;K\,{Q^2}\, = \;\;G{M^2} \\
\Rightarrow \;\;\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{{M^2}}}\; = \;\dfrac{G}{K} \\
\Rightarrow \;\;\dfrac{Q}{M}\; = \;\sqrt {\dfrac{G}{K}} \\
\]
$
G\; = \;6.67 \times {10^{ - 11}}\;N{m^2}/K{g^2} \\
K\; = \;9 \times {10^9}\;N{m^2}/{C^2} \\ $
So,
\[\dfrac{Q}{M} = {\left( {\dfrac{{6.67 \times {{10}^{ - 11}}\;\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}}}{{9 \times {{10}^9}\;\;\;N{m^2}/K{g^2}}}} \right)^{1/2}}\]
$\implies \dfrac{Q}{M} = {[0.7411\; \times \;{10^{ - 20}}\;\;{C^2}/K{g^2}]^{1/2}}$
$\therefore \dfrac{Q}{M} = 0.86\; \times \;{10^{ - 10}}\;\;C/Kg $
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
As they have asked the answer to be in SI units, so the values of K and G to be used should also be in SI. Only then the correct answer can be obtained. If values of K and G are used in some other units then the answer will be incorrect.Each body in this universe attracts other bodies towards itself with a force known as Gravitational Force, thus gravitation is a study of the interaction between two masses. Out of the two masses, the heavier one is called source mass and the lighter one is called test mass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




