
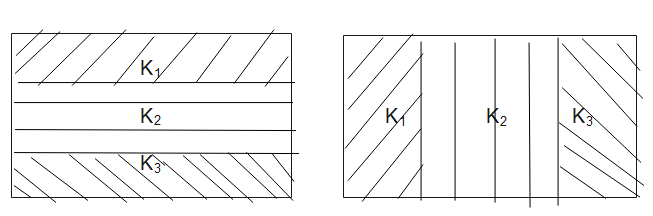
Two identical parallel plate capacitors, of capacitance C each, have plates of area A, separated by a distance d. The space between the plates of the two capacitors is filled with three dielectrics, of equal thickness and dielectric constants ${k_1}$, ${k_2}$ and ${k_3}$. The first capacitor is filled as shown in fig.-I, and the second one is filled as shown in fig.-II.
If these two modified capacitors are charged by the same potential V, the ratio of the energy stored in the two, would be (${E_1}$ refers to capacitor (I) and ${E_2}$ to capacitor (II) :

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Here, first we use the formula for parallel plate capacitor and find the total capacitance or equivalent capacitance. Further, we use the capacitor formula for series and find the total capacitance. The two finally obtained capacities will be used in finding the ratio of energy stored by the capacitor.
Formula used:
$C = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}AK}}{d}$
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}$
$\eqalign{
& C = \dfrac{{{ \in _0}KA}}{{3d}} \cr
& {C_{eq\prime }} = {C_1} + {C_2} + {C_{3}} \cr} $
$\dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq}}{V^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq'}}{V^2}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
A capacitor can be defined as a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Also, it is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance.
We know, the relation between capacitor and the dielectric constant is given by:
From figure 1)
$\eqalign{
& {C_{1}} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_1}}}{d} \cr
& {C_2} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_2}}}{d} \cr
& {C_3} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_3}}}{d} \cr} $
We also have the equivalent capacitance equation, which is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}$
Now, by putting the values in the above equation, we get:
$ \Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_1}{K_2}{K_3}}}{{d\left( {{K_1}{K_2} + {K_2}{K_3} + {K_3}{K_1}} \right)}}.....................(1)$
Further, from figure 2)
$\eqalign{
& {C_{1}} = \dfrac{{{ \in _0}{K_1}A}}{{3d}} \cr
& {C_{2}} = \dfrac{{{ \in _0}{K_2}A}}{{3d}} \cr
& {C_{3}} = \dfrac{{{ \in _{0}}{K_3}A}}{{3d}} \cr} $
Here, we have the equivalent capacitance, which is given by:
$\because {C_{eq\prime }} = {C_1} + {C_2} + {C_{3}}$
Now, by putting the values in the above equation, we get:
${C_{eq'}} = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{{3d}}({K_1} + {K_2} + {K_3})..............(2)$
We calculate the ratio of the energy stored in the two capacitors as:
$\dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq}}{V^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq'}}{V^2}}}$
Substituting the values of equation (1) and (2) in the above equation, we get:
$\therefore \dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{9{K_1}{K_2}{K_3}}}{{({K_1} + {K_2} + {K_3})\left( {{K_1}{K_2} + {K_2}{K_3} + {K_3}{K_1}} \right)}}$
Therefore, the ratio of the energy stored in the two capacitors is given by the above equation.
Additional information:
A capacitor consists of two or more parallel conductive or metal plates. These plates are not connected or touching each other, but rather they are electrically separated either by air or by some form of a good insulating material like waxed paper, mica, ceramic, plastic or some form of a liquid gel as used in electrolytic capacitors. This insulating layer between capacitor’s plates is commonly called the Dielectric.
The dielectric constant is defined as a measure of the amount of electric potential energy, in the form of induced polarization which is stored in a given volume of material under the action of an electric field.
Note:
Capacitance is measured in Farad, or can be said as one coulomb per volt. Capacitance is dependent on the dielectric constant as well as on the distance between the two plates. The parallel plate capacitor is the simplest form of capacitor.
Formula used:
$C = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}AK}}{d}$
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}$
$\eqalign{
& C = \dfrac{{{ \in _0}KA}}{{3d}} \cr
& {C_{eq\prime }} = {C_1} + {C_2} + {C_{3}} \cr} $
$\dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq}}{V^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq'}}{V^2}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
A capacitor can be defined as a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Also, it is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance.
We know, the relation between capacitor and the dielectric constant is given by:
From figure 1)
$\eqalign{
& {C_{1}} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_1}}}{d} \cr
& {C_2} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_2}}}{d} \cr
& {C_3} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_3}}}{d} \cr} $
We also have the equivalent capacitance equation, which is given by:
$\dfrac{1}{{{C_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{C_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{C_3}}}$
Now, by putting the values in the above equation, we get:
$ \Rightarrow {C_{eq}} = \dfrac{{3{ \in _0}A{K_1}{K_2}{K_3}}}{{d\left( {{K_1}{K_2} + {K_2}{K_3} + {K_3}{K_1}} \right)}}.....................(1)$
Further, from figure 2)
$\eqalign{
& {C_{1}} = \dfrac{{{ \in _0}{K_1}A}}{{3d}} \cr
& {C_{2}} = \dfrac{{{ \in _0}{K_2}A}}{{3d}} \cr
& {C_{3}} = \dfrac{{{ \in _{0}}{K_3}A}}{{3d}} \cr} $
Here, we have the equivalent capacitance, which is given by:
$\because {C_{eq\prime }} = {C_1} + {C_2} + {C_{3}}$
Now, by putting the values in the above equation, we get:
${C_{eq'}} = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{{3d}}({K_1} + {K_2} + {K_3})..............(2)$
We calculate the ratio of the energy stored in the two capacitors as:
$\dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq}}{V^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}{C_{eq'}}{V^2}}}$
Substituting the values of equation (1) and (2) in the above equation, we get:
$\therefore \dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{{E_2}}} = \dfrac{{9{K_1}{K_2}{K_3}}}{{({K_1} + {K_2} + {K_3})\left( {{K_1}{K_2} + {K_2}{K_3} + {K_3}{K_1}} \right)}}$
Therefore, the ratio of the energy stored in the two capacitors is given by the above equation.
Additional information:
A capacitor consists of two or more parallel conductive or metal plates. These plates are not connected or touching each other, but rather they are electrically separated either by air or by some form of a good insulating material like waxed paper, mica, ceramic, plastic or some form of a liquid gel as used in electrolytic capacitors. This insulating layer between capacitor’s plates is commonly called the Dielectric.
The dielectric constant is defined as a measure of the amount of electric potential energy, in the form of induced polarization which is stored in a given volume of material under the action of an electric field.
Note:
Capacitance is measured in Farad, or can be said as one coulomb per volt. Capacitance is dependent on the dielectric constant as well as on the distance between the two plates. The parallel plate capacitor is the simplest form of capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




