
Three identical charges, each having a value $ 1.0 \times {10^{ - 3}}C $ are placed at the corners of an equivalent triangle of side $ 20cm $ . Find the potential at the center of the triangle.
(A) $ 2.3 \times {10^6}V $
(B) $ 2.3 \times {10^5}V $
(C) $ 2.3 \times {10^4}V $
(D) $ 2.3 \times {10^3}V $
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint :Firstly, find the distance between the corner and the center. After finding the distance we can use the formula for the electric field because we are already provided with the value of charge and the length of the triangle. The formula of electric field is $ E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{Q}{R} $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Consider a triangle $ ABC $ as shown in the diagram. $ O $ is the center of the triangle on which we have to find the potential. Given that identical charges are placed at the corners each having value $ {10^{ - 3}}C $ and the sides of length $ 20cm $ .
Revising the concepts for electric potential, which is defined as the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from reference point to specific point against the electric field.
To Find distance $ OB $ we are taking the right-angled triangle $ ABD $
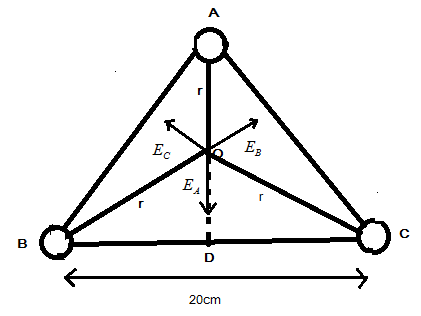
Using Pythagoras theorem,
$ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BD} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2} $
$ {\left( {20 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {10 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2} $
In this above statement we had taken the $ BD = \dfrac{{BC}}{2} $ because the centroid always bisects the base of the triangle. On calculating,
$ AD = 1.732 \times {10^{ - 2}}m $
Now finding the $ r $ which is comes to the two-third of the side $ AD $
$ r = \dfrac{2}{3}\left( {1.732 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right) = 1.15 \times {10^{ - 1}} $
Now simply substituting the values in the formula for electric potential:
$ V = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{1.15 \times {{10}^{ - 1}}}} $
Total potential comes out to be
$ \begin{gathered}
V = 3 \times 9 \times {10^9} \times {10^{ - 3 + 1}} \\
\\
\end{gathered} $
Hence the answer is approximately $ 2.3 \times {10^8}V $ .
Note :
Electric field at the center is zero due to identical charge placed at the corners of the triangle. This implies that unit positive charge experiences zero electric force. The potential is not zero at the center, that means work has to be done by an external agent to move the unit positive charge from infinity to the center of the triangle.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Consider a triangle $ ABC $ as shown in the diagram. $ O $ is the center of the triangle on which we have to find the potential. Given that identical charges are placed at the corners each having value $ {10^{ - 3}}C $ and the sides of length $ 20cm $ .
Revising the concepts for electric potential, which is defined as the amount of work needed to move a unit charge from reference point to specific point against the electric field.
To Find distance $ OB $ we are taking the right-angled triangle $ ABD $

Using Pythagoras theorem,
$ {\left( {AB} \right)^2} = {\left( {BD} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2} $
$ {\left( {20 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {10 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {AD} \right)^2} $
In this above statement we had taken the $ BD = \dfrac{{BC}}{2} $ because the centroid always bisects the base of the triangle. On calculating,
$ AD = 1.732 \times {10^{ - 2}}m $
Now finding the $ r $ which is comes to the two-third of the side $ AD $
$ r = \dfrac{2}{3}\left( {1.732 \times {{10}^{ - 2}}} \right) = 1.15 \times {10^{ - 1}} $
Now simply substituting the values in the formula for electric potential:
$ V = 9 \times {10^9} \times \dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^{ - 3}}}}{{1.15 \times {{10}^{ - 1}}}} $
Total potential comes out to be
$ \begin{gathered}
V = 3 \times 9 \times {10^9} \times {10^{ - 3 + 1}} \\
\\
\end{gathered} $
Hence the answer is approximately $ 2.3 \times {10^8}V $ .
Note :
Electric field at the center is zero due to identical charge placed at the corners of the triangle. This implies that unit positive charge experiences zero electric force. The potential is not zero at the center, that means work has to be done by an external agent to move the unit positive charge from infinity to the center of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




