
Total number of alkene obtained in reaction?
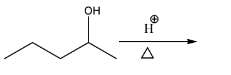
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 3

Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: The reaction is acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols. In acidic medium, alcohol forms carbocation. Then, we have to check for stable carbocation formation and since no nucleophile is provided, we will proceed with the elimination reaction and form the maximum number of products.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, elimination reactions produce unsaturated compounds. Alcohols undergo elimination to produce an alkene and alkyl halides undergo eliminations as well. An acid-catalyzed elimination is a second order reaction (E1), where carbocation is the intermediate and the rate of reaction is dependent on how quickly the carbocation can be formed. As soon as the carbocation is formed, the rest of the elimination reaction occurs very quickly (in case a nucleophile is not available).
We will perform this reaction in various steps as follows:-
-Formation of carbocation (an intermediate):-
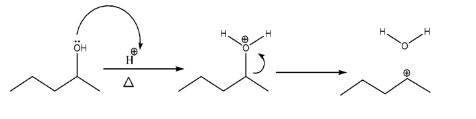
As we can see that the lone pairs of O atom attack the ${{H}^{+}}$ ion and form${{H}_{2}}{{O}^{+}}$. Since oxygen is an electronegative atom it would not bear positive charge on itself and would attract shared pair of electrons of bond with the carbon atom hence resulting in the formation of carbocation along with water molecules.
-Stability of carbocation:-
Before moving forward, it is always necessary to check the stability of the intermediate formed during the reaction. Since we know the order of stability of carbocation is: tertiary cation > secondary cation > primary cation. And in the given structure, there can be only 2 possibilities that are secondary and primary cation. Therefore, we prefer to choose a secondary as it also has the maximum number of hyperconjugative $\alpha H$ atoms .
-Elimination and formation of products:-
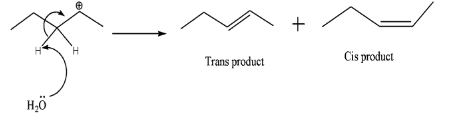
A.
B.
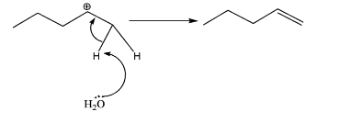
-Now, th ${{H}_{2}}{{O}}$ molecule will take one of the H- atoms present adjacent to the carbocation and the shared pair of electrons between C and H turns into double bonds. In case of (A), 2 products are possible due to cis and trans – isomers. Whereas in case of (B), no such thing is possible hence contributing for only 1 product. Therefore, total number of alkenes produced =3
Therefore the correct option is (d) 3 alkenes.
Note: -Intermediates play an important role in reactions and hence their stability must be checked and if they are not stable enough, then make them stable before the formation of the product.
-Sometimes we may require to expand or compress the ring system in the case of carbocation so as to reduce the strain and be more stable.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, elimination reactions produce unsaturated compounds. Alcohols undergo elimination to produce an alkene and alkyl halides undergo eliminations as well. An acid-catalyzed elimination is a second order reaction (E1), where carbocation is the intermediate and the rate of reaction is dependent on how quickly the carbocation can be formed. As soon as the carbocation is formed, the rest of the elimination reaction occurs very quickly (in case a nucleophile is not available).
We will perform this reaction in various steps as follows:-
-Formation of carbocation (an intermediate):-

As we can see that the lone pairs of O atom attack the ${{H}^{+}}$ ion and form${{H}_{2}}{{O}^{+}}$. Since oxygen is an electronegative atom it would not bear positive charge on itself and would attract shared pair of electrons of bond with the carbon atom hence resulting in the formation of carbocation along with water molecules.
-Stability of carbocation:-
Before moving forward, it is always necessary to check the stability of the intermediate formed during the reaction. Since we know the order of stability of carbocation is: tertiary cation > secondary cation > primary cation. And in the given structure, there can be only 2 possibilities that are secondary and primary cation. Therefore, we prefer to choose a secondary as it also has the maximum number of hyperconjugative $\alpha H$ atoms .
-Elimination and formation of products:-
A.

B.

-Now, th ${{H}_{2}}{{O}}$ molecule will take one of the H- atoms present adjacent to the carbocation and the shared pair of electrons between C and H turns into double bonds. In case of (A), 2 products are possible due to cis and trans – isomers. Whereas in case of (B), no such thing is possible hence contributing for only 1 product. Therefore, total number of alkenes produced =3
Therefore the correct option is (d) 3 alkenes.
Note: -Intermediates play an important role in reactions and hence their stability must be checked and if they are not stable enough, then make them stable before the formation of the product.
-Sometimes we may require to expand or compress the ring system in the case of carbocation so as to reduce the strain and be more stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




