
Two identical balls each having mass density $\rho $, mass $m$ and charge $q$ are suspended from a common point by two insulating massless strings of angle $\theta $ with the vertical. Now both the balls are immersed in a liquid. At equilibrium, $\theta $ remains the same. If the mass density of the liquid is $\sigma $ then the dielectric constant of liquid will be
a. $\dfrac{\sigma }{{\rho - \sigma }}$
b. $\dfrac{\rho }{{\rho - \sigma }}$
c. $\dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }$
d. $\dfrac{\rho }{\sigma }$
Answer
565.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question first we have to draw a proper diagram and then we will proceed further by equating the forces applied on the ball with the help of the diagram. We will use the concept of trigonometry along with the concept of electrostatics.
Formula used:
$w = mg$ ,
Upthrust $= V\sigma g$ ,
$V = \dfrac{m}{\rho }$
where $m$ = mass of the ball,
$g$ = acceleration due to gravity,
$V$ = volume of the submerged portion,
$\sigma $ = density of liquid,
$\rho $ = density of the ball.
Complete step by step answer:
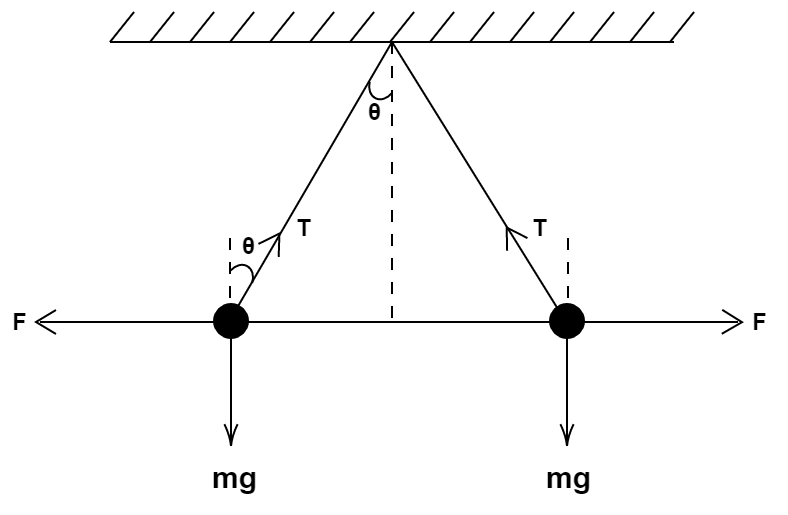
Initially, the forces acting on each ball are
- Tension
- Weight
The electrostatic force of repulsion $F$ for its equilibrium along vertical, where $\theta $ is the angle made by the string and the vertical
$T\cos \theta = mg$ ........ $\left( 1 \right)$
And along horizontal, we have
$T\sin \theta = F$ ......... $\left( 2 \right)$
Dividing equation $\left( 2 \right)$ by $\left( 1 \right)$ , we get
$\dfrac{{T\sin \theta }}{{T\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{F}{{mg}}$
On further solving we get,
$\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{F}{{mg}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{F}{{mg}}$ ........... $\left( 3 \right)$
Now, when the balls are suspended in a liquid of density $\sigma $ and dielectric constant $K$ , the electrostatic force will become $\dfrac{1}{K}$ times, i.e.
$F' = \dfrac{F}{K}$
While weight becomes original weight-upthrust.
But before that, let us know Upthrust, which can be defined as the upward force applied by a liquid on an object immersed (partially or fully) or floating in the liquid
Mathematically it can be written as
$Upthrust = V\sigma g$ .
This is also known as the buoyant force.
$mg' = mg - \text{Upthrust}$
$ \Rightarrow mg' = mg - V\sigma g$
As we know, $V = \dfrac{m}{\rho }$
Therefore, $mg' = mg - \left( {\dfrac{m}{\rho }} \right)\sigma g$
Taking $mg$ as common, we get
$mg' = mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]$ ............ $\left( 4 \right)$
Now, for the equilibrium of the balls, we need a relation between the new or apparent force and the apparent weight, given as below
$F' = mg'\tan \theta '$ ............. $\left( 5 \right)$
Angle changes from $\theta $ to $\theta '$ because of the apparent force applied
Now, let us substitute the value of $mg'$ from the equation $\left( 4 \right)$ in equation $\left( 5 \right)$
So we get:
$F' = mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]\tan \theta '$
Let us find the value of $\tan \theta '$ from the above equation:
$\tan \theta ' = \dfrac{{F'}}{{mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
And we know $F' = \dfrac{F}{K}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{F}{K}}}{{mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta ' = \dfrac{F}{{Kmg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$ ............ $\left( 6 \right)$
As we know from the given problem statement:
$\theta = \theta '$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \tan \theta '$
Now, from equation $\left( 6 \right)$ and equation $\left( 3 \right)$ , we have
$\tan \theta = \tan \theta '$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{mg}} = \dfrac{F}{{Kmg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
Let us now solve this equation to find the value of the dielectric constant $K$ .
$\dfrac{F}{{mg}} = \dfrac{F}{{Kmg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
$ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{{mg}}{{mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
On further simplifying the equation we get,
$K = \dfrac{1}{{\left[ {\dfrac{{\rho - \sigma }}{\rho }} \right]}}$
$ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{\rho }{{\rho - \sigma }}$
Thus, the dielectric constant of the liquid is $\dfrac{\rho }{{\rho - \sigma }}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The relative permittivity of a substance, or dielectric constant, is its permittivity expressed as a ratio to the permittivity of the vacuum. Permittivity is a material property that has an effect on the Coulomb force in the material between two point charges. Two or more solid objects in touch are exerting forces on one another.
Formula used:
$w = mg$ ,
Upthrust $= V\sigma g$ ,
$V = \dfrac{m}{\rho }$
where $m$ = mass of the ball,
$g$ = acceleration due to gravity,
$V$ = volume of the submerged portion,
$\sigma $ = density of liquid,
$\rho $ = density of the ball.
Complete step by step answer:

Initially, the forces acting on each ball are
- Tension
- Weight
The electrostatic force of repulsion $F$ for its equilibrium along vertical, where $\theta $ is the angle made by the string and the vertical
$T\cos \theta = mg$ ........ $\left( 1 \right)$
And along horizontal, we have
$T\sin \theta = F$ ......... $\left( 2 \right)$
Dividing equation $\left( 2 \right)$ by $\left( 1 \right)$ , we get
$\dfrac{{T\sin \theta }}{{T\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{F}{{mg}}$
On further solving we get,
$\dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{F}{{mg}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{F}{{mg}}$ ........... $\left( 3 \right)$
Now, when the balls are suspended in a liquid of density $\sigma $ and dielectric constant $K$ , the electrostatic force will become $\dfrac{1}{K}$ times, i.e.
$F' = \dfrac{F}{K}$
While weight becomes original weight-upthrust.
But before that, let us know Upthrust, which can be defined as the upward force applied by a liquid on an object immersed (partially or fully) or floating in the liquid
Mathematically it can be written as
$Upthrust = V\sigma g$ .
This is also known as the buoyant force.
$mg' = mg - \text{Upthrust}$
$ \Rightarrow mg' = mg - V\sigma g$
As we know, $V = \dfrac{m}{\rho }$
Therefore, $mg' = mg - \left( {\dfrac{m}{\rho }} \right)\sigma g$
Taking $mg$ as common, we get
$mg' = mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]$ ............ $\left( 4 \right)$
Now, for the equilibrium of the balls, we need a relation between the new or apparent force and the apparent weight, given as below
$F' = mg'\tan \theta '$ ............. $\left( 5 \right)$
Angle changes from $\theta $ to $\theta '$ because of the apparent force applied
Now, let us substitute the value of $mg'$ from the equation $\left( 4 \right)$ in equation $\left( 5 \right)$
So we get:
$F' = mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]\tan \theta '$
Let us find the value of $\tan \theta '$ from the above equation:
$\tan \theta ' = \dfrac{{F'}}{{mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
And we know $F' = \dfrac{F}{K}$
$\tan \theta = \dfrac{{\dfrac{F}{K}}}{{mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta ' = \dfrac{F}{{Kmg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$ ............ $\left( 6 \right)$
As we know from the given problem statement:
$\theta = \theta '$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \tan \theta '$
Now, from equation $\left( 6 \right)$ and equation $\left( 3 \right)$ , we have
$\tan \theta = \tan \theta '$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{F}{{mg}} = \dfrac{F}{{Kmg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
Let us now solve this equation to find the value of the dielectric constant $K$ .
$\dfrac{F}{{mg}} = \dfrac{F}{{Kmg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
$ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{{mg}}{{mg\left[ {1 - \dfrac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right]}}$
On further simplifying the equation we get,
$K = \dfrac{1}{{\left[ {\dfrac{{\rho - \sigma }}{\rho }} \right]}}$
$ \Rightarrow K = \dfrac{\rho }{{\rho - \sigma }}$
Thus, the dielectric constant of the liquid is $\dfrac{\rho }{{\rho - \sigma }}$
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The relative permittivity of a substance, or dielectric constant, is its permittivity expressed as a ratio to the permittivity of the vacuum. Permittivity is a material property that has an effect on the Coulomb force in the material between two point charges. Two or more solid objects in touch are exerting forces on one another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




