
Two free charges q and 4q are placed at a distance d apart. A third charge Q is placed between them at a distance x from the charge q such that the system is at equilibrium. What is the magnitude of charge and where, that is, at what distance it should be placed?
Answer
513k+ views
Hint:As a very first step, one could read the question well and hence note down the given important points from it. You could then make a neat diagram for better understanding. Then you could apply the condition for equilibrium in the given system and accordingly find the answer.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In the question, we are given a system where charges q and 4q are placed at d distance apart and another Q is placed at distance x from charge q between them. We are supposed to find this distance x as well as the magnitude of charge Q for the system to be at equilibrium.
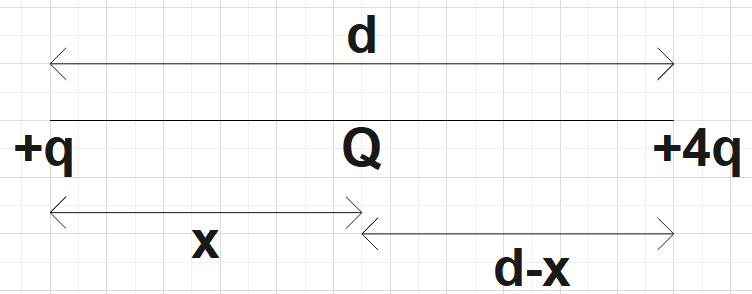
For the equilibrium point we have,
$\dfrac{kq}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k\left( 4q \right)}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{d}{3}$
The charge Q could be kept at this point. Let us assume that the charge Q is negative so as the net force on it could be zero as per the given system. Now, we could apply the condition for equilibrium again to get,
$\dfrac{kQ}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k\left( 4q \right)}{{{d}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{kQ}{{{\left( \dfrac{d}{3} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k\left( 4q \right)}{{{d}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow 9Q=4q$
$\therefore Q=\dfrac{4q}{9}$
Therefore, we found the magnitude of charge of Q to be $\dfrac{4q}{9}$and also the distance at which it should be kept from charge q to be $\dfrac{d}{3}$.
Note: The constant k that is used in the solution is given by, $k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$. Its value is given by $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$. The condition for equilibrium is basically derived from the fact that for a charge to be at equilibrium between two charges, the force due each of those charges on the new charge introduced would be 0.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In the question, we are given a system where charges q and 4q are placed at d distance apart and another Q is placed at distance x from charge q between them. We are supposed to find this distance x as well as the magnitude of charge Q for the system to be at equilibrium.
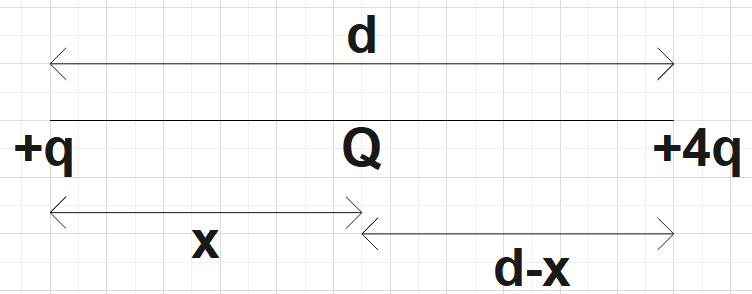
For the equilibrium point we have,
$\dfrac{kq}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k\left( 4q \right)}{{{\left( d-x \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{d}{3}$
The charge Q could be kept at this point. Let us assume that the charge Q is negative so as the net force on it could be zero as per the given system. Now, we could apply the condition for equilibrium again to get,
$\dfrac{kQ}{{{x}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k\left( 4q \right)}{{{d}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{kQ}{{{\left( \dfrac{d}{3} \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{k\left( 4q \right)}{{{d}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow 9Q=4q$
$\therefore Q=\dfrac{4q}{9}$
Therefore, we found the magnitude of charge of Q to be $\dfrac{4q}{9}$and also the distance at which it should be kept from charge q to be $\dfrac{d}{3}$.
Note: The constant k that is used in the solution is given by, $k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$. Its value is given by $9\times {{10}^{9}}N{{m}^{2}}{{C}^{-2}}$. The condition for equilibrium is basically derived from the fact that for a charge to be at equilibrium between two charges, the force due each of those charges on the new charge introduced would be 0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




