
How do transistors amplify signals?
Answer
550.5k+ views
Hint: Transistor is a semiconductor device with two junctions as it is made of three parts; the collector, base, emitter. It can act as an amplifier as well as switch. It acts as an amplifier when a small input voltage or signal gives rise to a large output voltage or signal.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device which is made of three semiconductors; emitter, base, collector. Transistors act as switches as well as amplifiers.
The collector-base junction is reverse biased while the emitter-base junction is forward biased. The transistor is able to amplify a signal by raising the strength of the signal.
In a common base circuit, a variable voltage is applied across the emitter-base junction such that it remains forward biased. The input circuit contains low resistance due to which a small change in the input causes a large change in the output. The input voltage gives rise to emitter current and it contributes to the collector current which is the output current and hence flows through the load resistance. The potential drop across the load resistance is large. The circuit depicting transistor as an amplifier is given as-
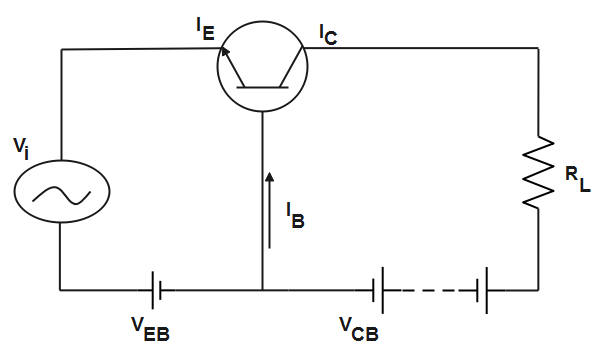
Therefore, the transistor acts as an amplifier as a small input voltage gives rise to a large output voltage.
Note:
The performance of the transistor can be judged by the current, voltage gain and power gain. The current gain is the ratio of collector current to the base current, the voltage gain is the ratio of output voltage to input voltage while the power gain is the ratio of input signal power to output signal power.
Complete answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device which is made of three semiconductors; emitter, base, collector. Transistors act as switches as well as amplifiers.
The collector-base junction is reverse biased while the emitter-base junction is forward biased. The transistor is able to amplify a signal by raising the strength of the signal.
In a common base circuit, a variable voltage is applied across the emitter-base junction such that it remains forward biased. The input circuit contains low resistance due to which a small change in the input causes a large change in the output. The input voltage gives rise to emitter current and it contributes to the collector current which is the output current and hence flows through the load resistance. The potential drop across the load resistance is large. The circuit depicting transistor as an amplifier is given as-

Therefore, the transistor acts as an amplifier as a small input voltage gives rise to a large output voltage.
Note:
The performance of the transistor can be judged by the current, voltage gain and power gain. The current gain is the ratio of collector current to the base current, the voltage gain is the ratio of output voltage to input voltage while the power gain is the ratio of input signal power to output signal power.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




