
Two dice are thrown at the same time and the product of the number appearing on them is noted. Find the probability that the product is a prime number.
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: Here we will first number of possible outcomes when we throw two dice at the same time by using the known value i.e. the number of possible events when we draw a single dice is $6$. Now we will list out all the outcomes that are present in the sample space. From this list we will calculate the product of each outcome, from this we will calculate the number of possible outcomes that are possible for the event that the product is a prime number.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that, Two dice are thrown at the same time.
We know that the total number of events in a sample space when one dice is thrown at a time is $n\left( {{S}_{1}} \right)=6$.
Now the number of events in a sample space when we throw two dice at same time is
$\begin{align}
& n\left( S \right)={{6}^{2}} \\
& n\left( S \right)=36 \\
\end{align}$
Now all the events in the sample space when we throw two dice at same time are
$S=\left\{ \begin{align}
& \left( 1,1 \right),\left( 1,2 \right),\left( 1,3 \right),\left( 1,4 \right),\left( 1,5 \right),\left( 1,6 \right) \\
& \left( 2,1 \right),\left( 2,2 \right),\left( 2,3 \right),\left( 2,4 \right),\left( 2,5 \right),\left( 2,6 \right) \\
& \left( 3,1 \right),\left( 3,2 \right),\left( 3,3 \right),\left( 3,4 \right),\left( 3,5 \right),\left( 3,6 \right) \\
& \left( 4,1 \right),\left( 4,2 \right),\left( 4,3 \right),\left( 4,4 \right),\left( 4,5 \right),\left( 4,6 \right) \\
& \left( 5,1 \right),\left( 5,2 \right),\left( 5,3 \right),\left( 5,4 \right),\left( 5,5 \right),\left( 5,6 \right) \\
& \left( 6,1 \right),\left( 6,2 \right),\left( 6,3 \right),\left( 6,4 \right),\left( 6,5 \right),\left( 6,6 \right) \\
\end{align} \right\}$
The product of elements in each event is given by
$x=\left\{ \begin{align}
& \left( 1\times 1=1 \right),\left( 1\times 2=2 \right),\left( 1\times 3=3 \right),\left( 1\times 4=4 \right),\left( 1\times 5=5 \right),\left( 1\times 6=6 \right) \\
& \left( 2\times 1=2 \right),\left( 2\times 2=4 \right),\left( 2\times 3=6 \right),\left( 2\times 4=8 \right),\left( 2\times 5=10 \right),\left( 2\times 6=12 \right) \\
& \left( 3\times 1=3 \right),\left( 3\times 2=6 \right),\left( 3\times 3=9 \right),\left( 3\times 4=12 \right),\left( 3\times 5=15 \right),\left( 3\times 6=18 \right) \\
& \left( 4\times 1=4 \right),\left( 4\times 2=8 \right),\left( 4\times 3=12 \right),\left( 4\times 4=16 \right),\left( 4\times 5=20 \right),\left( 4\times 6=24 \right) \\
& \left( 5\times 1=5 \right),\left( 5\times 2=10 \right),\left( 5\times 3=15 \right),\left( 5\times 4=20 \right),\left( 5\times 5=25 \right),\left( 5\times 6=30 \right) \\
& \left( 6\times 1=6 \right),\left( 6\times 2=12 \right),\left( 6\times 3=18 \right),\left( 6\times 4=24 \right),\left( 6\times 5=30 \right),\left( 6\times 6=36 \right) \\
\end{align} \right\}$
Now the total number of events for the event “That the product of the numbers when two dice are thrown” is $n\left( x \right)=36$
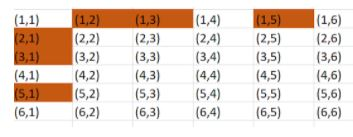
The possible outcomes for the event that the product of numbers on the two dice is prime are $\left( 1,2 \right),\left( 1,3 \right),\left( 1,5 \right),\left( 2,1 \right),\left( 3,1 \right),\left( 5,1 \right)$. Number of possible outcomes for the event is $n\left( A \right)=6$.
Hence the probability of the event $A$is
$\begin{align}
& P\left( A \right)=\dfrac{n\left( A \right)}{n\left( x \right)} \\
& P\left( A \right)=\dfrac{6}{36} \\
& P\left( A \right)=\dfrac{1}{6} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the probability of the required event is $\dfrac{1}{6}$.
Note: Students can also use the below picture to get the number of possible outcomes for the given condition.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that, Two dice are thrown at the same time.
We know that the total number of events in a sample space when one dice is thrown at a time is $n\left( {{S}_{1}} \right)=6$.
Now the number of events in a sample space when we throw two dice at same time is
$\begin{align}
& n\left( S \right)={{6}^{2}} \\
& n\left( S \right)=36 \\
\end{align}$
Now all the events in the sample space when we throw two dice at same time are
$S=\left\{ \begin{align}
& \left( 1,1 \right),\left( 1,2 \right),\left( 1,3 \right),\left( 1,4 \right),\left( 1,5 \right),\left( 1,6 \right) \\
& \left( 2,1 \right),\left( 2,2 \right),\left( 2,3 \right),\left( 2,4 \right),\left( 2,5 \right),\left( 2,6 \right) \\
& \left( 3,1 \right),\left( 3,2 \right),\left( 3,3 \right),\left( 3,4 \right),\left( 3,5 \right),\left( 3,6 \right) \\
& \left( 4,1 \right),\left( 4,2 \right),\left( 4,3 \right),\left( 4,4 \right),\left( 4,5 \right),\left( 4,6 \right) \\
& \left( 5,1 \right),\left( 5,2 \right),\left( 5,3 \right),\left( 5,4 \right),\left( 5,5 \right),\left( 5,6 \right) \\
& \left( 6,1 \right),\left( 6,2 \right),\left( 6,3 \right),\left( 6,4 \right),\left( 6,5 \right),\left( 6,6 \right) \\
\end{align} \right\}$
The product of elements in each event is given by
$x=\left\{ \begin{align}
& \left( 1\times 1=1 \right),\left( 1\times 2=2 \right),\left( 1\times 3=3 \right),\left( 1\times 4=4 \right),\left( 1\times 5=5 \right),\left( 1\times 6=6 \right) \\
& \left( 2\times 1=2 \right),\left( 2\times 2=4 \right),\left( 2\times 3=6 \right),\left( 2\times 4=8 \right),\left( 2\times 5=10 \right),\left( 2\times 6=12 \right) \\
& \left( 3\times 1=3 \right),\left( 3\times 2=6 \right),\left( 3\times 3=9 \right),\left( 3\times 4=12 \right),\left( 3\times 5=15 \right),\left( 3\times 6=18 \right) \\
& \left( 4\times 1=4 \right),\left( 4\times 2=8 \right),\left( 4\times 3=12 \right),\left( 4\times 4=16 \right),\left( 4\times 5=20 \right),\left( 4\times 6=24 \right) \\
& \left( 5\times 1=5 \right),\left( 5\times 2=10 \right),\left( 5\times 3=15 \right),\left( 5\times 4=20 \right),\left( 5\times 5=25 \right),\left( 5\times 6=30 \right) \\
& \left( 6\times 1=6 \right),\left( 6\times 2=12 \right),\left( 6\times 3=18 \right),\left( 6\times 4=24 \right),\left( 6\times 5=30 \right),\left( 6\times 6=36 \right) \\
\end{align} \right\}$
Now the total number of events for the event “That the product of the numbers when two dice are thrown” is $n\left( x \right)=36$
The possible outcomes for the event that the product of numbers on the two dice is prime are $\left( 1,2 \right),\left( 1,3 \right),\left( 1,5 \right),\left( 2,1 \right),\left( 3,1 \right),\left( 5,1 \right)$. Number of possible outcomes for the event is $n\left( A \right)=6$.
Hence the probability of the event $A$is
$\begin{align}
& P\left( A \right)=\dfrac{n\left( A \right)}{n\left( x \right)} \\
& P\left( A \right)=\dfrac{6}{36} \\
& P\left( A \right)=\dfrac{1}{6} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the probability of the required event is $\dfrac{1}{6}$.
Note: Students can also use the below picture to get the number of possible outcomes for the given condition.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




