
Two charged objects are separated by a distance $d$ as shown. The angle between the line joining the objects and the horizontal is $30^\circ $. Consider the (x,y) coordinate system with origin at the location of object 2. Calculate ${P_{21}}$the position vector of object 1 as measured from object 2. Express your answer in terms of $\hat i$, $\hat j$ and $d$ as needed.
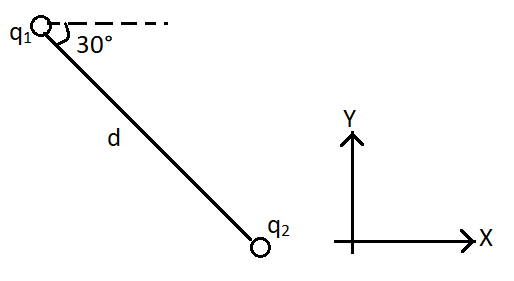

Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: From the question it is given that the angle between the line joining the 2 objects and horizontal is $30^\circ $. So we can find the x component and the y component of the position vector of the object 1. Then using those values, we can find the position vector $\Rightarrow {P_{21}}$ in terms of $\hat i$, $\hat j$ and $d$.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = x\hat i + y\hat j$
where ${P_{21}}$ is the position vector
$x$ is the x component of position and $y$ is the y component of position.
Complete step by step solution:
In the problem it is given that the origin is considered in the position of the object 2. So we can break the position vector of the object 1 in the terms of the x and y components.
We can redraw the image as,
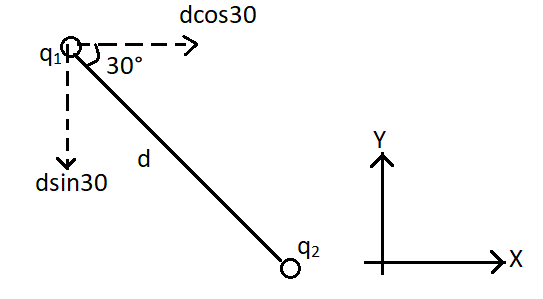
Now from the diagram, we can see that the horizontal component of the position vector is $d\cos 30^\circ $. This component coincides with the positive x axis and hence it is the x component. Therefore, $x = d\cos 30^\circ $. Again the vertical component of the position vector is $d\sin 30^\circ $. This component coincides with the negative y axis and hence it is the y component. Therefore, $y = d\sin 30^\circ $
Therefore, we can write the position vector as,
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = x\hat i + y\left( { - \hat j} \right)$
Substituting the values
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = d\cos 30\hat i + d\sin 30\left( { - \hat j} \right)$
Now the value of $\cos 30$is $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ and the value of $\sin 30$ is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
So substituting the values we get, ${P_{21}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}d\hat i - \dfrac{1}{2}d\hat j$
Now taking common we get,
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = \dfrac{d}{2}\left( {\sqrt 3 \hat i - \hat j} \right)$
This is the position vector of the object 1 with respect to the object 2.
Note:
In the solution we have taken the unit vector along the positive x axis as $\hat i$ and that along the positive y axis is $\hat j$. The y component of the position vector is directed towards the negative y axis. So we have used $\left( { - \hat j} \right)$ in the solution.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formula,
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = x\hat i + y\hat j$
where ${P_{21}}$ is the position vector
$x$ is the x component of position and $y$ is the y component of position.
Complete step by step solution:
In the problem it is given that the origin is considered in the position of the object 2. So we can break the position vector of the object 1 in the terms of the x and y components.
We can redraw the image as,

Now from the diagram, we can see that the horizontal component of the position vector is $d\cos 30^\circ $. This component coincides with the positive x axis and hence it is the x component. Therefore, $x = d\cos 30^\circ $. Again the vertical component of the position vector is $d\sin 30^\circ $. This component coincides with the negative y axis and hence it is the y component. Therefore, $y = d\sin 30^\circ $
Therefore, we can write the position vector as,
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = x\hat i + y\left( { - \hat j} \right)$
Substituting the values
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = d\cos 30\hat i + d\sin 30\left( { - \hat j} \right)$
Now the value of $\cos 30$is $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ and the value of $\sin 30$ is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
So substituting the values we get, ${P_{21}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}d\hat i - \dfrac{1}{2}d\hat j$
Now taking common we get,
$\Rightarrow {P_{21}} = \dfrac{d}{2}\left( {\sqrt 3 \hat i - \hat j} \right)$
This is the position vector of the object 1 with respect to the object 2.
Note:
In the solution we have taken the unit vector along the positive x axis as $\hat i$ and that along the positive y axis is $\hat j$. The y component of the position vector is directed towards the negative y axis. So we have used $\left( { - \hat j} \right)$ in the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




