
Three very large plates of the same area are kept parallel and close to each other. They are considered as ideal black surface sand and have very high thermal conductivity. The first and the third plates are maintained at temperature $2T$ and $3T$ respectively. The temperature of the middle (i.e., second) plate under a steady state condition is:
A. ${{\left( \dfrac{65}{2} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T$
B. ${{\left( \dfrac{97}{4} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T$
C. ${{\left( \dfrac{97}{2} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T$
D. ${{\left( 97 \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T$
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: Ideal black surfaces are the surfaces which can emit all the energy absorbed by the body. When a body absorbs energy from its surrounding the process is known as an endothermic process. In the endothermic process, the temperature of the body increases according to the energy absorbed.
Complete answer:
The temperature of plate 1 and two is $2T$ and $3T$ respectively.
When a plate (${{P}_{2}}$ ) is in the middle of the two plates (${{P}_{1}},{{P}_{3}}$) and all of them are of the same area and are parallel to each other. As shown below.
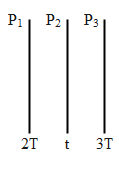
Under steady-state conditions, the rate of energy received by the middle plate will be equal to the energy radiated by the plate. Or in other words, the energy absorbed by the middle plate will be equivalent to the energy emitted by both plates 1 and 3.
Let, $t$ be the temperature of the middle plate
$A$ be the area of the plates
So the steady-state condition can mathematically be framed as,
\[\begin{align}
& \sigma A{{(3T)}^{4}}-\sigma A{{(t)}^{4}}=\sigma A{{(t)}^{4}}-\sigma A{{(2T)}^{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{(3T)}^{4}}-{{(t)}^{4}}={{(t)}^{4}}-{{(2T)}^{4}} \\
\end{align}\]
By taking similar terms aside.
\[\begin{align}
& ~2{{(t)}^{4}}={{T}^{4}}({{3}^{4}}+{{2}^{4}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}^{4}}=\dfrac{97{{T}^{4}}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow t={{\left( \dfrac{97}{2} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, the temperature of the middle plate will be ${{\left( \dfrac{97}{2} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The thermal processes are divided into two categories according to the exchange of head and change in the temperature. One is the exothermic process and another is the endothermic process. The process in which the temperature of the system is increased is known as the exothermic process. In steady-state conditions the temperature driving the condition is constant.
Complete answer:
The temperature of plate 1 and two is $2T$ and $3T$ respectively.
When a plate (${{P}_{2}}$ ) is in the middle of the two plates (${{P}_{1}},{{P}_{3}}$) and all of them are of the same area and are parallel to each other. As shown below.

Under steady-state conditions, the rate of energy received by the middle plate will be equal to the energy radiated by the plate. Or in other words, the energy absorbed by the middle plate will be equivalent to the energy emitted by both plates 1 and 3.
Let, $t$ be the temperature of the middle plate
$A$ be the area of the plates
So the steady-state condition can mathematically be framed as,
\[\begin{align}
& \sigma A{{(3T)}^{4}}-\sigma A{{(t)}^{4}}=\sigma A{{(t)}^{4}}-\sigma A{{(2T)}^{4}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{(3T)}^{4}}-{{(t)}^{4}}={{(t)}^{4}}-{{(2T)}^{4}} \\
\end{align}\]
By taking similar terms aside.
\[\begin{align}
& ~2{{(t)}^{4}}={{T}^{4}}({{3}^{4}}+{{2}^{4}}) \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}^{4}}=\dfrac{97{{T}^{4}}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow t={{\left( \dfrac{97}{2} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T \\
\end{align}\]
Thus, the temperature of the middle plate will be ${{\left( \dfrac{97}{2} \right)}^{\dfrac{1}{4}}}T$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
The thermal processes are divided into two categories according to the exchange of head and change in the temperature. One is the exothermic process and another is the endothermic process. The process in which the temperature of the system is increased is known as the exothermic process. In steady-state conditions the temperature driving the condition is constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




