
To get an $OR$ gate from a $NAND$ gate, we need:
A) Only two $NAND$ gates.
B) Two $NOT$ gates obtained from $NAND$ gates and one $NAND$ gate.
C) Four $NAND$ gates and two $AND$ gates obtained from $NAND$ gates.
D) None of the above.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint:
Boolean algebra needed:
1) Involution law: $\left( {X'} \right)' = X$
2) Idempotency law:
$
X + X = X \\
X.X = X \\
$
3) De-Morgan’s law:
$
\left( {X + Y} \right)' = X'.Y' \\
\left( {X.Y} \right)' = X' + Y' \\
$
Complete step by step answer:
Construct a $NOT$ gate using $NAND$ gate. For this, you will need to use idempotency law.
Connect $NOT$ gates to two terminals and connect a $NAND$ gate. Then, by using idempotency law, arrive at the result that you can also get simply by using $OR$ gate.
Complete step by step answer:
We will be using three laws of Boolean algebra. These are:
1) Involution law: $\left( {X'} \right)' = X$
2) Idempotency law:
$
X + X = X \\
X.X = X \\
$
3) De-Morgan’s law:
$
\left( {X + Y} \right)' = X'.Y' \\
\left( {X.Y} \right)' = X' + Y' \\
$
Our first step will be to make a $NOT$ gate using $NAND$ gate.
The symbol and result of $NOT$ gate is :$$
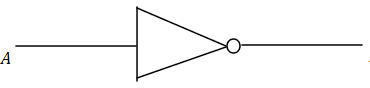
$NOT$ gate using $NAND$ gate is:
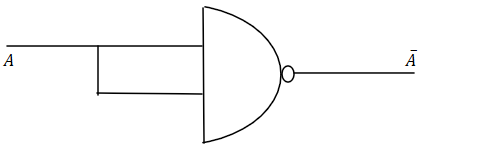
We will explain this construction using Idempotency law ( $X.X = X$ )
$A$ can be written as $A.A$ and vice versa. $\left( {A.A} \right)' = \left( A \right)'$ because we are using $NAND$ gate.
Our, desired gate is $OR$ gate, which is represented as
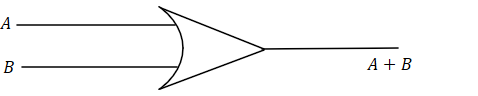
Our desired result is $A + B$. First using Involution law ( $\left( {X'} \right)' = X$ ), we get
$A + B = \left[ {\left( {A + B} \right)'} \right]'$ and then using De-Morgan’s law, we get $\left[ {\left( {A + B} \right)'} \right]' = \left[ {A'.B'} \right]'$
So, we have $\left[ {\left( {A + B} \right)'} \right]' = \left[ {A'.B'} \right]'$. Now, using Idempotency law ( $X.X = X$ ), we have
$\left[ {A'.B'} \right]' = \left[ {\left( {A.A} \right)'.\left( {B.B} \right)'} \right]'$
So, we have the entire expression as
$A + B = \left[ {\left( {A.A} \right)'.\left( {B.B} \right)'} \right]'$
From this expression, we can conclude that we need two $NOT$ gates using $NAND$ gates and then combine then using $NAND$ gate to get the desired results.
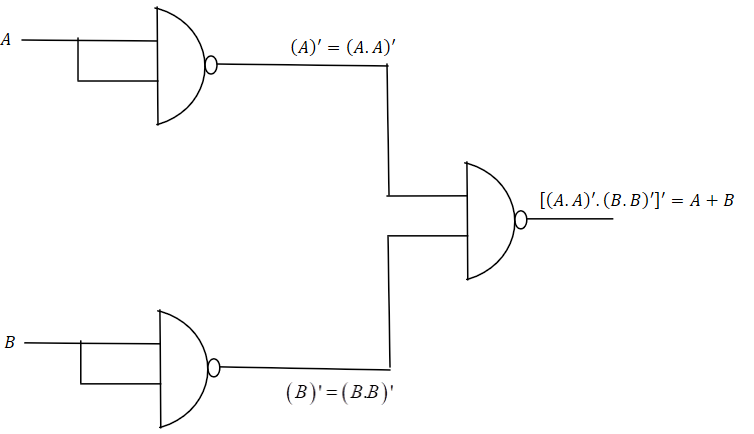
So, option C is correct.
Note:You can match your answers by comparing the truth tables. To construct different gates easily, one should be familiar and comfortable in any Boolean algebra laws. Do not get confused with symbols for different gates.
Boolean algebra needed:
1) Involution law: $\left( {X'} \right)' = X$
2) Idempotency law:
$
X + X = X \\
X.X = X \\
$
3) De-Morgan’s law:
$
\left( {X + Y} \right)' = X'.Y' \\
\left( {X.Y} \right)' = X' + Y' \\
$
Complete step by step answer:
Construct a $NOT$ gate using $NAND$ gate. For this, you will need to use idempotency law.
Connect $NOT$ gates to two terminals and connect a $NAND$ gate. Then, by using idempotency law, arrive at the result that you can also get simply by using $OR$ gate.
Complete step by step answer:
We will be using three laws of Boolean algebra. These are:
1) Involution law: $\left( {X'} \right)' = X$
2) Idempotency law:
$
X + X = X \\
X.X = X \\
$
3) De-Morgan’s law:
$
\left( {X + Y} \right)' = X'.Y' \\
\left( {X.Y} \right)' = X' + Y' \\
$
Our first step will be to make a $NOT$ gate using $NAND$ gate.
The symbol and result of $NOT$ gate is :$$

$NOT$ gate using $NAND$ gate is:

We will explain this construction using Idempotency law ( $X.X = X$ )
$A$ can be written as $A.A$ and vice versa. $\left( {A.A} \right)' = \left( A \right)'$ because we are using $NAND$ gate.
Our, desired gate is $OR$ gate, which is represented as

Our desired result is $A + B$. First using Involution law ( $\left( {X'} \right)' = X$ ), we get
$A + B = \left[ {\left( {A + B} \right)'} \right]'$ and then using De-Morgan’s law, we get $\left[ {\left( {A + B} \right)'} \right]' = \left[ {A'.B'} \right]'$
So, we have $\left[ {\left( {A + B} \right)'} \right]' = \left[ {A'.B'} \right]'$. Now, using Idempotency law ( $X.X = X$ ), we have
$\left[ {A'.B'} \right]' = \left[ {\left( {A.A} \right)'.\left( {B.B} \right)'} \right]'$
So, we have the entire expression as
$A + B = \left[ {\left( {A.A} \right)'.\left( {B.B} \right)'} \right]'$
From this expression, we can conclude that we need two $NOT$ gates using $NAND$ gates and then combine then using $NAND$ gate to get the desired results.

So, option C is correct.
Note:You can match your answers by comparing the truth tables. To construct different gates easily, one should be familiar and comfortable in any Boolean algebra laws. Do not get confused with symbols for different gates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




