
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
A. Is present in the ribosome and provides structural integrity
B. Usually has clover leaf-like structure
C. Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes
D. Codes for proteins
Answer
588.3k+ views
Hint: A transfer RNA (previously referred to as sRNA or soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA. It is around 76 to 90 nucleotides in length and it acts as the connection between the mRNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. The shape of transfer RNA can vary at the three stages but the most stable and studied form is at the secondary structure.
Complete answer:
The structure of tRNA can be studied under-
• Primary structure,
• Secondary structure (the cloverleaf structure),
• Tertiary structure.
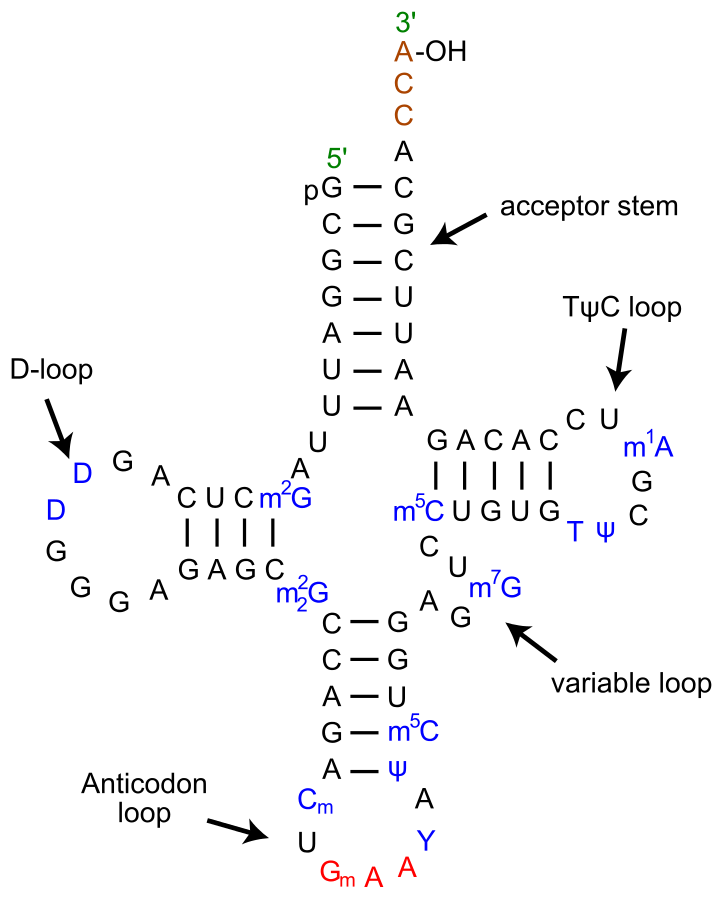
The tRNA structure consists of the following:
• A 5′-terminal phosphate group. The acceptor arm is a 7- to 9-base pair arm formed by the base pairing of the 5′-terminal nucleotide with the 3′-terminal nucleotide (which contains the CCA 3′-terminal group used to attach the amino acid).
• The CCA tail contains a cytosine-cytosine-adenine sequence at the 3′ end of the molecule. It forms aminoacyl-tRNA as the amino acid is loaded onto the tRNA by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. It is bonded to the 3′-hydroxyl group on the CCA tail. This is important for the recognition of tRNA by enzymes and critical in translation.
• The D arm is made up of 4- to 6-bp and forms a loop that often contains dihydrouridine.
• The anticodon arm is made up of 5 bp whose loop contains the anticodon.
• The T arm contains a 4- to 5- bp arm containing the sequence T$\Psi$C where $\Psi$ is pseudouridine (modified uridine).
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The molecular structure of tRNA can be explained by a cloverleaf model which was proposed by Holley. Some important facts are listed below:
• The 3′-terminal tRNA-like structures are termed as 'genomic tags'.
• The acceptor arm may be devoid of Watson-Crick base pairs.
• The CCA sequence in prokaryotes is transcribed in some tRNA sequences.
Complete answer:
The structure of tRNA can be studied under-
• Primary structure,
• Secondary structure (the cloverleaf structure),
• Tertiary structure.

The tRNA structure consists of the following:
• A 5′-terminal phosphate group. The acceptor arm is a 7- to 9-base pair arm formed by the base pairing of the 5′-terminal nucleotide with the 3′-terminal nucleotide (which contains the CCA 3′-terminal group used to attach the amino acid).
• The CCA tail contains a cytosine-cytosine-adenine sequence at the 3′ end of the molecule. It forms aminoacyl-tRNA as the amino acid is loaded onto the tRNA by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. It is bonded to the 3′-hydroxyl group on the CCA tail. This is important for the recognition of tRNA by enzymes and critical in translation.
• The D arm is made up of 4- to 6-bp and forms a loop that often contains dihydrouridine.
• The anticodon arm is made up of 5 bp whose loop contains the anticodon.
• The T arm contains a 4- to 5- bp arm containing the sequence T$\Psi$C where $\Psi$ is pseudouridine (modified uridine).
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: The molecular structure of tRNA can be explained by a cloverleaf model which was proposed by Holley. Some important facts are listed below:
• The 3′-terminal tRNA-like structures are termed as 'genomic tags'.
• The acceptor arm may be devoid of Watson-Crick base pairs.
• The CCA sequence in prokaryotes is transcribed in some tRNA sequences.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




