
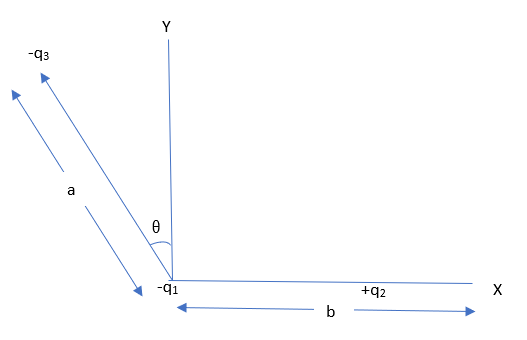
Three charges $ - {q_1} $ , $ + {q_2} $ and $ - {q_3} $ are placed as shown in the figure. The x-component of the force on $ - {q_1} $ is proportional to:
$
\left( {\text{A}} \right)\dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}} - \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\cos \theta \\
\left( {\text{B}} \right)\dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}} + \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta \\
\left( {\text{C}} \right)\dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}} + \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\cos \theta \\
\left( {\text{D}} \right)\dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}} - \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta \\
$

Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint : Since we have been given three charges, first try to find the forces on charge $ {q_1} $ due to the other two charges since we have to find the x-component of force on $ - {q_1} $ . The force between two charges is to be found out by coulombs formula. After this step find out the x-component of the force.
$ {\text{F = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}} $
Where F= electric force
k=Coulomb constant
$ {q_1},{q_2} $ = charges
r=distance of separation.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
we have been given three charges $ - {q_1} $ , $ + {q_2} $ and $ - {q_3} $ also we have been shown in the diagram about the placements of this charges. All we have to find is the x-component of the force $ - {q_1} $ .
We all know that the charges present in the given position will have repulsive and attractive forces between each other. Hence $ - {q_1} $ and $ - {q_3} $ will repel each other and this two charges will attract $ + {q_2} $ .
hence we will try to calculate the force between these charges. Since we have to find the x-component of force on $ - {q_1} $ , we will try to find the force on $ - {q_1} $ due to $ + {q_2} $ and $ - {q_3} $ .
We will use the formula $ {\text{F = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}} $
Where F= electric force
k=Coulomb constant
$ {q_1},{q_2} $ = charges
r=distance of separation.
Hence the force due to $ {q_2} $ on $ {q_1} $ is $ {{\text{F}}_{12}}{\text{ = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}} $ as the distance between this two charges is b.
The force due to $ {q_3} $ on $ {q_1} $ is $ {{\text{F}}_{13}}{\text{ = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}} $ as the distance between this two charges is a.
x-component of the force on $ {q_1} $ will be $ {F_{12}} + {F_{13}}\sin \theta $
hence $ {F_x} = {\text{k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}}{\text{ + k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta $
$ {F_x} $ $ \alpha \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta $
hence option (B) matches our solution.
Hence (B) $ \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta $ is the right answer.
Note :
While solving problems of this type, you should always draw a diagram indicating the forces on the charge. Also find out the directions of the vector by looking at the sign and draw in it the diagram. Since force is a vector, so when one or more charges exert pressure on the other, the net force on the charge is the vector sum of the individual forces.
$ {\text{F = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}} $
Where F= electric force
k=Coulomb constant
$ {q_1},{q_2} $ = charges
r=distance of separation.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
we have been given three charges $ - {q_1} $ , $ + {q_2} $ and $ - {q_3} $ also we have been shown in the diagram about the placements of this charges. All we have to find is the x-component of the force $ - {q_1} $ .
We all know that the charges present in the given position will have repulsive and attractive forces between each other. Hence $ - {q_1} $ and $ - {q_3} $ will repel each other and this two charges will attract $ + {q_2} $ .
hence we will try to calculate the force between these charges. Since we have to find the x-component of force on $ - {q_1} $ , we will try to find the force on $ - {q_1} $ due to $ + {q_2} $ and $ - {q_3} $ .
We will use the formula $ {\text{F = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}} $
Where F= electric force
k=Coulomb constant
$ {q_1},{q_2} $ = charges
r=distance of separation.
Hence the force due to $ {q_2} $ on $ {q_1} $ is $ {{\text{F}}_{12}}{\text{ = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}} $ as the distance between this two charges is b.
The force due to $ {q_3} $ on $ {q_1} $ is $ {{\text{F}}_{13}}{\text{ = k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}} $ as the distance between this two charges is a.
x-component of the force on $ {q_1} $ will be $ {F_{12}} + {F_{13}}\sin \theta $
hence $ {F_x} = {\text{k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}}{\text{ + k}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta $
$ {F_x} $ $ \alpha \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta $
hence option (B) matches our solution.
Hence (B) $ \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{{b^2}}}{\text{ + }}\dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{{a^2}}}\sin \theta $ is the right answer.
Note :
While solving problems of this type, you should always draw a diagram indicating the forces on the charge. Also find out the directions of the vector by looking at the sign and draw in it the diagram. Since force is a vector, so when one or more charges exert pressure on the other, the net force on the charge is the vector sum of the individual forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




