
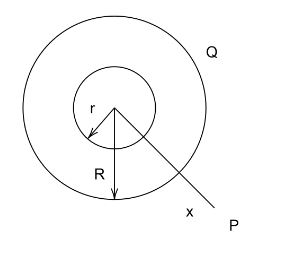
Two concentric hollow conducting spheres of radius $r$ and $R$ are shown. The charge on the outer shell is $Q$. What charge should be given to the inner sphere so that potential at any point $P$ outside the outer sphere is zero?
A. \[\dfrac{{ - Qr}}{R}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{ - QR}}{r}\]
C. \[ - Q\]
D. \[\dfrac{{ - 2QR}}{r}\]

Answer
483.6k+ views
Hint: We are given two concentric circles of radius r and R. We are asked to find the charge on the smaller circle if the potential outside the shell is zero. We can start to answer this question by writing down the values given in the question. We can then move onto finding the required solution. We can do this by using the value of total potential and equate it to zero and find the value of potential in the inner circle. This will lead us to the required solution.
Formulas used:
The potential outside the circles can be found using
\[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}}\]
Where $q$ is the charge of the smaller circle.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that, for the circle of radius R, the charge is Q. Potential can be defined as the work done to bring a charge from a reference point to a particular point. We can find the value of charge in the inner circle by using the formula,
\[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}}\]
When we equate it to zero, we get
\[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} \times \left( {Q + q} \right) = 0\]
We take the constant to the other side and get
\[Q + q = 0 \\
\therefore q = - Q\]
This gives us the value of charge on the inner circle to be negative of the charge on the outer circle.
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note: We can see that the value of total potential is taken as \[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}}\]. The value of distance is taken as R in both the cases. This is done because the radius of the bigger circle is considered in this type of problem. That is because the charges in both the circles behave as point charges.
Formulas used:
The potential outside the circles can be found using
\[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}}\]
Where $q$ is the charge of the smaller circle.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that, for the circle of radius R, the charge is Q. Potential can be defined as the work done to bring a charge from a reference point to a particular point. We can find the value of charge in the inner circle by using the formula,
\[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}}\]
When we equate it to zero, we get
\[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} \times \left( {Q + q} \right) = 0\]
We take the constant to the other side and get
\[Q + q = 0 \\
\therefore q = - Q\]
This gives us the value of charge on the inner circle to be negative of the charge on the outer circle.
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note: We can see that the value of total potential is taken as \[V = \dfrac{Q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}} + \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}R}}\]. The value of distance is taken as R in both the cases. This is done because the radius of the bigger circle is considered in this type of problem. That is because the charges in both the circles behave as point charges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




