
Two identical particles each of mass m and having charges –q and +q are revolving in a circle of radius r under the influence of electric attraction. Kinetic energy of each particle is
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{4r} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{2r} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{8r} \\
& \text{D}\text{. }\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{r} \\
\end{align}$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: In this question, both the particles are revolving under the influence of electric attraction force. So, we can equate centripetal force, i.e., $\left| {{F}_{c}} \right|=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$ to electric attraction force, i.e., $\left| {{F}_{e}} \right|=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{R}^{2}}}$ , and then deduce the equation for kinetic energy of the particle from it.
Complete step by step answer:
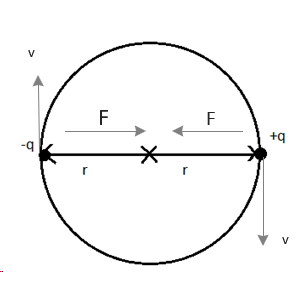
Electric attraction between two charge particle having charges -q and +q is given by,
$\left| {{F}_{e}} \right|=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Where, $F_e$ is the force and R is the distance of separation between two charges and k is the coulomb’s constant. The force is acting towards the other charge as shown in the above figure. In the electric attraction force, we have taken distance as 2r, because charges are separated by 2r distance (shown in the above figure).
Therefore, the equation becomes:
$\left| {{F}_{e}} \right|=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{\left( 2r \right)}^{2}}}$
Now, Centripetal force which keeps a particle moving around a circle of radius R, is felt toward the center of the circle. It is given by the equation,
$\left| {{F}_{c}} \right|=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$
But here, the radius is taken as r. so, the equation becomes,
$\left| {{F}_{c}} \right|=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
In the above question we have balanced two forces: centripetal force and electric attraction force under which these particles are revolving.
Charged particles are revolving under the electric attraction force, thus centric petal force is generated from this revolution, so we can write that
$F_e=F_c$
Substituting the values for each forces which we had already found, we get,
$\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{\left( 2r \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
Which can be further simplified as,
$m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{4r}$
Multiplying both the side by $\dfrac{1}{2}$ , we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{4r} \right)\]
Kinetic energy of a particle moving with velocity v is given by $KE=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$ , so we get,
\[KE=\left( \dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{8r} \right)\]
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Centripetal force is responsible for moving a particle in a circular path under some attractive force. This force contains a Kinetic energy term within it. It always acts towards the center of the circle.
Mathematically centripetal force is represented by $F=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$ .
Students can make errors in writing the r term in centripetal force, always remember it is the radius of circular path.
Complete step by step answer:

Electric attraction between two charge particle having charges -q and +q is given by,
$\left| {{F}_{e}} \right|=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{R}^{2}}}$
Where, $F_e$ is the force and R is the distance of separation between two charges and k is the coulomb’s constant. The force is acting towards the other charge as shown in the above figure. In the electric attraction force, we have taken distance as 2r, because charges are separated by 2r distance (shown in the above figure).
Therefore, the equation becomes:
$\left| {{F}_{e}} \right|=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{\left( 2r \right)}^{2}}}$
Now, Centripetal force which keeps a particle moving around a circle of radius R, is felt toward the center of the circle. It is given by the equation,
$\left| {{F}_{c}} \right|=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$
But here, the radius is taken as r. so, the equation becomes,
$\left| {{F}_{c}} \right|=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
In the above question we have balanced two forces: centripetal force and electric attraction force under which these particles are revolving.
Charged particles are revolving under the electric attraction force, thus centric petal force is generated from this revolution, so we can write that
$F_e=F_c$
Substituting the values for each forces which we had already found, we get,
$\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{{{\left( 2r \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$
Which can be further simplified as,
$m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{4r}$
Multiplying both the side by $\dfrac{1}{2}$ , we get,
\[\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{4r} \right)\]
Kinetic energy of a particle moving with velocity v is given by $KE=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$ , so we get,
\[KE=\left( \dfrac{k{{q}^{2}}}{8r} \right)\]
Thus, option C is the correct answer.
Note:
Centripetal force is responsible for moving a particle in a circular path under some attractive force. This force contains a Kinetic energy term within it. It always acts towards the center of the circle.
Mathematically centripetal force is represented by $F=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{r}$ .
Students can make errors in writing the r term in centripetal force, always remember it is the radius of circular path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




