
Total right angles $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ present in $P\,C{l_5}$,$P\,C{l_4}^ + ,P\,C{l_6}^ - $ are ______ respectively
a)$\,0,1,4$
b) $6,0,4$
c) $2,4,0$
d)$6,0,12$
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint:When two lines are perpendicular to each other or intersect each other at ${90^ \circ }$, it is known as right angle. So draw the figures of each structure and try to find the number of right angles present.
Complete step by step answer:
$P\,C{l_5}$ has a shape of Trigonal Bi Pyramidal geometry with a molecule of $s{p_3}d$. Total valence electron present in $P\,C{l_5}$ are:
$P\,C{l_5}$$ \to $ Cl in group $17$ so $5 \times 7 = 35$ and P is in group 15 so it has $5$ electrons
Total electrons $ = 35 + 5 = 40\,V.E.$
Now Phosphorous is going to be in center as it can hold a lot of bonds.

Five P-Cl bonds are formed.
There are $3$ bonds of $P - Cl$ which are at an angle of ${120^ \circ }$ and thus are known as equatorial bonds.
Other $2$$P - Cl$ bonds are called axial bonds as these are at right angles to the equatorial bonds, i.e. one above and one below the plane.
So now there are $2$ axial bonds where each of them are at right angles to $3$ equatorial bonds thus giving $6$ right angles. But $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ are $2$, so its answer is $2$
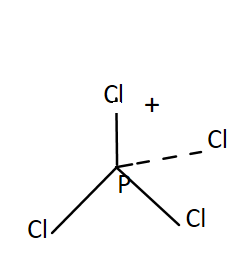
$P\,C{l_4}^ + $- It has a tetrahedral shape of tetrahedral. The oxidation state of P in $P\,C{l_4}^ + $ is $5$. Total valence electrons present in $P\,C{l_4}^ + $ is
$P\,C{l_4}^ + $$ \to $Cl has $4 \times 7 = 28\,V.E.$ and P has $5\,V.E.$
Total valence electrons$ = 5 + 28 - 1$, this minus one is due to presence of negative sign on top.
 OR
OR
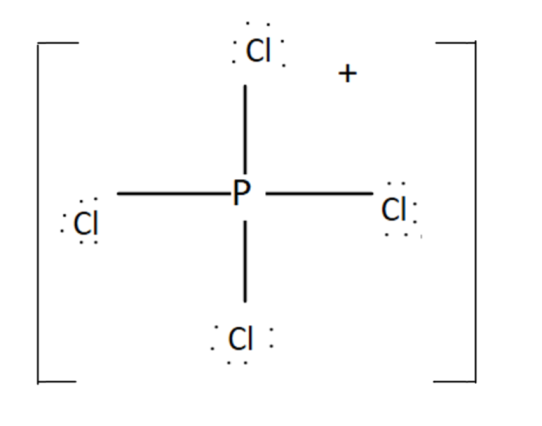
It has $4$ bonding pairs and no lone pair. The bonds are pointing towards the corners of a regular tetrahedron. It was $s{p^3}$ hybridisation. Thus $P\,C{l_4}^ + $ has four right angles $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$.
$P\,C{l_6}^ - $- It has octahedral structure and $s{p_3}{d_2}$ hybridization.
For $P\,C{l_6}^ - $ we have $ + 8$ valence electrons $(5 + (6 \times 7) + 1)$
Structure for $P\,C{l_6}^ - $ is as follow
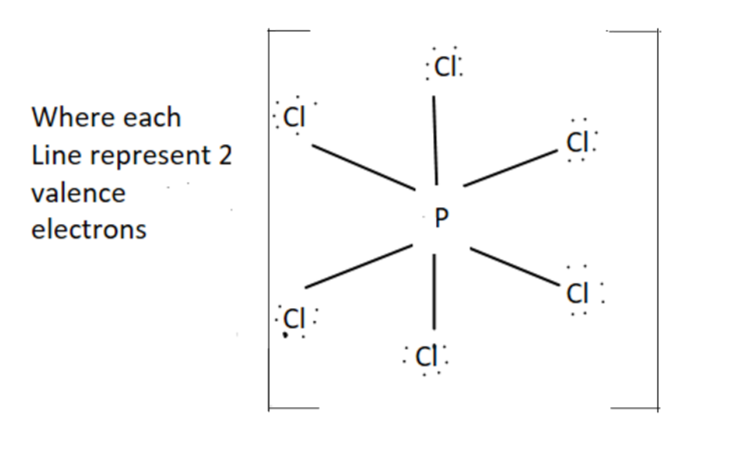
Hence we can see from the shape there is no right angle present between $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$. So it has zero right angles.
So correct option is C
$P\,C{l_5}$ has $2\,\,\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ right angles
$P\,C{l_4}^ + $ has $4\,\,\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ right angles
$P\,C{l_6}^ - $ has $0\,\,\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ right angles.
Note: As we all know that bond angles are the geometric angles between two adjacent bonds. The molecular structure and the bond angles are dependent on each other. The atoms except the central atom of molecule adjust themselves in such a way so that they can feel less repulsion from each other and to do so they acquire maximum bond angles as much as possible.
Complete step by step answer:
$P\,C{l_5}$ has a shape of Trigonal Bi Pyramidal geometry with a molecule of $s{p_3}d$. Total valence electron present in $P\,C{l_5}$ are:
$P\,C{l_5}$$ \to $ Cl in group $17$ so $5 \times 7 = 35$ and P is in group 15 so it has $5$ electrons
Total electrons $ = 35 + 5 = 40\,V.E.$
Now Phosphorous is going to be in center as it can hold a lot of bonds.

Five P-Cl bonds are formed.
There are $3$ bonds of $P - Cl$ which are at an angle of ${120^ \circ }$ and thus are known as equatorial bonds.
Other $2$$P - Cl$ bonds are called axial bonds as these are at right angles to the equatorial bonds, i.e. one above and one below the plane.
So now there are $2$ axial bonds where each of them are at right angles to $3$ equatorial bonds thus giving $6$ right angles. But $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ are $2$, so its answer is $2$
$P\,C{l_4}^ + $- It has a tetrahedral shape of tetrahedral. The oxidation state of P in $P\,C{l_4}^ + $ is $5$. Total valence electrons present in $P\,C{l_4}^ + $ is
$P\,C{l_4}^ + $$ \to $Cl has $4 \times 7 = 28\,V.E.$ and P has $5\,V.E.$
Total valence electrons$ = 5 + 28 - 1$, this minus one is due to presence of negative sign on top.


It has $4$ bonding pairs and no lone pair. The bonds are pointing towards the corners of a regular tetrahedron. It was $s{p^3}$ hybridisation. Thus $P\,C{l_4}^ + $ has four right angles $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$.
$P\,C{l_6}^ - $- It has octahedral structure and $s{p_3}{d_2}$ hybridization.
For $P\,C{l_6}^ - $ we have $ + 8$ valence electrons $(5 + (6 \times 7) + 1)$
Structure for $P\,C{l_6}^ - $ is as follow

Hence we can see from the shape there is no right angle present between $\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$. So it has zero right angles.
So correct option is C
$P\,C{l_5}$ has $2\,\,\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ right angles
$P\,C{l_4}^ + $ has $4\,\,\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ right angles
$P\,C{l_6}^ - $ has $0\,\,\angle Cl\,P\,Cl$ right angles.
Note: As we all know that bond angles are the geometric angles between two adjacent bonds. The molecular structure and the bond angles are dependent on each other. The atoms except the central atom of molecule adjust themselves in such a way so that they can feel less repulsion from each other and to do so they acquire maximum bond angles as much as possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




