
When two ice cubes are pressed over each other, they unite to form one cube, which of the following forces is responsible to hold them together?
A) Van der Waals force
B) Hydrogen bond formation
C) Covalent attraction
D) Ionic interaction
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Ice is a solid state of water. In ice every water molecule is associated with four other water molecules. It has an open cage like structure.
Complete answer:
Intermolecular force is the force of attraction that held the molecule together. There are various types of intermolecular forces like Van der Waals force, hydrogen bond, covalent attraction, ionic interaction etc. The type of intermolecular forces depends on the type of molecules.
Van der Waals force is weak intermolecular force which exhibit between two non polar molecules
Hydrogen bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction that binds the H-atom of one molecule with electronegative atoms of other molecules of the same substance.
Covalent compounds exhibit covalent force of attraction.
Ionic molecules are held together by an electrostatic force of attraction known as ionic force. There is ionic interaction between oppositely charged ions.
In ice every water molecule is associated with four other water molecules by hydrogen bonding in a tetrahedral fashion. Due to hydrogen bond formation ice has an open cage structure with a large empty space.
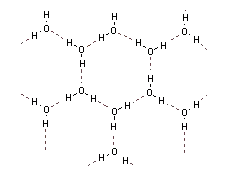
When two ice cubes are pressed together the water molecules present on the surface of the two cubes form hydrogen bonds with each other and so two cubes unite to form one cube.
Thus, the correct option is (B) Hydrogen bond formation.
Note: When a hydrogen atom is sandwiched between two highly electronegative elements (F,O,N) it shows a unique property to form a bridge between them and it is known as hydrogen bonding. Only molecules in which the H atom is bonded to either O,N or F show hydrogen bonding.
Complete answer:
Intermolecular force is the force of attraction that held the molecule together. There are various types of intermolecular forces like Van der Waals force, hydrogen bond, covalent attraction, ionic interaction etc. The type of intermolecular forces depends on the type of molecules.
Van der Waals force is weak intermolecular force which exhibit between two non polar molecules
Hydrogen bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction that binds the H-atom of one molecule with electronegative atoms of other molecules of the same substance.
Covalent compounds exhibit covalent force of attraction.
Ionic molecules are held together by an electrostatic force of attraction known as ionic force. There is ionic interaction between oppositely charged ions.
In ice every water molecule is associated with four other water molecules by hydrogen bonding in a tetrahedral fashion. Due to hydrogen bond formation ice has an open cage structure with a large empty space.

When two ice cubes are pressed together the water molecules present on the surface of the two cubes form hydrogen bonds with each other and so two cubes unite to form one cube.
Thus, the correct option is (B) Hydrogen bond formation.
Note: When a hydrogen atom is sandwiched between two highly electronegative elements (F,O,N) it shows a unique property to form a bridge between them and it is known as hydrogen bonding. Only molecules in which the H atom is bonded to either O,N or F show hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




