
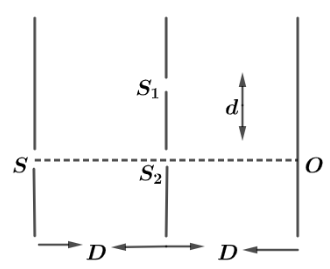
Two ideal slits ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$ are at a distance $d$ apart and illuminated by a light of wavelength $\lambda $ passing through an ideal source slit $S$ placed on the line through ${S_2}$ as shown in the figure. The distance between the planes of the slits is $D$. A screen is also held at a distance of $D$ from the plane of slits. The minimum value of $d$ for which there is darkness at point $O$ .
A. $\sqrt {\dfrac{{3\lambda D}}{2}} $
B. $\sqrt {\lambda D} $
C. $\sqrt {\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{2}} $
D. $\sqrt {3\lambda D} $

Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we need to find the path difference due to both slits at point $O$. And since point $O$ has a darkness point. In interference, a darkness point forms due to destructive interference whose path difference is given as $\Delta x = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first trace the wave in the given diagram and use the geometry of triangles to find the path difference between two slits. Now, in triangle $S{S_1}{S_2}$ using Pythagoras theorem, we get
${(S{S_1})^2} = {(S{S_2})^2} + {({S_1}{S_2})^2}$
$\Rightarrow S{S_1} = \sqrt {{D^2} + {d^2}} $
Hence total length $S{S_1}O = 2\sqrt {{D^2} + {d^2}} $
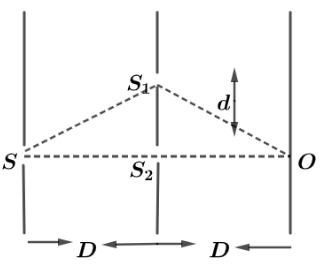
And the distance, $S{S_2}O = 2D$
So, path difference $\Delta x = $ $2\sqrt {{D^2} + {d^2}} - 2D$
$\Delta x = 2D(1 + \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{{D^2}}} - 1)$
$\Rightarrow \Delta x = \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D} \to (i)$
Now, using the destructive interference formula we know,
$\Delta x = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
From equation $(i)$ we get,
$\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D} = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
For minimum distance $n = 1$
$\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D} = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
$\therefore d = $ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{2}} $
So, minimum distance at which the destructive interference will happen or darkness occur at point $O$ is $d = $ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{2}} $
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: In destructive interference of light, light waves from both slits ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$ interferes destructively which mean both secondary light waves cancels each other positive displacement with other’s negative which results in no light hence such points have darkness whereas in Constructive interference such displacements add together and produce bright spots on screen which is called bright fringes or Constructive interference.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first trace the wave in the given diagram and use the geometry of triangles to find the path difference between two slits. Now, in triangle $S{S_1}{S_2}$ using Pythagoras theorem, we get
${(S{S_1})^2} = {(S{S_2})^2} + {({S_1}{S_2})^2}$
$\Rightarrow S{S_1} = \sqrt {{D^2} + {d^2}} $
Hence total length $S{S_1}O = 2\sqrt {{D^2} + {d^2}} $

And the distance, $S{S_2}O = 2D$
So, path difference $\Delta x = $ $2\sqrt {{D^2} + {d^2}} - 2D$
$\Delta x = 2D(1 + \dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{{{D^2}}} - 1)$
$\Rightarrow \Delta x = \dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D} \to (i)$
Now, using the destructive interference formula we know,
$\Delta x = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
From equation $(i)$ we get,
$\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D} = (2n - 1)\dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
For minimum distance $n = 1$
$\dfrac{{{d^2}}}{D} = \dfrac{\lambda }{2}$
$\therefore d = $ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{2}} $
So, minimum distance at which the destructive interference will happen or darkness occur at point $O$ is $d = $ $\sqrt {\dfrac{{\lambda D}}{2}} $
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: In destructive interference of light, light waves from both slits ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$ interferes destructively which mean both secondary light waves cancels each other positive displacement with other’s negative which results in no light hence such points have darkness whereas in Constructive interference such displacements add together and produce bright spots on screen which is called bright fringes or Constructive interference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




