
Two free parallel wires carrying currents in the opposite directions
A. Attract each other
B. Repel each other
C. do not affect each other
D. get rotated to be perpendicular to each other
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Analyse how the wires influence one another. Use the theory that a long straight wire, which is carrying some current produces magnetic field lines in the surroundings in the form of concentric circles. When a straight current carrying conductor is placed in an external magnetic field, the conductor experiences a magnetic force given by $\overrightarrow{F}=i\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$.
Formula used:
$\overrightarrow{F}=i\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$
Complete answer:
Consider two infinitely long straight wires. Let the two wires be placed free and parallel to each. The two wires carry currents ${{i}_{1}}$ and ${{i}_{2}}$. However, the directions of the both currents are opposite to each other. Let the perpendicular distance between them be d.
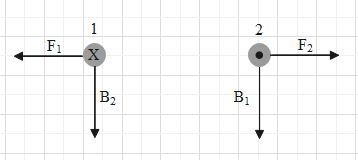
In the above figure, the direction of current in the left wire is inside the plane of the page and that of the current in the other wire is outside the same plane.
Let us analyse the influence of wire 1 on wire 2.
An infinitely long straight wire, which is carrying some current, produces magnetic field lines in the surroundings in the form of concentric circles. The centre of these circles is on the axis of wire 1. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the right hand rule.
So, according to right hand rule, the direction of the magnetic fields lines due to current in wire 1 is in the clockwise direction.
When a straight current carrying conductor is placed in an external magnetic field, the conductor experiences a magnetic force given by $\overrightarrow{F}=i\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$.
Here, i is the current in the conductor, $\overrightarrow{L}$ is the length vector of the conductor and its direction is along the direction of the current in the conductor. $\overrightarrow{B}$ is the external magnetic field at the point where we are finding the force.
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane in which $\overrightarrow{L}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$ lie.
Therefore, now we can understand the wire 1 will create an external magnetic field for wire 2. Due to this, wire 2 experiences a magnetic force.
Let us calculate the direction of the magnetic force.
The direction of magnetic field at the location of wire 2 will be in downwards direction. Let that magnetic field be $\overrightarrow{{{B}_{2}}}$. For wire 2, $\overrightarrow{L}$ is directed outside the plane as the current is coming out of the plane.
Therefore, the direction of the magnetic force on wire 2 is in the direction of the vector of $\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$. And it comes out to be directed towards the right.
That means that wire 1 applies a force on wire 2 such that it pushes it away from itself.
Now repeat the analysis from the other side of the plane and you will find a similar influence of wire 2 on wire 1.
Therefore, wire 2 will also apply a force on wire 1 that pushes it away from itself.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Note that two straight current carrying wires parallel to each other will not always repel each other.
It depends on the direction of the currents in both the wires.
If the directions of the currents are opposite, then the wires will repel each other.
If the directions of the currents are the same, then the wires will attract each other.
Formula used:
$\overrightarrow{F}=i\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$
Complete answer:
Consider two infinitely long straight wires. Let the two wires be placed free and parallel to each. The two wires carry currents ${{i}_{1}}$ and ${{i}_{2}}$. However, the directions of the both currents are opposite to each other. Let the perpendicular distance between them be d.

In the above figure, the direction of current in the left wire is inside the plane of the page and that of the current in the other wire is outside the same plane.
Let us analyse the influence of wire 1 on wire 2.
An infinitely long straight wire, which is carrying some current, produces magnetic field lines in the surroundings in the form of concentric circles. The centre of these circles is on the axis of wire 1. The direction of the magnetic field is given by the right hand rule.
So, according to right hand rule, the direction of the magnetic fields lines due to current in wire 1 is in the clockwise direction.
When a straight current carrying conductor is placed in an external magnetic field, the conductor experiences a magnetic force given by $\overrightarrow{F}=i\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$.
Here, i is the current in the conductor, $\overrightarrow{L}$ is the length vector of the conductor and its direction is along the direction of the current in the conductor. $\overrightarrow{B}$ is the external magnetic field at the point where we are finding the force.
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane in which $\overrightarrow{L}$ and $\overrightarrow{B}$ lie.
Therefore, now we can understand the wire 1 will create an external magnetic field for wire 2. Due to this, wire 2 experiences a magnetic force.
Let us calculate the direction of the magnetic force.
The direction of magnetic field at the location of wire 2 will be in downwards direction. Let that magnetic field be $\overrightarrow{{{B}_{2}}}$. For wire 2, $\overrightarrow{L}$ is directed outside the plane as the current is coming out of the plane.
Therefore, the direction of the magnetic force on wire 2 is in the direction of the vector of $\left( \overrightarrow{L}\times \overrightarrow{B} \right)$. And it comes out to be directed towards the right.
That means that wire 1 applies a force on wire 2 such that it pushes it away from itself.
Now repeat the analysis from the other side of the plane and you will find a similar influence of wire 2 on wire 1.
Therefore, wire 2 will also apply a force on wire 1 that pushes it away from itself.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Note that two straight current carrying wires parallel to each other will not always repel each other.
It depends on the direction of the currents in both the wires.
If the directions of the currents are opposite, then the wires will repel each other.
If the directions of the currents are the same, then the wires will attract each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




